Ariosophy

Ariosophy


アルマニズムとアリオゾフィーは、1890年から 1930年にかけて、グイド・フォン・リストとイェルク・ランツ・フォン・リーベンフェルスによってそれぞれオーストリアで開拓された秘教思想体系である。 アーリア人の知恵を意味する「アリオゾフィー」という言葉は、1915年にランツ・フォン・リーベンフェルスによって初めて作られ、1920年代には彼の 教義名となった。以下は、ウィキペディアのAriosophy(英語)項目からの引用と翻訳である。
| general description |
Armanism and
Ariosophy are esoteric ideological systems that were pioneered by Guido
von List and Jörg Lanz von Liebenfels respectively, in Austria between
1890 and 1930. The term 'Ariosophy', which means the wisdom of the
Aryans, was first coined by Lanz von Liebenfels in 1915 and in the
1920s, it became the name of his doctrine. In research on the topic,
such as Nicholas Goodrick-Clarke's book The Occult Roots of Nazism, the
term 'Ariosophy' is generically used to describe the Aryan-esoteric
theories of a subset of the 'Völkische Bewegung'.[1] This broader use
of the word is retrospective and it was not generally current among the
esotericists themselves. List actually called his doctrine 'Armanism',
while Lanz used the terms 'Theozoology' and 'Ario-Christianity' before
the First World War. The ideas of Von List and Lanz von Liebenfels were part of a general occult revival that occurred in Austria and Germany during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, a revival was loosely inspired by Christianity, historical Germanic paganism and holistic philosophy as well as by esoteric concepts that were influenced by German romanticism and Theosophy. The connection between this form of Germanic mysticism and historical Germanic culture is evident in the mystics' fascination with runes, in the form of Guido von List's Armanen runes. |
ア
ルマニズムとアリオゾフィーは、1890年から1930年にかけて、ギド・フォン・リストとイェルク・ランツ・フォン・リーベンフェルスによってそれぞれ
オーストリアで開拓された秘教思想体系である。アーリア人の知恵を意味する「アリオゾフィー」という言葉は、1915年にランツ・フォン・リーベンフェル
スによって初めて作られ、1920年代には彼の教義名となった。ニコラス・グドリック=クラークの著書『The Occult
Roots of Nazism』など、このテーマに関する研究において、「アリオス哲学」という言葉は、「Völkische
Bewegung」のサブセットのアーリア人秘教理論を一般的に表すために使われている[1]
この言葉の広い使用は回顧的で、秘教徒自身の間で一般的に流布されていたわけではないのだ。リストは実際に自分の教義を「アルマニズム」と呼び、ランツは
第一次世界大戦前に「テオゾロジー」と「アリオ・クリスチャン」という言葉を用いていた。 フォン・リストとランツ・フォン・リーベンフェルスの思想は、19世紀後半から20世紀初頭にかけてオーストリアとドイツで起こった一般的なオカルト・リ バイバルの一部だった。このリバイバルは、キリスト教、歴史的ゲルマン異教、全体論的哲学、さらにドイツ・ロマン主義や神智学の影響を受けた秘儀的概念か らゆるやかに影響を受けたものである。このゲルマン神秘主義と歴史的ゲルマン文化とのつながりは、グイド・フォン・リストのアルマーネン・ルーンという形 で、神秘主義者たちがルーン文字に魅了されたことに表れている。 |
| Overview |
The ideology regarding the Aryan
race (in the sense of Indo-Europeans, runic symbols, the swastika, and
sometimes occultism) are important elements of Ariosophy. By 1899 at
the earliest or by 1900 at the latest, esoteric notions entered Guido
List's thoughts.[2] In April 1903, he sent his manuscript, proposing
what Goodrick-Clarke calls a "monumental pseudoscience" concerning the
ancient German faith, to the Imperial Academy of Sciences in Vienna[3]
onwards. These Ariosophic ideas (together with, and influenced by,
Theosophy) contributed significantly to an occult counterculture in
Germany and Austria. A historic interest in this topic has stemmed from
the ideological relationship between Ariosophy and Nazism, and it is
obvious in such book titles as: The Occult Roots of Nazism by Nicholas Goodrick-Clarke Der Mann, der Hitler die Ideen gab (The Man Who Gave Hitler His Ideas), Wilfried Daim's biography of Lanz von Liebenfels However, Goodrick-Clarke's comprehensive study finds little evidence of direct influence, except in the case of the highly idiosyncratic ancient-German mythos that was elaborated by the "clairvoyant" SS-Brigadeführer Karl Maria Wiligut,[Note 1] of which the practical consequences were, first, the incorporation of Wiligut's symbolism into the ceremonies of an elite circle within the SS; and, secondly, the official censure of those occultists and runic magicians whom Wiligut stigmatized as heretics, which may have persuaded Heinrich Himmler to order the internment of several of them.[Note 2] The most notable other case is Himmler's Ahnenerbe. (For the debate on the direct relations to Nazi ideology, see Religious aspects of Nazism.) Goodrick-Clarke examines what evidence there is for influences on Hitler and other Nazis, but he concludes that "Ariosophy is a symptom of rather than an influence in the way that it anticipated Nazism".[7] |
アーリア人(インド・ヨーロッパ人という意味で)に関する思想、ルーン
文字、鉤十字、そして時にはオカルトも、アリオス哲学の重要な要素である。早ければ1899年、遅くとも1900年には、秘教的な概念がグイド・リストの
