Winch, Peter, The idea of a social science and its relation to philosophy, 1958, 2015. with a new introduction by Raimond Gaita (2015) This book can be explained as "In the fiftieth anniversary of this book's first release, Winch's argument remains as crucial as ever. Originally published in 1958, The Idea of a Social Science and Its Relation to Philosophy was a landmark exploration of the social sciences, written at a time when that field was still young and had not yet joined the Humanities and the Natural Sciences as the third great domain of the Academy. A passionate defender of the importance of philosophy to a full understanding of 'society' against those who would deem it an irrelevant 'ivory towers' pursuit, Winch draws from the works of such thinkers as Ludwig Wittgenstein, J.S. Mill and Max Weber to make his case. In so doing he addresses the possibility and practice of a comprehensive 'science of society'."- Nielsen BookData.
"Peter Winch saw himself as an uncompromising Wittgensteinian. He was not personally acquainted with Wittgenstein; Wittgenstein's influence upon him was mostly mediated through that of Rush Rhees (1905-1989), who was his colleague at the University College of Swansea, now known as Swansea University, and whom Wittgenstein appointed as one of his literary executors.[7] Winch's translation of Wittgenstein's Vermischte Bemerkungen (as edited by Georg Henrik von Wright) was published in 1980 as Culture and Value (with a new translation by Winch of a revised edition by Alois Pichler appearing in 1998).[8] After the death of Rhees in 1989, Winch took over his position as literary executor./ From Rush Rhees, Winch derived his interest in the religious writer Simone Weil. Part of the appeal was a break from Wittgenstein into a very different type of philosophy which could nevertheless be tackled with familiar methods. Also Weil's ascetic, somewhat Tolstoyan, form of religion harmonised with one aspect of Wittgenstein's personality./ At a time when most Anglo-American philosophers were heavily under the spell of Wittgenstein, Winch's own approach was strikingly original. While much of his work was concerned with rescuing Wittgenstein from what he took to be misreadings, his own philosophy involved a shift of emphasis from the problems that preoccupied Oxford style ‘linguistic’ philosophy, towards justifying and explaining 'forms of life' in terms of consistent language games. He took Wittgensteinian philosophy into areas of ethics and religion, which Wittgenstein himself had relatively neglected, sometimes showing considerable originality. An example is his illuminating treatment of the moral difference between someone who tries and fails to commit murder and someone who succeeds, in his essay "Trying" in Ethics and Action. With the decline of interest in Wittgenstein, Winch himself was increasingly neglected and the challenge his arguments presented to much contemporary philosophy was sidestepped or ignored. In insisting on the continuity of Wittgenstein's concerns from the Tractatus through to the Philosophical Investigations, Winch made a powerful case for Wittgenstein's mature philosophy, as he understood it, as the consummation and legitimate heir of the entire analytic tradition.[9]" - Peter Winch.
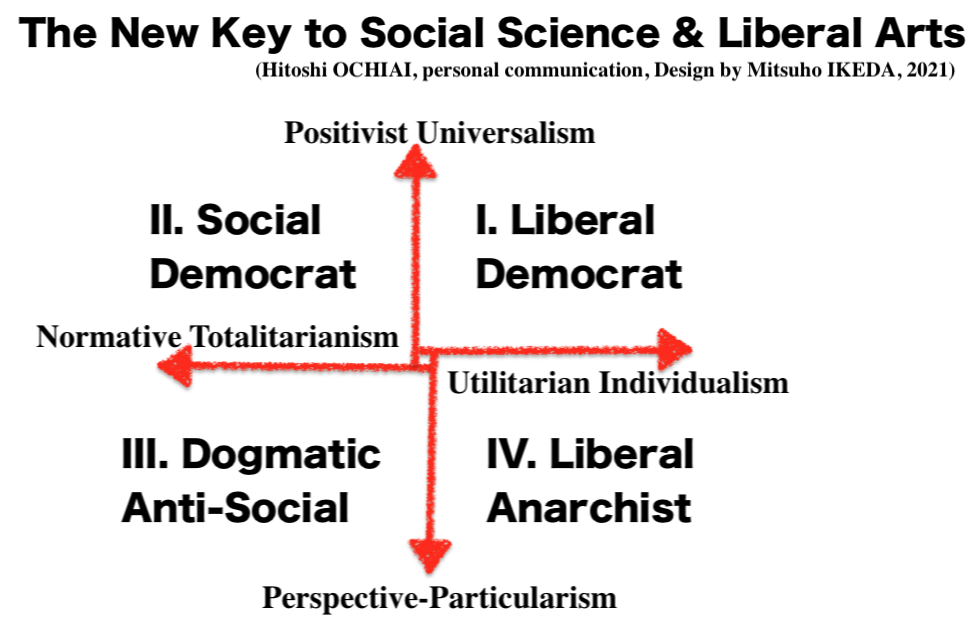
We need new key to idea of a social science and its relation to philosophy in post-colonial and post-modern new millenium century.
Links
- +
Bibliography
- +
Other informations