ドラッグ・カルテルとはなにか?
What is Drug cartel?
☆ 麻薬カルテルとは、違法薬物取引を支配し、利益を向上させるために、互いに結託する独立した麻薬王で構成される犯罪組織である。麻薬カルテルは、違法薬物 取引の供給をコントロールし、価格を高水準に維持する目的で結成される。麻薬カルテルの結成はラテンアメリカ諸国で一般的である。複数の麻薬カルテルが互 いに縄張り争いをしている(→「麻薬カルテルによるニッチ構築について」「ドラッグとの戦争」)。
| A drug cartel
is a criminal organization composed of independent drug lords who
collude with each other in order to improve their profits and dominate
the illegal drug trade. Drug cartels form with the purpose of
controlling the supply of the illegal drug trade and maintaining prices
at a high level. The formations of drug cartels are common in Latin
American countries. Rivalries between multiple drug cartels cause them
to wage turf wars against each other. The basic structure of a drug cartel is as follows: Falcons: Considered as the "eyes and ears" of the streets, the "falcons" are the lowest rank in any drug cartel. They are scouts, who are responsible for conducting reconnaissance, such as reporting the activities of the police, the military and rival groups.[1] Hitmen: The armed group within the drug cartel, responsible for carrying out assassinations, kidnappings, thefts and extortions, operating protection rackets, as well as defending their plaza (turf) from rival groups and the military.[2][3] Lieutenants: The second highest position in the drug cartel organization, responsible for supervising the hitmen and falcons within their own territory. They are allowed to carry out low-profile murders without permission from their bosses.[4] Drug lords: The highest position in any drug cartel, responsible for supervising the entire drug industry, appointing territorial leaders, making alliances, in addition to planning high-profile murders.[5] There are other operating groups within the drug cartels. For example, the drug producers and suppliers,[6] although not considered in the basic structure, are critical operators of any drug cartel, along with the smugglers, distributors, sales representatives, accountants and money launderers.[7][8][9] Furthermore, the arms suppliers operate in a completely different circle;[10] they are technically not considered part of the cartel's logistics. |
麻
薬カルテルとは、違法薬物取引を支配し、利益を向上させるために、互いに結託する独立した麻薬王で構成される犯罪組織である。麻薬カルテルは、違法薬物取
引の供給をコントロールし、価格を高水準に維持する目的で結成される。麻薬カルテルの結成はラテンアメリカ諸国で一般的である。複数の麻薬カルテルが互い
に縄張り争いをしている。 麻薬カルテルの基本構造は以下の通りである: ファルコン: 街頭の「目と耳」とみなされる「ハヤブサ」は、麻薬カルテルの最下層に位置する。彼らは斥候であり、警察、軍、敵対グループの活動を報告するなど、偵察を行う役割を担っている[1]。 ヒットマン: 麻薬カルテル内の武装集団で、暗殺、誘拐、窃盗、恐喝を実行し、身辺警護を行い、敵対グループや軍から自分たちのプラザ(縄張り)を守る役割を担う[2][3]。 警部補: 麻薬カルテル組織の中で2番目に高い地位にあり、自らの縄張り内で殺し屋や鷹を監督する責任を負う。彼らはボスの許可なしに目立たない殺人を実行することを許されている[4]。 麻薬王: 麻薬カルテルで最も高い地位にあり、注目を集める殺人を計画するだけでなく、麻薬業界全体を監督し、領土のリーダーを任命し、同盟を結ぶ責任がある[5]。 麻薬カルテル内には他にも活動グループがある。例えば、麻薬の生産者と供給者[6]は、基本構造では考慮されないが、密輸業者、流通業者、販売代理店、会 計士、マネーロンダリング業者[7][8][9]と並んで、あらゆる麻薬カルテルの重要なオペレーターである。さらに、武器の供給者は全く別のサークルで 活動している[10]。 |
| Africa See also: Taxi wars in South Africa, blood diamond, Kivu conflict § Conflict minerals, Barbary Coast, Piracy in Somalia, Al-Shabaab (militant group), Al-Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb, and Boko Haram Cape Verdean organized crime Mungiki[11] Organized crime in Nigeria[12][13][14][15][16][17] Confraternities in Nigeria Black Axe (organized crime group) Anini gang Mai-Mai militia gangs Moroccan hashish smugglers Ahmed organization |
アフリカ も参照のこと: 南アフリカのタクシー戦争、血のダイヤモンド、キブ紛争§紛争鉱物、バーバリー海岸、ソマリアの海賊、アル・シャバブ(過激派組織)、イスラム・マグレブのアルカイダ、ボコ・ハラムも参照のこと。 カーボベルデの組織犯罪 ムンギキ[11] ナイジェリアの組織犯罪[12][13][14][15][16][17]。 ナイジェリアのコンフラタニティ ブラック・アックス(組織犯罪集団) アニニ・ギャング マイマイ民兵ギャング モロッコのハシシ密輸業者 アハメド組織 |
| Americas See also: Illegal drug trade in Latin America North America Canada Rivard organization Red Scorpions Bacon Brothers United Nations gang Montreal West End Gang[18][19] Blass gang Dubois Brothers Indo-Canadian organized crime Punjabi Mafia ਜੌਹਲ ਗਿਰੋਹ (Canada)[19] Canadian mafia families Rizzuto crime family[19][20] Cuntrera-Caruana Mafia clan[19][20] Cotroni crime family[19][20] Musitano crime family[19][20] Papalia crime family[19][20] Luppino crime family[19][20] Perri crime family[19][20] Siderno Group[19][20] Commisso 'ndrina[19][20] |
アメリカ大陸 こちらも参照のこと: ラテンアメリカの違法薬物取引 北米 カナダ リバード組織 レッド・スコーピオンズ ベーコン兄弟 国民ギャング モントリオール ウエストエンド・ギャング[18][19] ブラス・ギャング デュボア兄弟 インド系カナダ人組織犯罪 パンジャビ・マフィア ਜਲ ਗਿ ਰੋਹ(カナダ)[19]。 カナダのマフィア・ファミリー リズート犯罪ファミリー[19][20]。 クントレラ=カルアナ・マフィア一族[19][20] コトローニ犯罪一族[19][20] ムジターノ犯罪一族[19][20] パパリア犯罪一家[19][20]。 ルッピーノ犯罪一族[19][20] ペリ犯罪一家[19][20] シデルノ・グループ[19][20] コミッソ・ンドリーナ[19][20] |
| Mexico Not to be confused with Mexican Mafia. 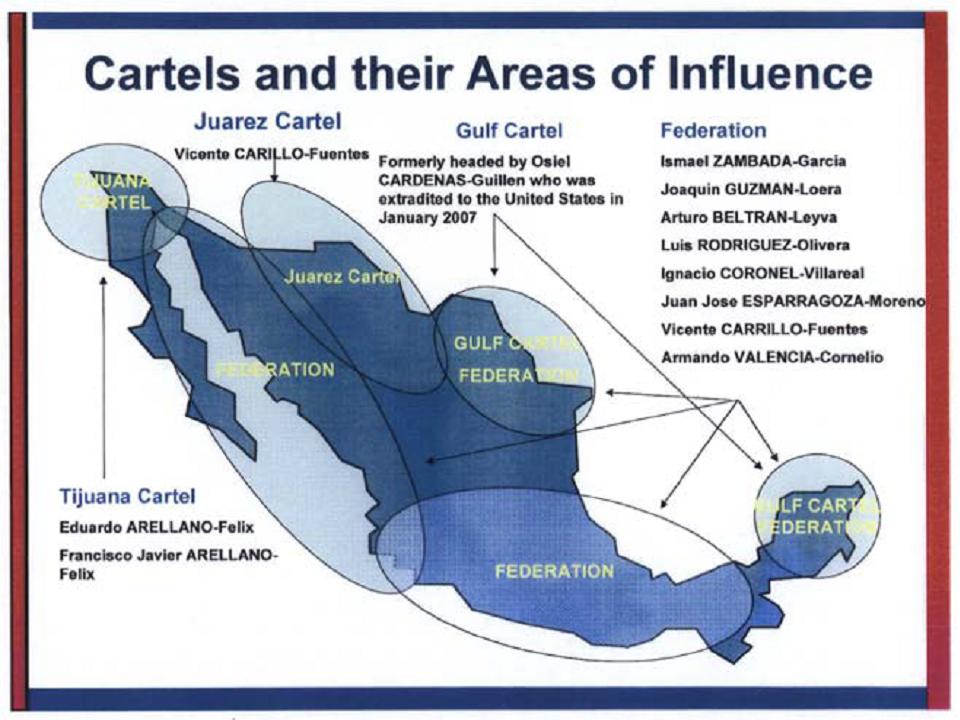 The Mérida Initiative, a U.S. Counter-Narcotics Assistance to Mexico Mexican cartels (also known in Mexico as: la Mafia (the mafia or the mob), La Maña (the skill / the bad manners),[21] narcotraficantes (narco-traffickers), or simply as narcos usually refers to several, rival, criminal organizations that are combated by the Mexican government in the Mexican War on Drugs (List sorted by branches and heritage):[22] Mexican academic Oswaldo Zavala, in his book Drug Cartels Do Not Exist, argues that academics, officials, journalists and writers are mistaken to label the criminal gangs as cartels, noting that they do not meet the definition due to the competitive nature of the drugs trade, and the lack of hierarchal structure. He states that the Mexican state perpetuates the label to justify their militarised response.[23] Note: As of 2020 the DEA considered the cartels of Sinaloa-Beltran, Juarez-Linea, Jalisco, Golfo-Noreste-Zetas, La Familia and Rojos-Guerreros to be the most influential cartels in Mexico.