思考に入り込み、1903年4月には、グドリック=クラークが言うところの古代ドイツ信仰に関する「記念すべき疑似科学」を提案した原稿をウィーンの帝国
科学アカデミーに送り[3]、以後は、グドリック=クラークが「記念すべき疑似科学」を提案するようになる。これらのアリオス派の思想は、神智学ととも
に、またその影響を受けて、ドイツやオーストリアのオカルト・カウンターカルチャーに大きく貢献した。このテーマに対する歴史的な関心は、有神論とナチズ
ムの思想的な関係からきており、それは次のような書名からも明らかである。 ニコラス・グドリック=クラーク著『ナチズムのオカルト的根源』。 ランツ・フォン・リーベンフェルスの伝記『ヒトラーにアイデアを与えた男』(ヴィルフリート・ダイム著)。 しかし、グドリック=クラークの包括的な研究は、「千里眼」のSS総統カール・マリア・ウィリグートによって練り上げられた極めて特異な古代ドイツの神話 [注 1]の場合を除いて、直接的な影響の証拠をほとんど発見していない。そして第二に、ヴィリグートが異端者としたオカルティストやルニック・マジシャンに対 する公式な非難であり、これはハインリッヒ・ヒムラーに彼らの何人かの抑留を命ずるように説得した可能性がある。 [注2)最も注目すべき他のケースは、ヒムラーのAhnenerbeである。(ナチスのイデオロギーとの直接的な関係についての議論は、ナチズムの宗教的 側面参照)。グドリック=クラークは、ヒトラーや他のナチスに影響を与えた証拠となるものを検証しているが、「アリウス主義はナチズムを先取りしたという 意味で、影響というよりはむしろその症状である」と結論づけている[7]。 |
| 'Ariosophic' writers and
organisations |
While a broad definition of the
term 'Ariosophy' is useful for some purposes, various of the later
authors, including Ellegaard Ellerbek, Philipp Stauff and Günther
Kirchoff, can more exactly be described as cultivating the Armanism of
List.[8] In a less broad approach, one could also treat rune occultism
separately. Although the Armanen runes go back to List, Rudolf John
Gorsleben distinguished himself from other völkisch writers by making
the esoteric importance of the runes central to his world view.
Goodrick-Clarke therefore refers to the doctrine of Kummer and
Gorsleben and his followers as rune occultism, a description that also
fits the eclectic work of Karl Spiesberger. Highly practical[further
explanation needed] systems of rune occultism, influenced mainly by
List, were developed by Friedrich Bernhard Marby and Siegfried Adolf
Kummer<Goodrick-Clarke 1985: 160–62). Also worthy of mention are
Peryt Shou, the occult novelist; A. Frank Glahn, noted more for his
pendulum dowsing; Rudolf von Sebottendorff and Walter Nauhaus, who
built up the Thule Society; and Karl Maria Wiligut, who was the most
notable occultist working for the SS. Organisations include: the Guido von List Society, the High Armanen Order, the Lumen Club, the Ordo Novi Templi, the Germanenorden (in which a schism occurred) and the Thule Society. |
アリオゾフィー」という言葉の広義の定義は、ある目的には有用である
が、Ellegaard Ellerbek、Philipp Stauff、Günther
Kirchoffを含む後期の作家の多くは、より正確にリストのアルマニズムを修めたと言うことができる[8]
広くないアプローチでは、ルーンのオカルティを別に扱うこともできるだろう。アルマーネのルーンはリストに遡るが、ルドルフ・ヨン・ゴルスレーベンはルー
ンの秘教的重要性を彼の世界観の中心に据えることで、他のヴェルキッシュ作家とは一線を画していた。そのため、グドリック=クラークはクマーとゴルスレー
ベンとその信奉者の教義をルーン・オカルティズムと呼んでいるが、これはカール・シュピースベルガーの折衷的な仕事にも当てはまる表現である。主にリスト
の影響を受けた高度に実用的な[さらなる説明が必要]ルーン・オカルトのシステムは、フリードリヒ・ベルンハルト・マービーとジークフリード・アドルフ・
クンマーによって開発された<Goodrick-Clarke 1985: 160-62>。)
また、オカルト小説家のペリット・ショウ、振り子ダウジングで有名なA・フランク・グラーン、トゥーレ協会を設立したルドルフ・フォン・セボッテンドルフ
やヴァルター・ナウハウス、SSのために働いた最も有名なオカルティストであるカール・マリア・ウィリグートも言及に値する人物である。 組織としては、グイド・フォン・リスト協会、ハイ・アルマネン騎士団、ルーメン・クラブ、オルド・ノヴィ・タンプリ、ゲルマンノーデン(分裂が起こっ た)、トゥーレ協会などがある。 |
| Armanism |
Guido von List elaborated a
racial religion premised on the concept of renouncing the imposed
Semitic creed of Christianity and returning to the native religions of
the ancient Indo-Europeans (List preferred the equivalent term
Ario-Germanen, or 'Aryo-Germanics'). List recognised the theoretical
distinction between the Proto-Indo-European language and its daughter
Proto-Germanic language but frequently obscured it by his tendency to
treat them as a single long-lived entity (although this framing is also
used in linguistics as the Germanic parent language).[9] In this, he
became strongly influenced by the Theosophical thought of Madame
Blavatsky, which he blended however with his own highly original
beliefs, founded upon Germanic paganism.[10] Before he turned to occultism, Guido List had written articles for German Nationalist newspapers in Austria, as well as four historical novels and three plays, some of which were "set in tribal Germany" before the advent of Christianity.[11] He also had written an anti-semitic essay in 1895. List adopted the aristocratic von between 1903 and 1907. List called his doctrine Armanism after the Armanen, supposedly a body of priest-kings in the ancient Aryo-Germanic nation. He claimed that this German name had been Latinized into the tribal name Herminones mentioned in Tacitus and that it actually meant the heirs of the sun-king: an estate of intellectuals who were organised into a priesthood called the Armanenschaft.[12] His conception of the original religion of the Germanic tribes was a form of sun worship, with its priest-kings (similar to the Icelandic goði) as legendary rulers of ancient Germany. Religious instruction was imparted on two levels. The esoteric doctrine (Armanism) was concerned with the secret mysteries of the gnosis, reserved for the initiated elite, while the exoteric doctrine (Wotanism) took the form of popular myths intended for the lower social classes.[13] List believed that the transition from Wotanism to Christianity had proceeded smoothly under the direction of the skalds, so that native customs, festivals and names were preserved under a Christian veneer and only needed to be 'decoded' back into their heathen forms.[14] This peaceful merging of the two religions had been disrupted by the forcible conversions under "bloody Charlemagne – the Slaughterer of the Saxons".[15] List claimed that the dominance of the Roman Catholic Church in Austria-Hungary constituted a continuing occupation of the Germanic tribes by the Roman empire, albeit now in a religious form, and a continuing persecution of the ancient religion of the Germanic peoples and Celts. |
グイド・フォン・リストは、押しつけられたセム系キリスト教信条を放棄
し、古代インド・ヨーロッパ人の土着宗教に回帰するという概念を前提とした人種的宗教を精緻化した(リストはこれに相当する用語としてアリオ・ゲルマン、
または「アーリオ・ゲルマン」を好んだ)。リストは、原インド・ヨーロッパ言語とその娘である原ゲルマン言語の間の理論的な区別を認識していたが、それら
を単一の長命な実体として扱う傾向によってしばしばそれを不明瞭にした(ただしこの枠組みは言語学においてゲルマン語の親言語として用いられる)[9]。
この中で彼はブラヴァツキー夫人の神智学思想に強い影響を受け、しかし彼はそれを、ゲルマン異教に基づく彼自身の非常に独自性のある信念と融合させること
になった[10]。 オカルトに傾倒する以前、グイド・リストはオーストリアのドイツ民族主義新聞に記事を書き、4つの歴史小説と3つの劇を書いたが、そのうちのいくつかはキ リスト教の出現以前の「部族のドイツを舞台とした」ものだった[11]。 また1895年には反ユダヤ主義のエッセイも書いている。リストは1903年から1907年にかけて貴族階級のフォンを採用した。 リストは自分の教義を、古代アーリオ・ゲルマン民族の神官王の組織とされるアルマーネンにちなんでアルマニズムと呼んだ。彼はこのドイツ語名がラテン語化 され、Tacitusに記載されている部族名Herminonesになり、実際には太陽王の相続人、すなわちArmanenschaftと呼ばれる神権に 組織された知識人の財産を意味すると主張した[12]。 ゲルマン民族の本来の宗教は太陽崇拝の一形態であり、その神官王(アイスランドのゴジに似ている)は古代ドイツの伝説的な支配者であったと彼は考えてい る。宗教的な教えは、2つのレベルで伝授された。秘教的な教義(アルマニズム)はグノーシスの秘密の神秘に関係し、イニシエーションを受けたエリートのた めに確保され、一方、外来的な教義(ウォータニズム)は下層社会階級のために意図された大衆の神話の形式をとっていた[13]。 リストは、ヴォータニズムからキリスト教への移行は、スカルの指示の下でスムーズに進行し、土着の習慣、祭り、名称はキリスト教の化粧板の下で保存され、 異教徒の形態に「解読」されるだけでよいと考えた[14]。この二つの宗教の平和的融合は「サクソン人の虐殺者-血まみれのカール大帝」による強制改宗で 乱された[15]。 [オーストリア=ハンガリーにおけるローマ・カトリック教会の支配は、宗教的な形ではあるが、ローマ帝国によるゲルマン民族の継続的な占領であり、ゲルマ ン民族とケルト人の古代宗教に対する継続的な迫害であるとリストは主張した。 |
| He also believed in the magical
powers of the old runes. From 1891
onwards he claimed that heraldry was based on a system of encoded
runes, so that heraldic devices conveyed a secret heritage in cryptic
form. In April 1903, he submitted an article concerning the alleged
Aryan proto-language to the Imperial Academy of Sciences in Vienna. Its
highlight was a mystical and occult interpretation of the runic
alphabet, which became the cornerstone of his ideology. Although the
article was rejected by the academy, it would later be expanded by List
and grew into his final masterpiece, a comprehensive treatment of his
linguistic and historical theories published in 1914 as Die Ursprache
der Ario-Germanen und ihre Mysteriensprache (The Proto-Language of the
Aryo-Germanics and their Mystery Language). List's doctrine has been described as gnostic, pantheist and deist.[16] At its core is the mystical union of God, man and nature. Wotanism teaches that God dwells within the individual human spirit as an inner source of magical power, but is also immanent within nature through the primal laws that govern the cycles of growth, decay and renewal. List explicitly rejects a Mind-body dualism of spirit versus matter or of God over or against nature. Humanity is therefore one with the universe, which entails an obligation to live in accordance with nature. But the individual human ego does not seek to merge with the cosmos. "Man is a separate agent, necessary to the completion or perfection of ‘God's work’".[17] Being immortal, the ego passes through successive reincarnations until it overcomes all obstacles to its purpose. List foresaw the eventual consequences of this in a future utopia on earth, which he identified with the promised Valhalla, a world of victorious heroes: Thus in the course of uncounted generations all men will become Einherjar, and that state – willed and preordained by the godhead – of general liberty, equality, and fraternity will be reached. This is that state which sociologists long for and which socialists want to bring about by false means, for they are not able to comprehend the esoteric concept that lies hidden in the triad: liberty, equality, fraternity, a concept which must first ripen and mature in order that someday it can be picked like a fruit from the World Tree.