[24] Gulf Cartel (The oldest Mexican criminal syndicate, started as Prohibition-era bootlegging gang) Los Zetas (Formerly part of the Gulf Cartel, now independent) La Familia Michoacana (Formerly a branch of the Gulf Cartel, then went independent)[25][26] Knights Templar Cartel (Splintered from La Familia Cartel)[27] Sinaloa Cartel (Spawned from the Guadalajara Cartel) Colima Cartel (members are now a branch of the Sinaloa Cartel)[28] Sonora Cartel (was reformed in 2018 and is still a branch of the Sinaloa Cartel)[28] Los Ántrax (enforcer squad) 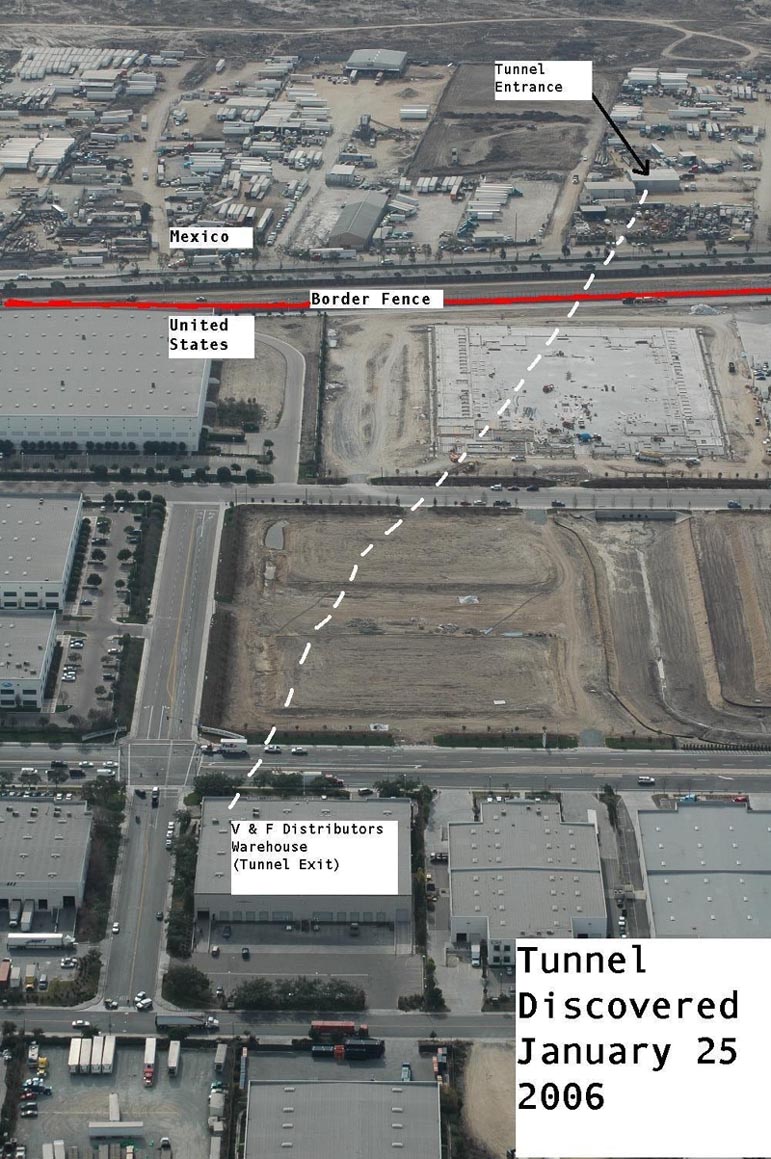 Drug trafficking tunnel under the U.S.-Mexico border used by the Sinaloa Cartel La Resistencia (Splintered from the Milenio Cartel; disbanded) Jalisco New Generation Cartel[29] (Independent remnants of the Milenio Cartel) Los Negros (Beltran-Leyva enforcement squad; disbanded) South Pacific Cartel (branch of the Beltran Leyva Cartel in Morelos)[30][31][32] 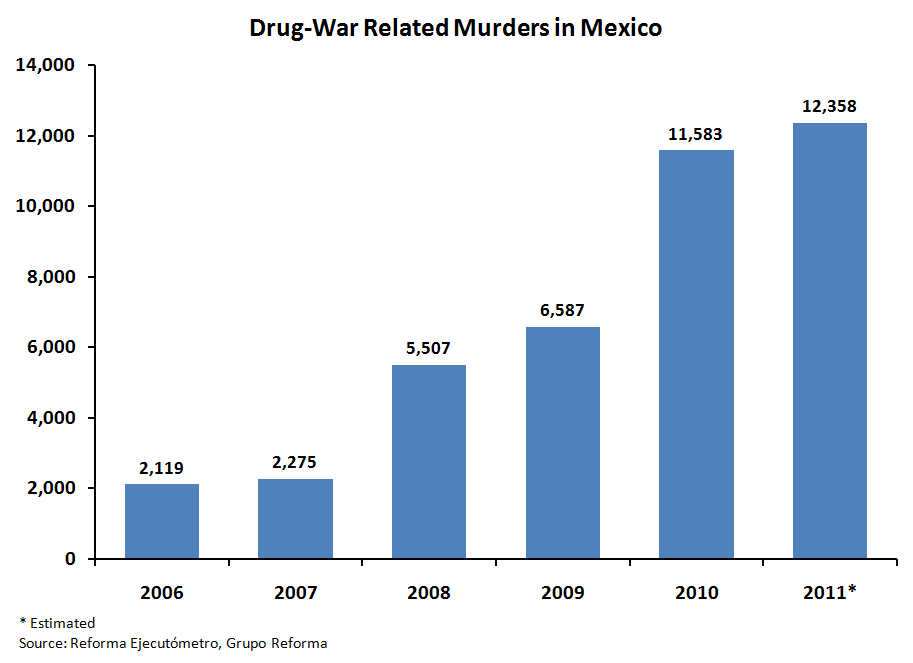 Drug War related murders in Mexico, 2006–2011 Independent Cartel of Acapulco[33] (Splinter from the Beltran-Leyva Cartel) La Barredora (gang)[34] La Mano Con Ojos (gang) (small cell of Beltran-Leyva members in the State of Mexico) (Disbanded) La Nueva Administración (Splintered from the Beltran-Leyva Cartel) (Disbanded) La Oficina (gang) (cell of the Beltran-Leyva Cartel in Aguascalientes) (Disbanded) Cártel de la Sierra (cell in Guerrero)[35][36] Cártel de La Calle (cell in Chiapas)[37][38] Los Chachos (gang in Tamaulipas) (Disbanded)[39][40] Tijuana Cartel (Spawned from the Guadalajara Cartel) Oaxaca Cartel (Was a branch of the disbanded Tijuana Cartel, its regional leader was captured in 2007) Juárez Cartel (Spawned from the Guadalajara Cartel) La Línea (Juárez Cartel enforcer squad) Barrio Azteca (U.S. street gang)[41] (Allied with La Linea)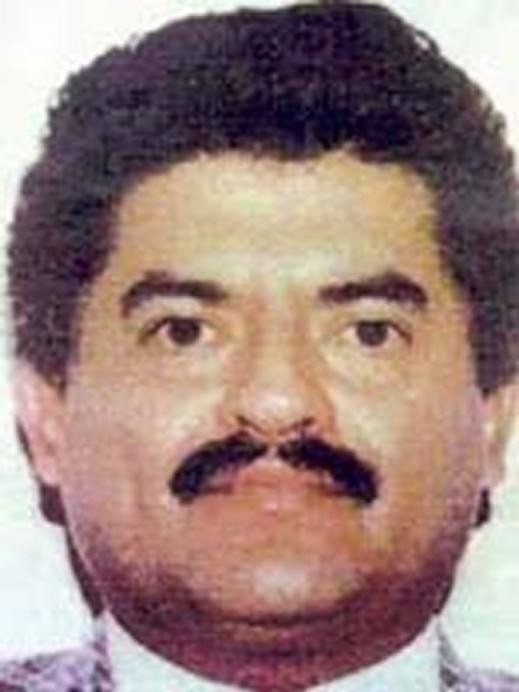  El Azul was a Mexican drug lord. He was a former Mexican secret police (DFS) agent. Santa Rosa de Lima Cartel Caborca Cartel Lesser-known small-criminal organizations: Los Mexicles (U.S. street gang)[42] Los Texas (street gang) (disbanded)[43] Government officials: Other organizations that have been involved in drug trade or traffic in Mexico: Mexican officials: Municipal, state, and Federal Police forces in Mexico[44][45][46] Mexican Armed Forces (Army and Navy[47][48][49][50][51][52]) Mexico City International Airport[53] Club Xoloitzcuintles (football)[54][55] United States officials: U.S. Customs and Border Protection[56][57] |
メキシコ メキシコ・マフィアと混同しないように  米国の対メキシコ麻薬支援「メリダ・イニシアティブ」 メキシコの麻薬カルテル(メキシコでは、ラ・マフィア(マフィアまたはマフィア)、ラ・マーニャ(腕利き/行儀の悪い)[21]、ナルコトラフィカンテス (麻薬密売人)、または単にナルコとも呼ばれる)は、通常、メキシコ麻薬戦争でメキシコ政府によって撲滅されているいくつかの、ライバルの犯罪組織を指す (リストは支部と遺産でソートされている)[22]。 メキシコの学者であるオズワルド・サバラは、著書『麻薬カルテルは存在しない』の中で、学者、政府関係者、ジャーナリスト、作家が犯罪組織をカルテルと呼 ぶのは間違いであると主張し、麻薬取引の競争的性質や階層構造の欠如から、カルテルの定義に当てはまらないと指摘している。彼は、メキシコ国家が自分たち の軍事的対応を正当化するために、このレッテルを広めていると述べている[23]。 注:2020年現在、DEAはシナロア-ベルトラン、フアレス-リネア、ハリスコ、ゴルフ-ノレステ-セタス、ラ・ファミリア、ロホス-ゲレロスのカルテルをメキシコで最も影響力のあるカルテルとみなしている[24]。 ガルフ・カルテル(メキシコ最古の犯罪組織で、禁酒法時代の密造ギャングとして始まった) ロス・セタス(以前はガルフ・カルテルの一部だったが、現在は独立している) ラ・ファミリア・ミチョアカナ(元はガルフ・カルテルの支部だったが、その後独立)[25][26]。 テンプル騎士団カルテル(ラ・ファミリア・カルテルから分裂)[27] シナロア・カルテル(グアダラハラ・カルテルから産まれた) コリマ・カルテル(メンバーは現在シナロア・カルテルの支部となっている)[28]。 ソノラ・カルテル(2018年に再結成され、現在もシナロア・カルテルの支部となっている)[28]。 ロス・アントラックス(執行部隊)  シナロア・カルテルが使用する米墨国境下の麻薬密売トンネル ラ・レジステンシア(ミレニオ・カルテルから分裂。) ハリスコ新世代カルテル[29](ミレニオ・カルテルの独立残党) ロス・ネグロス(ベルトラン・レイバ執行部隊、解散) 南太平洋カルテル(モレロスのベルトラン・レイバ・カルテルの支部)[30][31][32]。  メキシコにおける麻薬戦争関連の殺人事件(2006年~2011年 アカプルコ独立カルテル[33](ベルトラン・レイバ・カルテルからの分派組織) ラ・バレドーラ(ギャング)[34] ラ・マノ・コン・オホス(ギャング)(メキシコ州のベルトラン・レイバ・メンバーの小集団)(解散) ラ・ヌエバ・アドミニストラシオン(ベルトラン・レイバ・カルテルから分裂)(解散) ラ・オフィシナ(ギャング)(アグアスカリエンテスにおけるベルトラン・レイバ・カルテルの下部組織)(解散) カテル・デ・ラ・シエラ(ゲレーロのセル)[35][36]。 カテル・デ・ラ・カジェ(チアパスのセル)[37][38]。 ロス・チャチョス(タマウリパスのギャング)(解散)[39][40]。 ティフアナカルテル(グアダラハラカルテルから産まれた) オアハカ・カルテル(解散したティフアナ・カルテルの支部だったが、地域リーダーは2007年に捕まった) フアレス・カルテル(グアダラハラ・カルテルから生まれた) ラ・リエネア(フアレス・カルテルの執行部隊) バリオ・アステカ(米国のストリートギャング)[41](ラ・リネアと同盟を結ぶ)  エル・アズールはメキシコの麻薬王である。元メキシコ秘密警察(DFS)のエージェントだった。 サンタ・ロサ・デ・リマ・カルテル カボルカ・カルテル あまり知られていない小規模犯罪組織 ロス・メキシクルズ(アメリカのストリートギャング)[42]。 ロス・テキサス(ストリートギャング)(解散)[43]。 政府関係者 その他、メキシコで麻薬取引や麻薬密輸に関与した組織: メキシコ政府関係者 メキシコの自治体、州、連邦警察[44][45][46]。 メキシコ軍(陸軍、海軍[47][48][49][50][51][52]) メキシコシティ国際空港[53] クラブ・ゾロイツクイントルス(サッカー)[54][55]。 アメリカ合衆国の関係者 米国税関・国境警備局[56][57]。 |
United States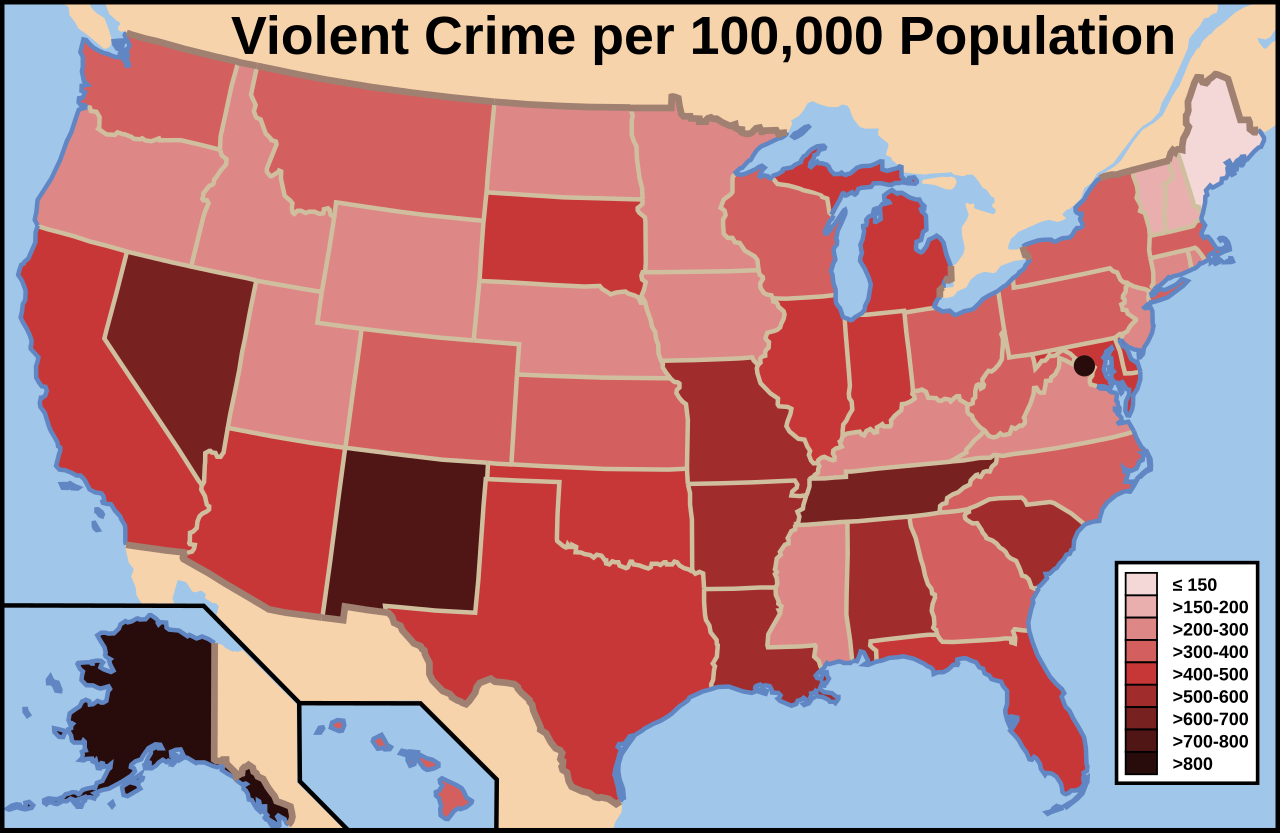 Map of violent crime per 100,000 people in the US by state in 2016 The United States of America is the world's largest consumer of cocaine[58] and other illegal drugs.[59][60][61] This is a list of American criminal organizations involved in illegal drug traffic, drug trade and other related crimes in the United States: National Crime Syndicate[18][62] Seven Group[18][62] Murder, Inc.[18][63] Polish Mob Saltis-McErlane Gang[62] Kielbasa Posse[64] The Greenpoint Crew[65] Flats Mob The Flathead gang[66] Prohibition-era gangs Galveston Downtown Gang Beach Gang The Maceo syndicate Shelton Brothers Gang[62][67] Sheldon Gang[62] Broadway Mob[62] The Lanzetta Brothers Circus Cafe Gang[62] Wandering Family Remus organization Hispanic-American Marielitos The Corporation[18] Paisas Nuestra Familia  Area of influence map of the Jalisco New Generation Cartel in the United States. Surenos or SUR 13 Nortenos or Norte 14 Puerto Rican mafia Agosto organization La ONU Martinez Familia Sangeros Solano organization Negri organization Márquez gambling ring Polanco-Rodriguez organization[14] Los Angeles (See also Rampart scandal) Nash gang[68] Wonderland Gang[68] Crips or Locs Bloods or B Dogs Dixie Mafia[62] Cornbread Mafia[69] Greek-American organized crime Philadelphia Greek Mob[70] Velentzas Family[71] Assyrian/Chaldean mafia[72] Hawaii The Company Leota mob Wall gang Elkins mob The Chickens and the Bulls Binion mob Johnston gang |