[18] List was familiar with the cyclical notion of time, which he encountered in Norse mythology and in the theosophical adaptation of the Hindu time cycles. He had already made use of cosmic rhythms in his early journalism on natural landscapes.[19] In his later works[Note 3] List combined the cyclical concept of time with the "dualistic and linear time scheme" of western apocalyptic which counterposes a pessimism about the present world with an ultimate optimism regarding the future one.[21] In Das Geheimnis der Runen,[22] List addresses the seeming contradiction by explaining the final redemption of the linear time frame as an exoteric parable that stands for the esoteric truth of renewal in many future cycles and incarnations. However, in the original Norse myths and Hinduism, the cycle of destruction and creation is repeated indefinitely, thus offering no possibility of ultimate salvation.[23] |
彼はまた、古いルーン文字が持つ不思議な力を信じていた。1891年以
降、彼は紋章学は暗号化されたルーン文字の体系に基づいており、紋章の装飾は暗号化された形で秘密の遺産を伝えていると主張した。1903年4月、彼は
アーリア人の原初言語に関する論文をウィーンの帝国科学アカデミーに提出した。その内容は、ルーン文字を神秘的かつオカルト的に解釈したもので、彼の思想
の根幹をなすものであった。この論文はアカデミーで却下されたが、その後リストによって拡大解釈され、1914年に出版された言語学・歴史学の理論を包括
した『アーリオ・ゲルマン原語とその謎の言語』(Die Ursprache der Ario-Germanen und ihre
Mysteriensprache)として彼の最後の傑作に成長することになる。 リストの教義はグノーシス主義、汎神論、神義論などと評される[16]。その核心は、神、人間、自然の神秘的結合である。ヴォータニズムは、神が魔法の力 の内なる源として個々の人間の精神の中に宿ると同時に、成長、衰退、再生のサイクルを支配する原初の法則を通じて自然の中に内在していると教えている。リ ストは、精神対物質、神対自然という心身二元論を明確に否定している。したがって、人類は宇宙と一体であり、自然に従って生きる義務がある。しかし、個々 の人間の自我は、宇宙と融合しようとはしない。人間は「神の仕事」を完成させるために必要な独立した存在である」[17]。不死である自我は、その目的に 対するすべての障害を克服するまで輪廻転生を繰り返す。リストは、このことが将来の地上のユートピアに帰結することを予見し、それを約束されたヴァルハ ラ、すなわち勝利した英雄たちの世界と同一視していた。 こうして、数え切れないほどの世代を経て、すべての人間はアインヘリヤルとなり、一般的な自由、平等、友愛という、神の意志によってあらかじめ定められた 状態に到達するのである。なぜなら彼らは、自由、平等、友愛という三位一体の中に隠されている難解な概念を理解することができないからである。 リストは北欧神話やヒンドゥー教の時間サイクルの神智学的翻案で遭遇した時間の循環的概念に精通していた。また、初期の自然風景に関するジャーナリズムで は、すでに宇宙のリズムを利用していた[19] 後半の作品では[注3]、リストは時間の循環的な概念を、現在の世界に対する悲観と未来の世界に対する究極の楽観を対置する西洋の終末論における「二元的 かつ線形の時間体系」と組み合わせた[21]。 [21] リストは『Das Geheimnis der Runen』[22]において、線形時間枠の最後の救済を、将来の多くの周期と転生における再生の秘教的真理を示す外来的譬えとして説明し、この一見矛盾 する問題に対処している。しかし、本来の北欧神話やヒンドゥー教では、破壊と創造のサイクルが無限に繰り返されるため、究極の救済の可能性はない [23]。 |
|
| Guido von List Society and High
Armanen Order |
Already in 1893 Guido List[Note
4] together with Fanny Wschiansky, had founded the Literarische
Donaugesellschaft, a literary society .[24] In 1908 the Guido von List Society (Guido-von-List-Gesellschaft) was founded primarily by the Wannieck family (Friedrich Wannieck and his son Friedrich Oskar Wannieck being prominent and enthusiastic Armanists) as an occult völkisch organisation, with the purpose of financing and publishing List's research.[25] The List Society was supported by many leading figures in Austrian and German politics, publishing, and occultism.[Note 5] Although one might suspect a völkisch organisation to be antisemitic, the society included at least two Jews among its members: Moritz Altschüler, a rabbinical scholar,[26] and Ernst Wachler.[27] The List Society published List's works under the series Guido-List-Bücherei (GLB).[28][Note 6] List had established exoteric and esoteric circles in his organisation. The High Armanen Order (Hoher Armanen Orden) was the inner circle of the Guido von List Society. Founded in midsummer 1911, it was set up as a magical order or lodge to support List's deeper and more practical work. The HAO conducted pilgrimages to what its members considered "holy Armanic sites", Stephansdom in Vienna, Carnuntum etc. They also had occasional meetings between 1911 and 1918, but the exact nature of these remains unknown. In his introduction to List's The Secret of the Runes, Stephen E. Flowers notes: "The HAO never really crystallized in List's lifetime – although it seems possible that he developed a theoretical body of unpublished documents and rituals relevant to the HAO that have only been put into full practice in more recent years".[29] |
すでに1893年にグイド・リスト[注
4]はファニー・ヴシャンスキーとともに文学会であるLiterarische Donaugesellschaftを設立していた[24]。 1908年、リストの研究に資金を提供し出版することを目的としたオカルト・ヴェルキッシュ組織として、ヴァニエック家(Friedrich Wannieckとその息子Friedrich Oskar Wannieckは著名で熱心なアルマニスト)によってグイド・フォンリスト協会 (Guido-von-List-Gesellschaft) が主に設立された[25] リスト協会はオーストリアとドイツの政治、出版、オカルティスムの多くの有力者によって支持されていた。 注5] ヴェルキッシュ組織といえばアンチセミティクと思われるが、協会は少なくとも2人のユダヤ人をそのメンバーとして含んでいた。リスト協会はリストの著作を 『Guido-List-Bücherei』(GLB)シリーズとして出版した[28][注釈 6]。 リストは自分の組織の中に外典と秘伝のサークルを設立していた。高位アルマネン騎士団(Hoher Armanen Orden)は、グイド・フォン・リスト協会の内部サークルであった。1911年の真夏に設立されたこの団体は、リストのより深く、より実践的な活動を支 援するための魔術的な秩序、またはロッジとして設立された。HAOは、メンバーが「アルマンの聖地」と考える、ウィーンのシュテファン大聖堂やカルヌン トゥムなどへの巡礼を行っていた。また、1911年から1918年にかけては、時折会合を開いていたが、その正確な内容は不明である。リストの『ルーンの 秘密』の序文で、スティーブン・E・フラワーズは次のように記している。「HAOはリストの存命中には決して結晶化しなかった-彼がHAOに関連する未発 表の文書や儀式の理論体系を発展させた可能性はあるが、それはより近年に初めて本格的に実践されるようになった」[29]と述べている。 |
| Listians under the Third Reich |
List died on 17 May 1919, a few
months before Adolf Hitler joined a minor Bavarian political party and
formed it into the NSDAP. After the Nazis had come to power, several
advocates of Armanism fell victim to the suppression of esotericism in
Nazi Germany. The main reason for the persecution of occultists was the Nazi policy of systematically closing down esoteric organisations (although Germanic paganism was still practised by some Nazis on an individual basis), but the instigator in certain cases[citation needed] was Himmler's personal occultist, Karl Maria Wiligut. Wiligut identified the monotheistic religion of Irminism as the true ancestral belief, claiming that Guido von List's Wotanism and runic row constituted a schismatic false religion[citation needed]. Among the Listians – Kummer and Marby are not mentioned by Goodrick-Clarke[30] among the signatories who endorsed the List Society around 1905 but both men were indebted to "Listian" ideas[31] – who were subjected to censure were the rune occultists Friedrich Bernhard Marby and Siegfried Adolf Kummer, both of whom were denounced by Wiligut in 1934 in a letter to Himmler.[32] Flowers[33] writes: "The establishment of [an] 'official NS runology' under Himmler, Wiligut, and others led directly to the need to suppress the rune-magical 'free agents' such as Marby". Despite having openly supported the Nazis,[34] Marby was arrested by the Gestapo in 1936 as an anti-Nazi occultist and was interned in Welzheim, Flossenbürg and Dachau concentration camps.[35][36][37] Kummer disappears from History after Wiligut's denunciation in 1934, and his fate is unknown. He may have died in a concentration camp.[38] According to Rudgley,[39] "[u]nsubstantiated rumours" have him fleeing Nazi Germany in exile to South America, but "it is more likely that he perished in one of the camps that Marby was to survive or died during the Allied bombing of Dresden." Günter Kirchhoff, a List Society member whom Wiligut had recommended to Himmler on the strength of his researches into prehistory, is reported to have written that Wiligut by intrigue had ensured that Ernst Lauterer (a.k.a. "Tarnhari") – another List Society member, who claimed a secret clan tradition that rivalled Wiligut's own – was committed to a concentration camp as an "English agent". Flowers and Moynihan[40] reproduce Kirchhoff's testimony as reported by both Adolf Schleipfer and researcher Manfred Lenz (but doubted by Wiligut's former secretary Gabriele Dechend). |
リ
ストは1919年5月17日に死去したが、これはアドルフ・ヒトラーがバイエルンの小政党に参加し、NSDAPとして結成される数ヶ月前のことであった。
ナチスが政権を握った後、ナチス・ドイツにおける秘教弾圧の犠牲となったのは、アルマニズムの提唱者たちであった。 オカルティスト迫害の主な理由は、ナチスが秘教的な組織を組織的に閉鎖する政策にあったが(ただし、ゲルマン邪教は一部のナチスが個人的にまだ実践してい た)、特定のケースにおける扇動者は、ヒムラーの個人的オカルティスト、カール・マリア・ウィリグートだった[citation needed]。ヴィリグートはイルミニズムという一神教を真の祖先信仰とし、グイド・フォン・リストのヴォータニズムやルーン文字列は分裂的な偽宗教を 構成すると主張した[citation needed]。 リスト派-クマーとマービーは1905年頃にリスト協会を支持した署名者の中でグドリック=クラークによって言及されていないが[30]、二人とも「リス ト派」の思想にお世話になった[31]-非難にさらされたのはルーンのオカルティストのフリードリヒ・ベルンハルト・マービーとジークフリード・アドル フ・クマーで、二人は1934年にヴィリグートによってヒムラーへの手紙に告発されることになる。 [32] フラワーズ[33]は、「ヒムラーやヴィリグートらの下で『公式のNSルーン学』を確立することは、マービーのようなルーン魔術の『フリーエージェント』 を弾圧する必要性に直接つながった」と書いている。公然とナチスを支持していたにもかかわらず[34]、マービーは1936年に反ナチスのオカルト主義者 としてゲシュタポに逮捕され、ウェルツハイム、フローセンビュルク、ダッハウの強制収容所に収容された[35][36][37] クマーは1934年のヴィリグートによる非難以降歴史から消え、その運命も不明であった。ラドグリーによれば[39]、「根拠のない噂」ではナチス・ドイ ツから南米に亡命したとされているが、「マービーが生き残ることになった収容所の一つで死んだか、連合軍のドレスデン爆撃で死んだ可能性が高い」 [40]。 ウィリグートが先史学研究の強みを生かしてヒムラーに推薦したリスト協会員ギュンター・キルヒホフは、ウィリグートが陰謀によってエルンスト・ラウテラー (別名「タルンハリ」)-ウィリグートと並ぶ秘密の氏族伝統を主張する別のリスト協会員-を「イギリスのエージェント」として強制収容所に収容するように したと書いていると伝えられている。フラワーズとモイニハン[40]は、アドルフ・シュライプファーと研究者マンフレート・レンツが報告したキルヒホフの 証言(ただしヴィリグートの元秘書ガブリエレ・デチェンドは疑っている)をそのまま再現している。 |