米国 2016年のアメリカの州別人口10万人当たりの暴力犯罪マップ アメリカ合衆国は、コカイン[58]やその他の違法薬物の世界最大の消費国である[59][60][61]。これは、アメリカ合衆国の違法薬物取引、麻薬取引、その他の関連犯罪に関与するアメリカの犯罪組織のリストである: 国民犯罪シンジケート[18][62]。 セブン・グループ[18][62]。 マーダー・インク[18][63]。 ポーランド・マフィア サルティス=マッケラン・ギャング[62] キールバサ・ポッセ[64] グリーンポイント・クルー[65] フラッツ・モブ フラットヘッド・ギャング[66] 禁酒法時代のギャング ガルベストン ダウンタウンギャング ビーチギャング メーセオ・シンジケート シェルトン・ブラザーズ・ギャング[62][67] シェルドン・ギャング[62] ブロードウェイ・モブ[62] ランゼッタ・ブラザーズ サーカス・カフェ・ギャング[62] 放浪家族 リーマス組織 ヒスパニック系アメリカ人 マリエリトス ザ・コーポレーション[18] パイザス ヌエストラ・ファミリア  ハリスコ新世代カルテルのアメリカにおける勢力範囲地図。 スレンノス(SUR)13 ノルテノスまたはノルテ14 プエルトリコのマフィア アゴスト組織 ラONU マルティネス・ファミリア・サンゲロス ソラノ組織 ネグリ組織 マルケス賭博組織 ポランコ・ロドリゲス組織[14] ロサンゼルス(ランパートのスキャンダルも参照) ナッシュ・ギャング[68] ワンダーランド・ギャング[68] クリップスまたはロックス ブラッズまたはBドッグス ディキシー・マフィア[62] コーンブレッド・マフィア[69] ギリシャ系アメリカ人組織犯罪 フィラデルフィア・グリーク・マフィア[70] ヴェレンツァス・ファミリー[71] アッシリア/カルデア系マフィア[72] ハワイ ザ・カンパニー レオタ・マフィア ウォールギャング エルキンズマフィア ニワトリと雄牛 ビニオンギャング ジョンストン・ギャング |
| American Mafia Italian immigrants to the United States in the early 19th century formed various small-time gangs which gradually evolved into sophisticated crime syndicates which dominated organized crime in America for several decades. Although government crackdowns and a less-tightly knit Italian-American community have largely reduced their power, they remain an active force in the underworld. Active crime families American Mafia The Commission[20] The Five Families of New York City[12][18][20] Bonanno[12][18][19][20][15][73] Indelicato crew The Motion Lounge Crew Colombo[12][18][19][20][15] Scarpa crew Genovese[12][18][19][20][15][73][74] 116th Street Crew[20] Greenwich Village Crew[18] New Jersey Crew[15] Gambino[12][18][19][20][15][73] Ozone Park Boys[75] DeMeo crew[20] Baltimore Crew South Florida faction New Jersey faction The Bergin Crew Cherry Hill Gambinos Lucchese[12][19][20][15][74] The Jersey Crew[15] The Vario Crew[18] 107th Street gang Magaddino crime family[18][20] DeCavalcante crime family[18][20][15] The Chicago Outfit[12][18][72][20][66] (see also Unione Siciliane) Las Vegas crew (defunct) Philadelphia crime family[18][19][20][15] Pittsburgh crime family[20][62] Patriarca crime family[20] Angiulo Brothers crew[20] Cleveland crime family[20][66] Los Angeles crime family[20] Kansas City crime family[20] Trafficante crime family[20] Detroit Partnership[20][62][66] Milwaukee crime family[20] New Orleans crime family[18][20][62] Defunct mafia families Morello crime family[18][20] Genna crime family[20] Porrello crime family[20] St. Louis crime family[20] Rochester Crime Family[20] Bufalino crime family[20] Dallas crime family[20] Denver crime family[20] San Francisco crime family[20] San Jose crime family[20] Seattle crime family Omaha crime family Licavoli Mob[18][20] Cardinelli gang New York Camorra East Harlem Purple Gang[74] Jewish mafia New York City Schultz gang The Bugs and Meyer Mob[63] Shapiro Brothers[63] Yiddish Black Hand[63] Rothstein organization Kaplan gang Rosenzweig gang Boston 69th Street Gang[63] Sagansky organization Solomon organization[63] Los Angeles Mickey Cohen gang (mix between Jewish and Italian members)[20][62][63] The Purple Gang[18][63][66] Zwillman gang[63] Kid Cann's gang[63] Birger mob[67] Cleveland Syndicate African-American organized crime New York City The Council[76][14][73] Harlem numbers racket[73] Bumpy Johnson gang[73] Supreme Team[77] The Bebos The Country Boys[73][77] Matthews Organization[73] The Family Detroit Black Mafia Family[78] Young Boys, Inc.[14] Chambers Brothers[14] Philadelphia Black Mafia[18][73][77] Junior Black Mafia[16] Oakland, California 69 Mob[77] Baltimore Williams organization (drug trafficking)[77] Washington, D.C. Rayful Edmond organization[77] Chicago Theodore Roe's gambling ring Stokes organization Atlantic City Aso Posse Miami Miami Boys Rosemond Organization Irish Mob Prohibition-era Chicago gangs North Side Gang[18][62][79] James Patrick O'Leary organization John Patrick Looney gang Valley Gang[62] Ragen's Colts[62] Touhy gang Boston Mullen Gang[79] Winter Hill Gang[18][79] Gustin Gang[79] Charlestown Mob Killeen gang[79] Danny Hogan's gang Danny Walsh gang Tom Dennison empire Danny Greene's Celtic Club[18][79] Nucky Johnson's Organization K&A Gang Enright gang New York Dwyer gang The Westies[18][79] White Hand Gang[18] Higgins gang St Louis Hogan Gang Egan's Rats[62][79] |
アメリカン・マフィア 19世紀初頭にアメリカに移住したイタリア系移民が、さまざまな小規模ギャングを結成し、それが次第に洗練された犯罪組織へと発展し、数十年にわたってア メリカの組織犯罪を支配した。政府の取り締まりやイタリア系アメリカ人コミュニティの結束の弱まりにより、その勢力はほぼ縮小したが、裏社会では依然とし て活発な勢力である。 活動中の犯罪組織 アメリカン・マフィア 委員会[20] ニューヨークの5つのファミリー[12][18][20] Bonanno[12][18][19][20][15][73] インデリカート・クルー モーション・ラウンジ・クルー Colombo[12][18][19][20][15] スカルパ・クルー Genovese[12][18][19][20][15][73][74] 116丁目クルー[20] グリニッチビレッジ・クルー[18] ニュージャージー・クルー[15] Gambino[12][18][19][20][15][73] オゾン・パーク・ボーイズ[75] デメオ・クルー[20] ボルチモアクルー 南フロリダ派 ニュージャージー派 バーギン・クルー チェリーヒル・ガンビーノス Lucchese[12][19][20][15][74] ジャージー・クルー[15] バリオ・クルー[18] 107丁目ギャング マガッディーノ犯罪一家[18][20] デカヴァルカンテ犯罪一家[18][20][15] シカゴ・アウトフィット[12][18][72][20][66](ユニオネ・シチリアーネも参照のこと) ラスベガス一味(消滅) フィラデルフィア犯罪一家[18][19][20][15] ピッツバーグ犯罪一家[20][62] パトリアルカ・クライム・ファミリー[20] アンジュロ・ブラザーズ・クルー[20] クリーブランド犯罪一家[20][66] ロサンゼルス犯罪一家[20] カンザスシティ犯罪一家[20] トラッカンテ犯罪一家[20] Detroit Partnership[20][62][66] ミルウォーキー犯罪一家[20] ニューオーリンズ犯罪一家[18][20][62] 消滅したマフィア・ファミリー モレロ犯罪一家[18][20] ジェンナ犯罪一家[20] ポレッロ犯罪一家[20] セントルイス犯罪一家[20] ロチェスター犯罪一家[20] ブファリーノ犯罪一家[20] ダラス犯罪一家[20] デンバー犯罪一家[20] サンフランシスコ犯罪一家[20] サンノゼ犯罪一家[20] シアトル犯罪一家 オマハ犯罪一家 リカボリ・モブ[18][20] カルディネリ・ギャング ニューヨーク・カモッラ イーストハーレムパープルギャング[74] ユダヤ系マフィア ニューヨーク シュルツ・ギャング バグズ・アンド・メイヤー・マフィア[63] シャピロ・ブラザーズ[63] イディッシュ・ブラックハンド[63] ロススタイン組織 カプラン・ギャング ローゼンツヴァイク・ギャング ボストン 69丁目ギャング[63] サガンスキー組織 ソロモン組織[63] ロサンゼルス ミッキー・コーエン・ギャング(ユダヤ系とイタリア系メンバーのミヘ)[20][62][63]。 