| Theozoology |
.In 1903–04, a Viennese
ex-Cistercian monk, Bible scholar and inventor named Jörg
Lanz-Liebenfels (subsequently, Jörg Lanz von Liebenfels) published a
lengthy article under the Latin title "Anthropozoon Biblicum" ("The
Biblical Man-Animal") in a journal for Biblical studies edited by
Moritz Altschüler, a Jewish admirer of Guido von List. The author
undertook a comparative survey of ancient Near Eastern cultures, in
which he detected evidence from iconography and literature that seemed
to point to the continued survival, into early historical times, of
hominid ape-men similar to the dwarfish Neanderthal men known from
fossil remains in Europe, or the Pithecanthropus (now called Homo
erectus) from Java.[41] Furthermore, Lanz systematically analysed the
Old Testament in the light of his hypothesis, identifying and
interpreting coded references to the ape-men that substantiated an
illicit practice of interbreeding between humans and "lower" species in
antiquity. In 1905 he expanded these researches into a fundamental statement of doctrine titled Theozoologie oder die Kunde von den Sodoms-Äfflingen und dem Götter-Elektron[42] ("Theozoology, or the Science of the Sodomite-Apelings and the Divine Electron"). He claimed that "Aryan" peoples originated from interstellar deities (termed Theozoa) who bred by electricity, while "lower" races were a result of interbreeding between humans and ape-men (or Anthropozoa). The effects of racial crossing caused the atrophy of paranormal powers inherited from the gods, but these could be restored by the selective breeding of pure Aryan lineages. The book relied on somewhat lurid sexual imagery, decrying the abuse of white women by ethnically inferior but sexually active men. Thus, Lanz advocated mass castration of racially "apelike" or otherwise "inferior" males.[43] In the same year, Lanz commenced publication of the journal Ostara (named after a pagan Germanic goddess of spring) to promote his vision of racial purity. |
1903-04年、ウィーンの元シトー会修道士で聖書学者、発明家の
イェルク・ランツ・リーベンフェルス(後にイェルク・ランツ・フォン・リーベンフェルス)は、グイド・フォン・リストの崇拝者だったユダヤ人のモーリッ
ツ・アルトシューラーが編集した聖書学の雑誌に「聖書的人間・動物(Anthropozoon
Bibleum)」という題の長い記事を発表した。著者は古代近東文化の比較調査を行い、図像や文献から、ヨーロッパの化石で知られる小柄なネアンデル
タール人やジャワ島のピテカントロプス(現在はホモ・エレクトス)と同様の猿人が歴史初期まで生存していたことを示唆するような証拠を発見した[41]。
[さらに、ランツは、旧約聖書を自分の仮説に照らして体系的に分析し、古代において人類と「下等」種との間で不正な交配が行われていたことを立証する猿人
についての暗号化された言及を特定し解釈した。 1905年、彼はこれらの研究を『動物誌学、あるいはソドムの猿人と神の電子の科学』(Theozoologie oder die Kunde von den Sodoms-Äfflingen und dem Götter-Elektron[42] )という教義の基本声明に発展させることに成功する。彼は、「アーリア人」は電気で繁殖した星間神(テオゾアと呼ばれる)に由来し、「下等」人種は人間と 猿人(または人類)の交雑の結果であると主張した。人種交配の結果、神々から受け継いだ超能力が衰えたが、純粋なアーリア人の系統を選択的に繁殖させるこ とで回復させることができる。この本は、民族的には劣等だが性的に活発な男性による白人女性の虐待を批判し、やや薄気味悪い性的なイメージに頼っている。 このように、ランツは人種的に「類人猿的」あるいはその他の「劣った」男性の大量去勢を提唱した[43]。同年、ランツは人種的純化のビジョンを促進する ために雑誌『オスタラ』(異教徒のゲルマン人の春の女神から名付けられた)の発行を開始した。 |
| Secret Society Order of the New
Templars |
On December 25, 1900, he founded
the fascist secret society Order of the New Templars (Ordo Novi Templi,
or ONT) – a project to bring rightwing extremists together and mobilise
them in favor of Nazism in Germany by using esotericism to justify
violence such as castration of innocent people to establish fascism in
Germany and defend it against communism.[44] The ONT was modelled after
the catholic military order Knight Templars and similar in its
hierarchical structure as the Order of Cistercians which was the group
that trained the New Templars founder and political agitator Adolf