パープルギャング[18][63][66] ズウィルマンギャング[63] キッド・カンのギャング[63] ビルガー・マフィア[67] クリーブランド・シンジケート アフリカ系アメリカ人組織犯罪 ニューヨーク カウンシル[76][14][73] ハーレムナンバーズ騒動[73] バンピー・ジョンソン・ギャング[73] スプリーム・チーム[77] ベボーズ カントリー・ボーイズ[73][77] マシューズ・オーガニゼーション[73] ザ・ファミリー デトロイト ブラック・マフィア・ファミリー[78] ヤングボーイズ社[14] チェンバーズ・ブラザーズ[14] フィラデルフィア ブラックマフィア[18][73][77] ジュニア・ブラック・マフィア[16] カリフォルニア州オークランド 69マフィア[77] ボルチモア ウィリアムズの組織(麻薬密売)[77]。 ワシントンD.C. レイフル・エドモンド組織[77] シカゴ セオドア・ローの賭博組織 ストークス組織 アトランティックシティ 麻生ポッセ マイアミ マイアミ・ボーイズ ローズモンド組織 アイリッシュ・モブ 禁酒法時代のシカゴのギャング ノースサイド・ギャング[18][62][79] ジェームズ・パトリック・オリアリー組織 ジョン・パトリック・ルーニー・ギャング バレー・ギャング[62] レーゲンズ・コルツ[62] トウヒ・ギャング ボストン マレン・ギャング[79] ウィンターヒル・ギャング[18][79] グスティン・ギャング[79] チャールスタウン・マフィア キリーン・ギャング[79] ダニー・ホーガンのギャング ダニー・ウォルシュ・ギャング トム・デニソン帝国 ダニー・グリーンのセルティック・クラブ[18][79] ナッキー・ジョンソンの組織 K&Aギャング エンライトギャング ニューヨーク ドワイヤーギャング ウェスティズ[18][79] ホワイトハンド・ギャング[18] ヒギンズ・ギャング セントルイス ホーガン・ギャング イーガンズ・ラッツ[62][79] |
| Caribbean See also: Piracy in the Caribbean and Illegal drugs in Puerto Rico Chadee gang (Trinidad and Tobago) Jamaican Yardies & Posses[18][14][16][80] Shower Posse[16][80] POW Posse Tottenham Mandem[81] Star Gang Klans Massive[82] No Limit Soldiers (Curaçao) Phantom death squad (Guyana) Suri-kartel (Suriname) Zoe Pound (Haitian, see also Tonton Macoute) Dominican drug cartels[83] Paulino organization[84] Féliz organization |
カリビアン こちらも参照のこと: カリブ海の海賊、プエルトリコの違法薬物 チャディー・ギャング(トリニダード・トバゴ) ジャマイカのヤーディー&ポッセ[18][14][16][80]。 シャワー・ポッセ[16][80]。 ポウ・ポッセ トッテナム・マンデム[81] スター・ギャング クランズ・マッシブ[82] ノー・リミット・ソルジャーズ(キュラソー) ファントム・デス・スクワッド(ガイアナ) スリ・カルテル(スリナム) ゾーイ・パウンド(ハイチ、トントン・マクーテも参照) ドミニカ麻薬カルテル[83] パウリーノ組織[84] フェリス組織 |
| South America Brazil Primeiro Comando da Capital, based in São Paulo Comando Vermelho, based in Rio de Janeiro Terceiro Comando, based in Rio de Janeiro (disbanded[85]) Terceiro Comando Puro, based in Rio de Janeiro Amigos dos Amigos, based in Rio de Janeiro Família do Norte, based in Amazonas Guardiões do Estado, based in Ceará Bolivia Bolivian drug cartels (See also García Meza regime drug trafficking) Chapare Cartel La Corporación Santa Cruz Cartel Colombia Main article: Illegal drug trade in Colombia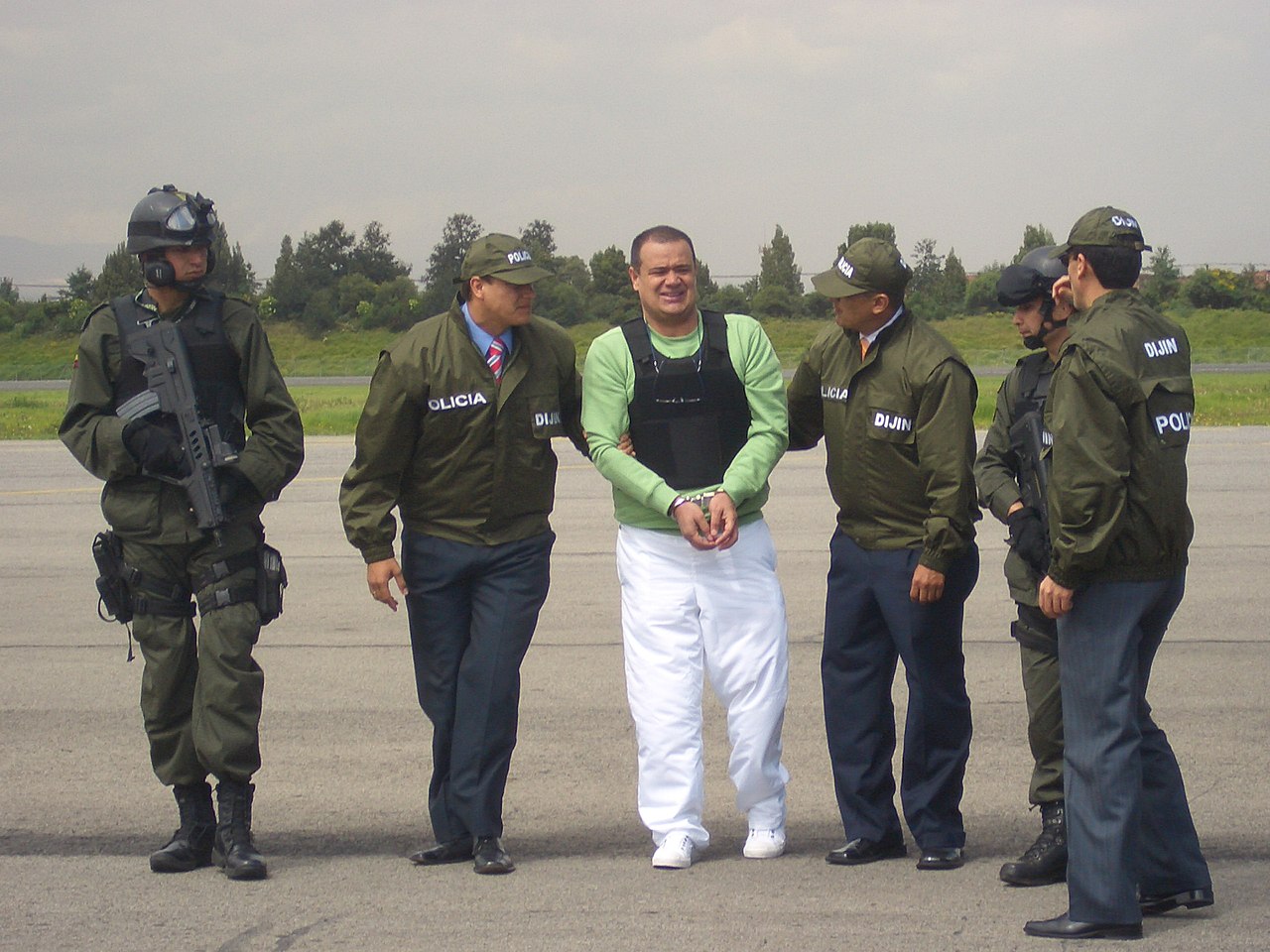  Luis Hernando Gomez-Bustamante, also known as "Rasguño", arrest performed by the National Police of Colombia Colombia is the largest producer of cocaine in the world,[86] and cocaine production in Colombia reached an all-time high in 2017.[87] Active Colombian drug cartels: The Black Eagles Clan del Golfo Oficina de Envigado National Liberation Army (Colombia) FARC dissidents Los Rastrojos Historical Colombian drug cartels: Medellín Cartel Cali Cartel Norte del Valle Cartel North Coast Cartel United Self-Defense Forces of Colombia Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia Peru Peruvian drug cartels (see also Vladimiro Montesinos) Zevallos organisation Venezuela Historically Venezuela has been a path to the United States for illegal drugs originating in Colombia, through Central America and Mexico and Caribbean countries such as Haiti, the Dominican Republic, and Puerto Rico. According to the United Nations, there has been an increase of cocaine trafficking through Venezuela since 2002.[88] In 2005, Venezuela severed ties with the United States Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA), accusing its representatives of spying.[89] Following the departure of the DEA from Venezuela and the expansion of DEA's partnership with Colombia in 2005, Venezuela became more attractive to drug traffickers.[90] Between 2008 and 2012, Venezuela's cocaine seizure ranking among other countries declined, going from being ranked fourth in the world for cocaine seizures in 2008[91] to sixth in the world in 2012.[92] The cartel groups involved include: The Cuntrera-Caruana Mafia clan moved to Venezuela,[93] which became an important hideout as the clan bought hotels and founded various businesses in Caracas and Valencia, as well as an extended ranch in Barinas, near the Colombian border. "Venezuela has its own Cosa Nostra family as if it is Sicilian territory," according to the Italian police. "The structure and hierarchy of the Mafia has been entirely reproduced in Venezuela." The Cuntrera-Caruana clan had direct links with the ruling Commission of the Sicilian Mafia, and are acknowledged by the American Cosa Nostra.[93] Pasquale, Paolo and Gaspare Cuntrera were expelled from Venezuela in 1992, "almost secretly smuggled out of the country, as if it concerned one of their own drug transports. It was imperative they could not contact people on the outside who could have used their political connections to stop the expulsion." Their expulsion was ordered by a commission of the Venezuelan Senate headed by Senator Cristobal Fernandez Dalo and his money laundering investigator, Thor Halvorssen Hellum. They were arrested in September 1992 at Fiumicino airport (Rome),[94][95] and in 1996 were sentenced to 13–20 years.[93] Norte del Valle Cartel : In 2008 the leader of the Colombian Norte del Valle Cartel, Wilber Varela, was found murdered in a hotel in Mérida in Venezuela.[96] The Cartel of the Suns According to Jackson Diehl. Deputy Editorial Page Editor of The Washington Post, the Bolivarian government of Venezuela shelters "one of the world's biggest drug cartels". There have also been allegations that former president Hugo Chávez and Diosdado Cabello being involved with drug trafficking.[97] In May 2015, The Wall Street Journal reported from United States officials that drug trafficking in Venezuela increased significantly with Colombian drug traffickers moving from Colombia to Venezuela due to pressure from law enforcement.[98] One United States Department of Justice official described the higher ranks of the Venezuelan government and military as "a criminal organization", with high ranking Venezuelan officials, such as National Assembly President Diosdado Cabello, being accused of drug trafficking.[98] Those involved with investigations stated that Venezuelan government defectors and former traffickers had given information to investigators and that details of those involved in government drug trafficking were increasing.[98] |
南米 ブラジル プリメイロ・コマンド・ダ・キャピタル(本拠地:サンパウロ コマンド・ヴェルメーリョ(リオデジャネイロを拠点とする リオデジャネイロを拠点とするテルセイロ・コマンド(解散[85])。 テルセイロ・コマンド・プロ(リオデジャネイロを拠点とする アミーゴス・ドス・アミーゴス(リオデジャネイロを拠点とする ファミリア・ド・ノルテ(アマゾナス州を拠点とする セアラ州を拠点とするGuardiões do Estado(Guardiões do Estado ボリビア ボリビアの麻薬カルテル(ガルシア・メザ政権の麻薬密売も参照のこと) チャパレ・カルテル ラ・コーポラシオン サンタ・クルス・カルテル コロンビア 主な記事 コロンビアの違法薬物取引  ルイス・エルナンド・ゴメス=ブスタマンテ、通称「ラスグーニョ」、コロンビア国民警察による逮捕劇 コロンビアは世界最大のコカイン生産国であり[86]、コロンビアにおけるコカイン生産量は2017年に過去最高を記録した[87]。 活動中のコロンビアの麻薬カルテル ブラック・イーグルス クラン・デル・ゴルフォ オフィシナ・デ・エンビガド 国民解放軍(コロンビア) FARC反体制派 ロス・ラストロホス コロンビアの歴史的麻薬カルテル メデジン・カルテル カリ・カルテル ノルテ・デル・バジェ・カルテル 北海岸カルテル コロンビア連合自衛隊 コロンビア革命軍 ペルー ペルーの麻薬カルテル(ウラジミーロ・モンテシーノスも参照) ゼバロス組織 ベネズエラ 歴史的にベネズエラは、コロンビアを起源とする違法薬物が、中米、メキシコ、ハイチ、ドミニカ共和国、プエルトリコなどのカリブ海諸国を経由して米国に至る経路となってきた。 国連によると、2002年以降、ベネズエラ経由のコカイン密売が増加している[88]。2005年、ベネズエラは、米国麻薬取締局(DEA)の代表者がス パイ行為を行っていると非難し、DEAとの関係を断絶した[89]。 [2008年から2012年にかけて、ベネズエラのコカイン押収量ランキングは他国の中で低下し、2008年にはコカイン押収量で世界第4位だった [91]が、2012年には世界第6位となった[92]。 関係するカルテルグループは以下の通り: クントレラ=カルアナ・マフィア一族はベネズエラに移り住み[93]、カラカスとバレンシアでホテルを買い、さまざまな事業を立ち上げるとともに、コロン ビア国境に近いバリナスに牧場を拡張し、重要な隠れ家となった。イタリア警察によれば、「ベネズエラには、まるでシチリアの領土であるかのように、独自の コーザ・ノストラ・ファミリーがある」。「マフィアの構造とヒエラルキーはベネズエラで完全に再現されている」。クントレラ=カルアナ一族はシチリア・マ フィアの支配委員会と直接的なつながりがあり、アメリカのコーザ・ノストラも認めている[93]。 パスクアーレ、パオロ、ガスパーレ・クントレラは1992年にベネズエラから追放され、「まるで自分たちの麻薬輸送に関係するかのように、ほとんど密かに 国外に密輸された。国外追放を阻止するために政治的コネクションを利用できる外部の人間と接触できないようにすることが不可欠だった」。彼らの追放は、ク リストバル・フェルナンデス・ダロ上院議員とマネーロンダリング調査官のトール・ハルボルセン・ヘルムが率いるベネズエラ上院の委員会によって命じられ た。彼らは1992年9月にフィウミチーノ空港(ローマ)で逮捕され[94][95]、1996年に13年から20年の刑を言い渡された[93]。 ノルテ・デル・バジェ・カルテル:2008年、コロンビアのノルテ・デル・バジェ・カルテルのリーダー、ウィルベル・バレラがベネズエラのメリダのホテルで殺害されているのが発見された[96]。 ジャクソン・ディールによれば、「太陽のカルテル」。ワシントン・ポスト紙の論説副編集長によると、ベネズエラのボリバル政府は「世界最大級の麻薬カルテ ル」を匿っている。また、ウゴ・チャベス前大統領とディオスダド・カベジョが麻薬密売に関与しているという疑惑もある[97]。 2015年5月、ウォール・ストリート・ジャーナル紙は米国当局者の話として、法執行機関からの圧力によりコロンビアの麻薬密売人がコロンビアからベネズ エラに移動し、ベネズエラでの麻薬密売が著しく増加したと報じた。 [98] 米国司法省のある高官は、ベネズエラ政府と軍の上層部を「犯罪組織」と表現しており、国民議会議長のディオスダド・カベロなどのベネズエラ高官が麻薬密売 で告発されている[98]。捜査関係者は、ベネズエラ政府の脱北者や元密売人が捜査当局に情報を提供しており、政府の麻薬密売に関与している者の詳細が増 加していると述べている[98]。 |
| Central America Honduras Honduran drug cartels Matta organization Cachiros El Salvador Mara Salvatrucha Nicaragua Nicaraguan drug cartels (see also Contras) Oscar Danilo Blandón |
中央アメリカ ホンジュラス ホンジュラス麻薬カルテル マタ組織 カチロス エルサルバドル マラ・サルバトルチャ ニカラグア ニカラグアの麻薬カルテル(コントラも参照のこと) オスカー・ダニロ・ブランドン |
| Asia East Asia Korea Korean criminal organizations (see also North Korea's illicit activities) Japan Japanese criminal organizations See also: Kenji Doihara § Criminal activities The yakuza of Japan are similar to the Italian mafias in that they originated centuries ago and follow a rigid set of traditions, but have several aspects that make them unique, such as their full-body tattoos and their fairly open place in Japanese society. Many yakuza groups are umbrella organizations, smaller gangs reporting to a larger crime syndicate. Active yakuza groups Roku-daime Yamaguchi-gumi 六代目山口組[12][13][18][99] Yon-daime Yamaken-gumi 四代目山健組[18][99] Ni-daime Kodo-kai 二代目弘道会[18] Ni-daime Takumi-gumi 二代目宅見組[99] Go-daime Kokusui-kai 五代目國粹会[99] Inagawa-kai 稲川会[12][18][99] Sumiyoshi-kai 住吉会[13][18][99] Sumiyoshi-ikka Shinwa-kai 住吉一家親和会 Kansuke Juni-daime 勘助十二代目 Kobe Yamaguchi-gumi Matsuba-kai 松葉会[99] Kyokuto-kai 極東会[99] Dojin-kai[99] 道仁会 Kitamura-gumi Yon-daime Kudo-kai[99] 四代目工藤會 Roku-daime Aizu-Kotetsu-kai 六代目会津小鉄会[99] Okinawa Kyokuryu-kai 沖縄旭琉会[99] Kyushu Seido-kai 九州誠道会 Go-daime Kyosei-kai 五代目共政会[99] San-daime Fukuhaku-kai 三代目福博会 Soai-kai 双愛会[99] Yon-daime Kyokuryu-kai 四代目旭琉会[99] San-daime Kyodo-kai 三代目俠道会[99] Taishu-kai 太州会[99] Shichi-daime Goda-ikka 七代目合田一家[99] Toa-kai 東亜会[18] Ni-daime Azuma-gumi 二代目東組[99] Yon-daime Asano-gumi 四代目浅野組[99] Hachi-daime Sakaume-gumi 八代目酒梅組 Yon-daime Kozakura-ikka 四代目小桜一家[99] Ni-daime Shinwa-kai 二代目親和会[99] Defunct yakuza groups Kantō-kai 関東会[99] Ni-daime Honda-kai 二代目本多会[99] Yamaguchi-gumi Goto-gumi 後藤組[99] Suishin-kai 水心会[100] Ichiwa-kai 一和会[13][99] San-daime Yamano-kai 三代目山野会[99] Nakano-kai 中野会[18][99] Kyokuto Sakurai-soke-rengokai 極東桜井總家連合会[99] |
Asia East Asia Korea Korean criminal organizations (see also North Korea's illicit activities) Japan Japanese criminal organizations See also: Kenji Doihara § Criminal activities The yakuza of Japan are similar to the Italian mafias in that they originated centuries ago and follow a rigid set of traditions, but have several aspects that make them unique, such as their full-body tattoos and their fairly open place in Japanese society. Many yakuza groups are umbrella organizations, smaller gangs reporting to a larger crime syndicate. Active yakuza groups(活動をしているヤクザ集団) Roku-daime Yamaguchi-gumi 六代目山口組[12][13][18][99] Yon-daime Yamaken-gumi 四代目山健組[18][99] Ni-daime Kodo-kai 二代目弘道会[18] Ni-daime Takumi-gumi 二代目宅見組[99] Go-daime Kokusui-kai 五代目國粹会[99] Inagawa-kai 稲川会[12][18][99] Sumiyoshi-kai 住吉会[13][18][99] Sumiyoshi-ikka Shinwa-kai 住吉一家親和会 Kansuke Juni-daime 勘助十二代目 Kobe Yamaguchi-gumi Matsuba-kai 松葉会[99] Kyokuto-kai 極東会[99] Dojin-kai[99] 道仁会 Kitamura-gumi Yon-daime Kudo-kai[99] 四代目工藤會 Roku-daime Aizu-Kotetsu-kai 六代目会津小鉄会[99] Okinawa Kyokuryu-kai 沖縄旭琉会[99] Kyushu Seido-kai 九州誠道会 Go-daime Kyosei-kai 五代目共政会[99] San-daime Fukuhaku-kai 三代目福博会 Soai-kai 双愛会[99] Yon-daime Kyokuryu-kai 四代目旭琉会[99] San-daime Kyodo-kai 三代目俠道会[99] Taishu-kai 太州会[99] Shichi-daime Goda-ikka 七代目合田一家[99] Toa-kai 東亜会[18] Ni-daime Azuma-gumi 二代目東組[99] Yon-daime Asano-gumi 四代目浅野組[99] Hachi-daime Sakaume-gumi 八代目酒梅組 Yon-daime Kozakura-ikka 四代目小桜一家[99] Ni-daime Shinwa-kai 二代目親和会[99] Defunct yakuza groups Kantō-kai 関東会[99] Ni-daime Honda-kai 二代目本多会[99] Yamaguchi-gumi Goto-gumi 後藤組[99] Suishin-kai 水心会[100] Ichiwa-kai 一和会[13][99] San-daime Yamano-kai 三代目山野会[99] Nakano-kai 中野会[18][99] Kyokuto Sakurai-soke-rengokai 極東桜井總家連合会[99] |