Lanz.[44] Members used code names so that betrayal was difficult.[44] The ideological association was headquartered at Burg Werfenstein, a castle in Upper Austria overlooking the river Danube. Its declared aim was to use pseudo-science and religion to make people believe in racist concepts. Rituals were designed to beautify life in accordance with Aryan aesthetics, and to express the Order's theological system that Lanz called Ario-Christianity. The Order was the first to use the swastika in an "Aryan" meaning, displaying on its flag the device of a red swastika facing right, on a yellow-orange field and surrounded by four blue fleurs-de-lys above, below, to the right and to the left. The ONT declined from the mid-1930s and – even though it had pioneered many ideas that the Nazis later adopted – it was suppressed by the Gestapo in 1942. By this time it had established seven communities in Austria, Germany and Hungary. Though suspending its activities in the Greater German Reich, the ONT survived in Hungary until around the end of World War II.[45] It went underground in Vienna after 1945, but was contacted in 1958 by a former Waffen-SS lieutenant, Rudolf Mund, who became Prior of the Order in 1979.[46] Mund also wrote biographies of Lanz and Wiligut. |
1900年12月25日、彼はファシスト秘密結社新テンプル騎士団
(Ordo Novi Templi,
ONT)を設立した。これは右翼過激派を集め、ドイツにおけるナチズムを支持するために動員するプロジェクトで、密教を使って無実の人々の去勢などの暴力
を正当化してドイツにファシズムを確立し共産主義から防衛しようとするものであった[44]。 [44]
ONTはカソリックの軍事教団であるテンプル騎士団をモデルにしており、その階層構造は新テンプル騎士団の創設者で政治的扇動者であるアドルフ・ランツを
訓練したグループであるシトー会にも類似していた[44]。 この思想団体は、ドナウ川を見下ろす上オーストリアにある城、ブルク・ヴェルフェンシュタインに本部を置いていた。その目的は、擬似科学と宗教を利用し て、人種差別的な概念を人々に信じさせることであると宣言された。儀式はアーリア人の美学に従って生活を美化し、ランツがアリオ・クリスチャンと呼んだ教 団の神学体系を表現するために考案された。教団の旗には、黄色とオレンジの地に右向きの赤い鉤十字が描かれ、上下左右に4本の青い花菱が描かれている。 ONTは1930年代半ばから衰退し、後にナチスが採用した多くのアイデアを開拓したにもかかわらず、1942年にゲシュタポによって弾圧された。この 時、オーストリア、ドイツ、ハンガリーに7つの共同体を設立していた。1945年以降、ウィーンに潜伏していたが、1958年に元Waffen-SS中尉 のルドルフ・ムントが接触し、1979年に修道院長となった[46]。 |
| Ariosophy |
The term "Ariosophy" (wisdom
concerning the Aryans) was coined by Lanz von Liebenfels in 1915, with
"Theozoology" describing its Genesis and "Ario-Christianity" as the
label for the overall doctrine in the 1920s.[Note 7] This terminology was taken up by a group of occultists, formed in Berlin around 1920 and referred to by one of its main figures, Ernst Issberner-Haldane, as the 'Swastika-Circle'. Lanz's publisher, Herbert Reichstein, made contact with the group in 1925 and formed it into an institute with himself as director. This association was named the Ariosophical Society in 1926, renamed the Neue Kalandsgesellschaft (from Kaland, Guido von List's term for a secret lodge or conventicle) in 1928, and renamed again as the Ariosophische Kulturzentrale in 1931, the year in which it opened an Ariosophical School at Pressbaum that offered courses and lectures in runic lore, biorhythms, yoga and Qabalah. The institute maintained a friendly collaboration with Lanz, its guiding intellect and inspiration, but also acknowledged an indebtedness to List, declaring itself as the successor to the Armanen priest-kings and their hierophantic tradition. Reichstein's circle therefore establishes the historical precedent for a broad conception that was followed by Nicholas Goodrick-Clarke in 1985 when he redefined Ariosophy as a general term to describe Aryan-centric occult theories and hermetic practices, including both Lanz's Ario-Christianity and the earlier Armanism of List, as well as later derivatives of either or both systems. If the term is employed in this extended sense, then Guido von List, and not Lanz von Liebenfels, was the founder of Ariosophy. The justification for the broad definition is that List and Lanz were mutually influencing. The two men joined one another's societies; List figures in Lanz's pedigree of initiated predecessors; and Lanz is cited several times by List in The Religion of the Aryo-Germanic Folk: Esoteric and Exoteric (1910). |
1915年にランツ・フォン・リーベンフェルスによって「アリオゾ
フィー」(アーリア人に関する知恵)という言葉が作られ、1920年代にはその創世記を表す「テオゾロジー」、教義全体を表すラベルとして「アリオ・クリ
スチャンティ」が使われた[注 7]。 この用語は、1920年頃にベルリンで結成されたオカルティストのグループによって取り上げられ、その中心人物の一人であるエルンスト・イシュベルナー= ハルダーネが「スワスティカ・サークル」と呼んだものである。ランツの出版社であるヘルベルト・ライヒシュタインは、1925年にこのグループと接触し、 自らを責任者とする協会を設立した。1931年にはAriosophische Kulturzentraleと改名し、プレスバウムにAriosophical Schoolを開設し、ルーン文字、バイオリズム、ヨガ、カバラの講座や講義を行った。 この研究所は、指導的な知性とインスピレーションを持つランツとの友好的な協力関係を維持しながらも、リストへの恩義を認め、自らをアルマーネンの司祭王 とそのヒエログリフの伝統の後継者であると宣言している。ライヒシュタインのサークルは、1985年にニコラス・グドリック=クラークが、ランツのアリ オ・クリスチャンとリストのアルマニズム、さらにその派生系を含むアーリア人中心のオカルト理論や秘儀の総称としてアリオス哲学を再定義した際に踏襲され た広義の概念の歴史的先例を確立することになった。このように広義にとらえると、ランツ・フォン・リーベンフェルスではなく、グイド・フォン・リストがア リオゾフィーの創始者ということになる。 このような広義の定義が正当化されるのは、リストとランツが相互に影響を及ぼし合っていたからである。二人は互いの学会に参加し、リストはランツのイニシ エーションの先達の血統に名を連ね、ランツはリストによって『アーリオ・ゲルマン民族の宗教』の中で何度も引用されている。エソテリックとエクソテリッ ク』(1910)の中で、ランツは何度も引用されている。 |
| Germanenorden |
Although List had been concerned