| Chinese See also: Tiandihui and Kuomintang in Burma § CIA connection and opium trade The Triads is a popular name for a number of Chinese criminal secret societies, which have existed in various forms over the centuries (see for example Tiandihui). However, not all Chinese gangs fall into line with these traditional groups, as many non-traditional criminal organizations have formed, both in China and the Chinese diaspora. Hong Kong-based Triads 14K Group 十四K Wo Group 和字頭 Wo Shing Wo 和勝和 Wo On Lok (Shui Fong) 和安樂(水房) Wo Hop To 和合圖(老和)[101] Sun Yee On 新義安(老新) Luen Group 聯字頭 Big Circle Gang 大圈 Sio Sam Ong (小三王) Chinese-American gangs (See also Tongs) Wah Ching 華青[102] Ping On Black Dragons 黑龍[103] Jackson Street Boys 積臣街小子[104] Taiwan-based Triads United Bamboo Gang 竹聯幫[105] Four Seas Gang 四海幫[105] Celestial Alliance Mainland Chinese crime groups (see also Hanlong Group) Chongqing group 重慶組 Defunct Honghuzi gangs Green Gang 青帮 Triads in Cholon Wu Bang |
中国語 も参照のこと: 天地匯とビルマの国民党 § CIAとのつながりとアヘン取引 トライアドは、何世紀にもわたってさまざまな形態で存在してきた中国の犯罪秘密結社の通称である(たとえば天地匯を参照)。しかし、すべての中国のギャン グがこれらの伝統的なグループに当てはまるわけではなく、多くの非伝統的な犯罪組織が中国と中国のディアスポラの両方で形成されている。 香港を拠点とするトライアド 14Kグループ 十四K 呉グループ和字頭 ウー・シン・ウー和勝和 沃温洛(水房)和安樂(水房) ウォ・ホップ・トー和合圖(老和)[101] (Wo Hop To 和合圖(老和)) サンイーオン 新義安(老新) ルエン・グループ 聯字頭 ビッグ・サークル・ギャング 大圈 シオ・サム・オング(小三王) 中国系アメリカ人ギャング(トンも参照) ワウ・チン華青[102] (Wah Ching 華青 ピン・オン ブラック・ドラゴンズ(Black Dragons) 黑龍[103 ジャクソン・ストリート・ボーイズ 積臣街小子[104] 台湾を拠点とするトライアド ユナイテッド・バンブー・ギャング 竹聯幫[105] フォーシーズ・ギャング 四海幫[105] セレスティアル・アライアンス 中国本土の犯罪グループ(漢龍集団も参照のこと) 重慶組 消滅 ホンフジ・ギャング グリーン・ギャング 青帮 チョロンのトライアド ウー・バン |
| Southeast Asia See also: Manchukuo § Drug trafficking Golden Triangle[12][18][76][14][106] Burmese drug cartels (see also Myanmar Nationalities Democratic Alliance Army) Khun Sa cartel[18][14] (see also Mong Tai Army) Red Wa (see also United Wa State Army and National Democratic Alliance Army) Hawngleuk Militia Han cartel Laotian drug cartels (see also Ouane Rattikone) See also: Piracy in the Strait of Malacca Chao pho Red Wa Filipino crime gangs (See also Abu Sayyaf and New People's Army) Kuratong Baleleng[12] Waray-Waray gangs[107] Bahala Na Gang Sigue Sigue Sputnik Putik gang (defunct) Cambodian crime gangs Teng Bunma organization Malaysian crime gangs Mamak Gang[108] Secret societies in Singapore Ang Soon Tong 洪順堂 Ghee Hin Kongsi 義興公司 Hai San 海山 Wah Kee華記 Ah Kong 阿公 Vietnamese Xã Hội Đen Bình Xuyên[109] Đại Cathay's mafia during the 60s Năm Cam's mafia of the 90s[12][18] Khánh Trắng's "Đồng Xuân Labor Union", a crime syndicate under the guise of a legal entity Dung Hà's gang Vũ Xuân Trường's gang: a crime syndicate led by Vũ Xuân Trường, a government official and also a drug lord. |
東南アジア も参照のこと: 満州国§麻薬密売 Golden Triangle[12][18][76][14][106] ビルマ麻薬カルテル(ミャンマー民族民主同盟軍も参照) クン・サ・カルテル[18][14](モンタイ軍も参照) レッド・ワー(統一ワー国軍、国民民主同盟軍も参照) ホーングルック民兵 ハン・カルテル ラオスの麻薬カルテル(ウアン・ラティコーンも参照) 以下も参照のこと: マラッカ海峡における海賊行為 チャオフォー レッド・ワ フィリピンの犯罪組織(アブ・サヤフ、新人民軍も参照) クラトン・バレレン[12] ワライ・ワライ・ギャング[107] バハラ・ナ・ギャング シゲシゲ・スプートニク プティック・ギャング(消滅) カンボジアの犯罪組織 テン・ブンマ組織 マレーシアの犯罪組織 ママク・ギャング[108] シンガポールの秘密結社 アン・スン・トン 洪順堂 ゲー・ヒン・コングシ義興公司 ハイ・サン海山 ワウ・キー華記 アーコン阿公 ベトナム語 Xã Hội Đen ビン・スェン[109](Bình Xuyên 60年代のダイ・キャセイのマフィア 90年代のナム・カムのマフィア[12][18]。 カイン・チャンの「ドン・スアン労働組合」(法人を装った犯罪組織 ズンハー一味 Vũ Xuân Trường一味:政府高官で麻薬王でもあるVũ Xuân Trườngが率いる犯罪組織。 |
| South Asia See also: Haqqani Network and Zomi Revolutionary Army Mafia Raj Dacoit gangs India Indian mafia (See also Insurgency in Northeast India) Mumbai D-Company डी कंपनी[13][18] Chhota Rajan gang राजन गिरोह[13] Gawli gang गवली गिरोह[13] Bada Rajan gang Surve gang Mudaliar gang Mastan gang Budesh gang Kalani gang Kala Kaccha Gangs Chaddi Baniyan Gangs Singh gang Veerappan gang Devi gang Pathan mafia Lala gang Uttar Pradesh Ansari gang Yadav gang Bangalore Rai gang Ramachandra gang Jayaraj gang Sri Lanka Sri Lankan criminal groups Pakistan Pakistani mafia (See also Peoples' Aman Committee, Tehrik-i-Taliban Pakistan, Muttahida Qaumi Movement and ISI involvement with drugs) Chotu gang Lyari Gang Afridi Network Afghanistan Golden Crescent[12][14] Afghan drug cartels[13][72] (see also Taliban) Noorzai Organization[110] Khan organization Karzai organization (alleged) Bagcho organization Central Asia Uzbek mafia (See also Islamic Movement of Uzbekistan) Rakhimov organization Kyrgyz mafia Erkinbayev group Akmatbayev group Kolbayev group |
南アジア 関連項目:ハッカーニ・ネットワーク、ゾミ革命軍 マフィア・ラージ ダコイト・ギャング インド インドのマフィア(関連項目:インド北東部の反乱) ムンバイ D-カンパニー डी कंपनी[13][18] チョータ・ラジャン・ギャング राजन गिरोह[13] ガウリ・ギャング गवली गिरोह[13] バダ・ラジャン・ギャング サーヴ・ギャング ムダリアール・ギャング マスタン・ギャング ブデシュ・ギャング カラニ・ギャング カラ・カチャ・ギャング チャディ・バニヤン・ギャング シン・ギャング ヴィラッパン・ギャング デヴィ・ギャング パタン・マフィア ララ・ギャング ウッタル・プラデーシュ アンサリ・ギャング ヤダフ・ギャング バンガロール ライ・ギャング ラマチャンドラ・ギャング ジャヤラージ・ギャング スリランカ スリランカの犯罪組織 パキスタン パキスタンのマフィア(関連項目:人民安全委員会、パキスタン・タリバン運動、ムッタヒダ・カウミ運動、および ISI の麻薬関与) チョトゥ・ギャング リヤリ・ギャング アフリディ・ネットワーク アフガニスタン ゴールデン・クレセント[12][14] アフガニスタンの麻薬カルテル[13][72](タリバンも参照) ノルザイ組織[110] カーン組織 カルザイ組織(疑惑) バグチョ組織 中央アジア ウズベキスタン・マフィア(ウズベキスタン・イスラム運動も参照) ラヒモフ組織 キルギス・マフィア エルキンバエフ・グループ アクマトバエフ・グループ コルバエフ・グループ |
| West Asia See also: Shabeeha, al-Qaeda in Iraq, Islamic State in Iraq and the Levant, Mokhtar Belmokhtar, and Piracy in the Persian Gulf [111][112] Israeli mafia[12][72][113] (see also Stern Gang) Abergil Crime Family משפחת הפשע אברג'יל[12][13] Alperon crime family משפחת הפשע אלפרון[12] Zeev Rosenstein organization ארגון זאב רוזנשטיין[12] Palestinian organized crime (See also Abu Nidal Organization) Doghmush clan Turkish mafia[12][13][114] Crime groups in Turkey (see also Deep state and Yüksekova Gang) Kılıç gang[18] Çakıcı gang[18][114] Yaprak Family Topal organisation Söylemez Gang Kurdish clans (see also Kurdistan Workers' Party#Involvement in drug trafficking) Baybaşin crime family[114] Cantürk gang Arifs[80][115] Turkish organised crime in Germany Arabacı clan[116] İmaç clan (Netherlands) Iranian organized crime (see also Jundallah and illegal activities of the IRGC) Tahvili crime family[117] Lebanese mafia (See also Lebanese Civil War militias) Arab crime clans Miri-Clan Al-Zein Clan Ibrahim clan |
西アジア こちらも参照のこと: シャビーハ、イラクのアルカイダ、イラクとレバントのイスラム国、モフタール・ベルモフタール、ペルシャ湾の海賊も参照のこと。 [111][112] イスラエルのマフィア[12][72][113](スターン・ギャングも参照のこと) アベルギル犯罪一家 משפשעאברגת'הפ[12][13] アルペロン・クライム・ファミリー משפחת הäשע אלפרון[12]. ゼーブ・ローゼンスタイン組織 ארגון זאב רון[12] パレスチナの組織犯罪(アブ・ニダル組織も参照のこと) ドグムシュ一族 トルコのマフィア[12][13][114]。 トルコの犯罪組織(ディープ・ステート、ユクセコバ・ギャングも参照) クルチ・ギャング[18] チャク・ギャング[18][114] ヤプラク・ファミリー トパル組織 セイレメズ・ギャング クルド人一族(クルド労働者党#麻薬密売への関与も参照のこと) ベイバシン犯罪一家[114] カントゥルク一味 アリフス[80][115] ドイツのトルコ系組織犯罪 アラバク一族[116] イマチ一族(オランダ) イランの組織犯罪(JundallahおよびIRGCの非合法活動も参照のこと) タフヴィリ犯罪一族[117] レバノンマフィア(レバノン内戦民兵も参照) アラブの犯罪一族 ミリ一族 アル・ザイン一族 イブラヒム一族 |
| Eurasia Russia Although organized crime existed in the Soviet era, the gangs really gained in power and international reach during the transition to capitalism. The term Russian Mafia, 'mafiya' or mob is a blanket (and somewhat inaccurate) term for the various organized crime groups that emerged in this period from the 15 former republics of the USSR and unlike their Italian counterparts does not mean members are necessarily of Russian ethnicity or uphold any ancient criminal traditions, although this is the case for some members. Russian-Jewish mafia Brighton Beach Agron gang[18][118] Nayfeld gang[118] Balagula gang[118] Mogilevich organization[13][119] Brothers' Circle (Existence is debatable) Russian mafia (See also Lubyanka Criminal Group, Three Whales Corruption Scandal and Sergei Magnitsky) Moscow Izmaylovskaya gang[13][119] Solntsevskaya bratva[12][13][18][119] New York branch[119] Orekhovskaya gang[119] St Petersburg (See also Baltik-Eskort) Tambov Gang[119] Togliatti mafia Uralmash gang Lazovsky gang Vladivostok gang Kurganskaya group Tsapok gang 'Elephants' group Kazan gang North Caucasia See also Caucasus Emirate Chechen mafia[12][13][119] (See also Special Purpose Islamic Regiment and Kadyrovtsy) Obschina[119] Labazanov gang[18] Georgia Georgian mafia[119] (See also Mkhedrioni and Forest Brothers) Kutaisi clan[119][120] Tbilisi clan[120] 21st Century Association Armenia Armenian mafia[121] Mirzoyan-Terdjanian organization[121] Armenian Power[121] Azerbaijan Azeri mafia Janiev organization[12 |
ユーラシア ロシア 組織犯罪はソビエト時代にも存在したが、暴力団は資本主義への移行期に勢力を拡大し、国際的な影響力を持つようになった。ロシアン・マフィア、マフィア、 マフィアという用語は、この時代にソ連の15の旧共和国から出現したさまざまな組織犯罪集団に対する包括的な(そしてやや不正確な)用語であり、イタリア のそれとは異なり、構成員が必ずしもロシア系民族であるとか、古くからの犯罪の伝統を守っているという意味ではない。 ロシア系ユダヤ人マフィア ブライトンビーチ アグロンギャング[18][118] ネイフェルド・ギャング[118] バラグラ・ギャング[118] Mogilevich organization[13][119] ブラザーズ・サークル(存在については議論の余地がある) ロシア・マフィア(ルビャンカ犯罪グループ、3頭のクジラ汚職スキャンダル、セルゲイ・マグニツキーも参照のこと) モスクワ イズマイロフスカヤ・ギャング[13][119]。 Solntsevskaya bratva[12][13][18][119] ニューヨーク支部[119] オレホフスカヤ・ギャング[119] サンクトペテルブルク(バルチク・エスコートも参照のこと) タンボフ・ギャング[119] トリアッティ・マフィア ウラルマッシュ・ギャング ラゾフスキーギャング ウラジオストク・ギャング クルガンスカヤ・ギャング ツァポック・ギャング エレファンツ」グループ カザンギャング 北コーカサス コーカサス首長国も参照 チェチェン・マフィア[12][13][119](イスラム特別目的連隊、カディロフツィーも参照) オブスチナ[119] ラバザノフ一味[18] グルジア グルジアマフィア[119](ムケドリオーニ、フォレスト・ブラザーズも参照) クタイシ一族[119][120]。 トビリシ組[120] 21世紀協会 アルメニア アルメニア・マフィア[121] ミルゾヤン=テルジャニアン組織[121] アルメニアン・パワー[121] アゼルバイジャン アゼルバイジャンマフィア ジャニエフ組織[12 |
| Europe Sweden Original Gangsters[123] Fucked For Life[123] Uppsalamaffian Chosen Ones Werewolf Legion Asir Vårvädersligan Netherlands Organized crime in the Netherlands Bruinsma drug gang[18] Holleeder gang[18] Moroccan mafia France French Milieu (See also Service d'Action Civique) Corsican mafia[18][106][124] (see also National Liberation Front of Corsica) Unione Corse[76][14] Brise de Mer gang[124] Les Caïds Des Cités Faïd gang The Barbarians[125] Wigs gang North African Brigade (see also Carlingue) Tractions Avant gang[126] Bande des Trois Canards French gypsy gangs Hornec gang[124] Greece Greek mafia Ireland Ireland Dublin Cahill gang[18][80] Gilligan gang[18][80] Foley gang Hyland gang Dunne gang The Westies Limerick McCarthy-Dundon Keane-Collopy Rathkeale Rovers Kinahan Organised Crime Group Spain Spain Galician mafia Romani clans El Clan De La Paca Poland Poland (See also Group 13) Pruszków mafia Wołomin mafia Slovakia Slovak mafia Hungaro-Slovak mafia Hungary Raffael clan Sztojka clan Czech Republic Mrázek organization Krejčíř organization Italy Sicilian Mafia[12][13][18][20][17][113] Sicilian Mafia Commission Mandamenti See also List of Sicilian Mafia clans Cuntrera-Caruana Mafia clan Inzerillo Mafia clan Corleonesi[12][18] Greco Mafia clan Motisi Mafia clan 'Ndrangheta[12][18][17] La Provincia See also List of 'ndrine Honoured Society (Melbourne)[127] Mammoliti 'ndrina Bellocco 'ndrina Cataldo 'ndrina Commisso 'ndrina Cordì 'ndrina De Stefano 'ndrina Pesce 'ndrina Barbaro 'ndrina Piromalli 'ndrina Serraino 'ndrina Siderno Group[19] Camorra[12][18][72][17] Secondigliano Alliance Licciardi clan[17] Contini clan[17] Lo Russo clan[17] Mallardo clan[17] Di Lauro Clan[17] Casalesi clan[17] Fabbrocino clan[17] Vollaro clan[17] Scissionisti di Secondigliano[17] La Torre clan[17] Polverino clan Rinaldi clan De Luca Bossa clan Aprea-Cuccaro clan Cesarano clan Puca clan Sacra Corona Unita[12][13][18][17] Società foggiana[128][129] Stidda[18] Mala del Brenta[17] Banda della Magliana[130] Mafia Capitale Sinti Casamonica clan Clan Spada di Ostia Milanese gangs Banda della Comasina[131] Turatello crew Balkans Balkan organized crime gained prominence in the chaos following the communist era, notably the transition to capitalism and the wars in former Yugoslavia. Albanian mafia[12][13][17] Kosovan mafia Albania Gang of Çole Gang of Gaxhai Gang of Pusi i Mezinit Lazarat marijuana growers Rudaj Organization[132] (New York City) Gang of Ismail Lika Dobroshi gang[133] (International) Naserligan[123] (Sweden) K-Falangen (Sweden) Bosnian mafia[12] Prazina gang[113] Bajramović gang Delalić gang M-Falangen (Sweden) Bulgarian mafia[13][18] (see also Multigroup) VIS[13][18] SIC Karamanski gang TIM Naglite Rashkov clan Serbian mafia[12][13] Arkan clan[13][113] Zemun Clan[13] Joca Amsterdam gang Magaš clan Giška gang Pink Panthers[134] Serb mafia in Scandinavia Kotur mob Yugoslav Brotherhood Montenegrin mafia[12][13] (see also allegations of Milo Đukanović's involvement in cigarette smuggling) Romanian mafia Băhăian organisation Great Britain See also: List of organisations known as the Irish Republican Army and Ulster loyalism § Paramilitary and vigilante groups London Adams crime family[18][115] The Richardson Gang[18][80][135] The Firm[18][80][135] The Syndicate Comer gang Buttmarsh Boys Interwar era mobs Messina Brothers[18][80][135] Sabini syndicate[18][80][135] Hoxton Gang[80][135] Elephant and Castle Mob[80][135] Birmingham Boys[18][135] Essex Boys Manchester Quality Street Gang[80] Noonan firm[80] Cheetham Hillbillies The Gooch Close Gang Liverpool Curtis Warren's drug empire[18] Whitney gang Aggi Crew[115] Glasgow McGraw firm[18] Thompson firm[18][80] Delta Crime Syndicate Bestwood Cartel Ukraine Ukrainian mafia Donetsk Clan Salem gang Lithuania Lithuanian mafia Vilnius Brigade[136] Estonia Estonian mafia/Obtshak Linnuvabriku group Transnistria Transnistrian mafia |
ヨーロッパ スウェーデン オリジナル・ギャングスターズ[123] ファックド・フォー・ライフ[123] ウプサラマフィアン 選ばれし者たち 狼男軍団 アシール 人狼軍団 オランダ オランダの組織犯罪 ブルインズマ・ドラッグ・ギャング[18] ホリーダー・ギャング[18] モロッコマフィア フランス フランス・ミリュウ(Service d'Action Civiqueも参照) コルシカ・マフィア[18][106][124](コルシカ国民解放戦線も参照)。 ユニオネ・コルセ[76][14](Unione Corse ブリーズ・ド・メールギャング[124] レ・ケイド・デ・シテス ファイド・ギャング バーバリアンズ[125] かつらギャング 北アフリカ旅団(カーリングーも参照のこと) トラクション・アヴァン・ギャング[126] バンデ・デ・トロワ・カナール フランスのジプシー・ギャング ホーネック・ギャング[124] ギリシャ ギリシャマフィア アイルランド アイルランド ダブリン ケーヒル・ギャング[18][80] ギリガン・ギャング[18][80] フォーリーギャング ハイランド・ギャング ダン・ギャング ウェスティーズ リムリック マッカーシー-ダンドン キーン・コロピー ラスキール・ローヴァーズ キナハン組織犯罪グループ スペイン スペイン ガリシアン・マフィア ロマニ族 エル・クラン・デ・ラ・パカ ポーランド ポーランド(グループ13も参照) プルシュクフ・マフィア ヴォウォミンマフィア スロバキア スロバキアマフィア ハンガロ=スロバキア・マフィア ハンガリー ラファエル一族 シュトイカ一族 チェコ共和国 ムラーチェク組織 クレジュ組織 イタリア Sicilian Mafia[12][13][18][20][17][113] シチリアマフィア委員会 マンダメンティ シチリアマフィアのクランの一覧も参照のこと。 クントレラ=カルアナ・マフィア一族 インゼリッロ・マフィア一族 コルレオーネシ[12][18](Corleonesi グレコ・マフィア一族 モティシマフィア 'Ndrangheta[12][18][17] ラ・プロヴィンシア ンドラインのリストも参照のこと。 名誉協会(メルボルン)[127] ンドリーナ ベロッコンドリーナ カタルドンドリーナ コミッソンドリーナ コルディ デ・ステファノ ペッシェ バルバロ ピローマッリ セライノ シデルノグループ[19] Camorra[12][18][72][17] セコンディリアーノ同盟 リチャルディ一族[17] コンティーニ一族[17] ロ・ルッソ一族[17] マッラルド一族[17] ディ・ラウロ氏族[17] カサレシ一族[17] ファブロチーノ一族[17] ヴォッラーロ氏族[17] スキッショニスティ・ディ・セコンディリアーノ氏族[17] ラ・トーレ一族[17] ポルヴェリーノ一族 リナルディ一族 デ・ルカ・ボッサ一族 アプレア=クッカロ一族 チェザラーノ一族 プーカ一族 サクラ・コローナ・ウニタ[12][13][18][17] ソシエタ・フォッジアーナ[128][129]。 スティッダ[18] マーラ・デル・ブレンタ[17] バンダ・デッラ・マリアーナ[130] マフィア・キャピターレ シンティ・カサモニカ一族 スパーダ・ディ・オスティア一族 ミラノのギャング バンダ・デッラ・コマシーナ[131] トゥラテッロ一味 バルカン半島 バルカン半島の組織犯罪は、共産主義時代後の混乱期、特に資本主義への移行と旧ユーゴスラビアでの戦争で脚光を浴びた。 アルバニア・マフィア[12][13][17]。 コソビアのマフィア アルバニア ギャング・オブ・チョレ ギャング・オブ・ギャクシャイ プシ・イ・メジニットのギャング ラザラット大麻栽培者 ルダージ組織[132](ニューヨーク市) イスマイル・リカのギャング ドブロシ・ギャング[133](インターナショナル) ナセルリガン[123](スウェーデン) Kファランゲン(スウェーデン) ボスニア・マフィア[12] プラジナギャング[113] バジャモヴィッチ・ギャング デラリッチ・ギャング M-ファランゲン(スウェーデン) ブルガリアマフィア[13][18](マルチグループも参照) ヴィス[13][18] SIC カラマンスキー一味 TIM ナグライト ラシュコフ一族 セルビアマフィア[12][13] アルカン一族[13][113] ゼムン一族[13] ジョカ・アムステルダム組 マガシュ一族 ジシュカ・ギャング ピンクパンサー[134] スカンジナビアのセルビア系マフィア コトゥール・マフィア ユーゴスラビア同胞団 モンテネグロのマフィア[12][13](ミロ・ドゥカノヴィッチのタバコ密輸関与疑惑も参照)。 ルーマニアマフィア バハイアン組織 イギリス 以下も参照のこと: アイルランド共和国軍として知られる組織のリストとアルスター忠誠主義§パラミリタリーと自警団グループ ロンドン アダムズ犯罪一家[18][115] リチャードソン・ギャング[18][80][135] ザ・ファーム[18][80][135]。 シンジケート コマー・ギャング バットマーシュ・ボーイズ 戦間期のマフィア メッシーナ・ブラザーズ[18][80][135] サビーニ・シンジケート[18][80][135] ホクストン・ギャング[80][135] エレファント・アンド・キャッスル・モブ[80][135] バーミンガム・ボーイズ[18][135] エセックス・ボーイズ マンチェスター クオリティ・ストリート・ギャング[80] ヌーナンファーム[80] チーサム・ヒルビリーズ グーチ・クローズ・ギャング リバプール カーティス・ウォーレンの麻薬帝国[18] ホイットニー・ギャング アギ・クルー[115] グラスゴー マグロー・ファーム[18] トンプソン・ファーム[18][80] デルタ犯罪シンジケート ベストウッドカルテル ウクライナ ウクライナマフィア ドネツク一族 セーラムギャング リトアニア リトアニアマフィア ヴィリニュス旅団[136] エストニア エストニアのマフィア/オブシャク リヌヴァブリク・グループ トランスニストリア トランスニストリアマフィア |
| Australia See also: Federated Ship Painters and Dockers Union and Nugan Hand Bank Sydney 5T gang[137] (1985–1999) Freeman gang (defunct) Lenny's gang (1960s) Mr Sin's gang Razor gangs[138] (1920s) Melbourne Carlton Crew[18][127] Moran family[127] Williams family[127] Pettingill family Richmond gang Perth Salvator cartel[139] |
オーストラリア 以下も参照のこと: 連邦船舶塗装港湾労働組合およびヌーガン・ハンド・バンク シドニー 5Tギャング[137](1985年~1999年) フリーマン・ギャング(消滅) レニー・ギャング(1960年代) ミスター・シン・ギャング レイザー・ギャング[138](1920年代) メルボルン カールトン・クルー[18][127] モラン・ファミリー[127] ウィリアムズ・ファミリー[127] ペッティンギル・ファミリー リッチモンドギャング パース サルバトール・カルテル[139] |
| https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drug_cartel |
|
ハッパノミクス : 麻薬カルテルの経済学 / トム・ウェインライト [著] ; 千葉敏生訳, 東京 : みすず書房 ,
2017.12/Narconomics : how to run a drug cartel / Tom Wainwright,
PublicAffairs , 2017 [eBook] |
リ ンク
文 献
そ の他の情報
Copyleft, CC, Mitzub'ixi Quq Chi'j, 1996-2099
☆
 ☆
☆