"to awaken German nationalist consciousness",[48] the High Armanen
Order had addressed itself to the upper and middle class Germans in
Austria,[48] and here List had preferred the "role of the
mystagogue"[49] over political activism. List's disciples, however,
became active in the Reichshammerbund and the Germanenorden, two
"historically significant", "virulently antisemitic groups"[49] in
Germany. Both groups were organized by the political activist Theodor
Fritsch, a major figure in German antisemitism. Fritsch, born 1852, was
the son of Saxon peasants, and he was concerned about the "small
tradesmen and craftsmen"[49] and their threat from what he perceived to
be the large 'Jewish' industry. The List-inspired Germanenorden (Germanic Order or Teutonic Order, not to be confused with the medieval German order of the Teutonic Knights) was a völkisch secret society in early 20th-century Germany. It was founded in Berlin in 1912 by Theodor Fritsch and several prominent German occultists including Philipp Stauff, who held office in the List Society and High Armanen Order as well as Hermann Pohl, who became the Germanenorden's first leader. The group was a clandestine movement aimed at the upper echelons of society and was a sister movement to the more mainstream Reichshammerbund.[50] The order, whose symbol was a swastika, had a hierarchical fraternal structure similar to Freemasonry. Local groups of the sect met to celebrate the summer solstice, an important neopagan festivity in völkisch circles (and later in Nazi Germany), and more regularly to read the Eddas as well as some of the German mystics.[51] In addition to occult and magical philosophies, it taught to its initiates nationalist ideologies of Nordic racial superiority and antisemitism, then rising throughout the Western world. As was becoming increasingly typical of völkisch organisations,[citation needed] it required its candidates to prove that they had no non-Aryan bloodlines and required from each a promise to maintain purity of his stock in marriage. In 1916, during World War I, the Germanenorden split into two parts. Eberhard von Brockhusen became the Grand Master of the "loyalist" Germanenorden. Pohl, previously the order's Chancellor, founded a schismatic offshoot: the Germanenorden Walvater of the Holy Grail.[52][53] He was joined in the same year by Rudolf von Sebottendorff (formerly Rudolf Glauer), a wealthy adventurer with wide-ranging occult and mystical interests. A Freemason and a practitioner of sufism and astrology, Sebottendorff was also an admirer of Guido von List and Lanz von Liebenfels. Convinced that the Islamic and Germanic mystical systems shared a common Aryan root, he was attracted by Pohl's runic lore and became the Master of the Walvater's Bavarian province late in 1917. Charged with reviving the province's fortunes, Sebottendorff increased membership from about a hundred in 1917 to 1500 by the autumn of the following year.[54] |
リストは「ドイツの民族主義的意識を呼び起こす」ことに関心を抱いてい
たが[48]、高位アルマネン騎士団はオーストリアの上・中産階級のドイツ人を対象としており[48]、ここでリストは政治活動よりも「神秘主義者の役
割」[49]を優先していた。しかし、リストの弟子たちは、ドイツにおける「歴史的に重要な」「激しい反ユダヤ主義的な」2つのグループであるライヒシャ
ンマーブンドとゲルマンノルデンで活動するようになる[49]。両団体は、ドイツの反ユダヤ主義の主要人物である政治活動家テオドール・フリッチュによっ
て組織されていた。1852年生まれのフリッチは、ザクセンの農民の息子であり、「小さな商人や職人」[49]と彼が考える大規模な「ユダヤ人」産業から
の脅威について懸念していた。 リスト・イン・ジャーマン・ノルデン(Germanic Order or Teutonic Order、中世ドイツの騎士団「チュートニック騎士団」と混同しないように)は、20世紀初頭のドイツにおけるヴェルキッシュ系の秘密結社であった。 1912年にベルリンでテオドール・フリッチュと、リスト協会やハイ・アルマーネン騎士団の役職にあったフィリップ・シュタウフや、ゲルマンノーデンの初 代指導者となったヘルマン・ポールら、ドイツの著名なオカルティストたちによって設立された。このグループは社会の上層部を対象とした秘密運動であり、よ り主流なライヒシャンベルクの姉妹運動であった[50]。 スワスティカをシンボルとするこの教団は、フリーメーソンに似た階層的な友愛構造を持っていた。この宗派の地方グループは、ヴェルキッシュ界(後にナチ ス・ドイツ)において重要な新教徒の祭りである夏至を祝うために集まり、より定期的にエッダやドイツの神秘主義者の一部を読むために集まった[51]。 オカルトや魔術的な哲学に加えて、北欧の人種的優越と反ユダヤ主義という当時西側世界全体で高まっていた民族主義的なイデオロギーを入門者に教えていた。 ヴェルキッシュの組織でますます典型的になりつつあったように[citation needed]、それは候補者に非アーリア人の血統を持たないことを証明するよう求め、結婚において自分の家系の純度を維持することを各人に約束させるよ うに要求した。 第一次世界大戦中の1916年、ゲルマンノルデンは2つに分裂した。エバーハルト・フォン・ブロックヒューゼンが「忠実派」ゲルマンノルデンのグランドマ スターとなった。ポールは、以前は教団の総長であったが、分裂主義的な分派として、聖杯のゲルマンフォルデン・ヴァルヴァターを設立した[52] [53]。フリーメイソンで、スーフィズムと占星術を実践していたセボッテンドルフは、グイド・フォン・リストとランツ・フォン・リーベンフェルスを敬愛 していた。イスラムとゲルマンの神秘主義がアーリア人の共通のルーツであると確信していた彼は、ポールのルーン文字伝承に惹かれ、1917年末にヴァル ヴァーターのバイエルン州のマスターとなった。州の運勢を復活させることを課せられたセボッテンドルフは、1917年に約100人だった会員数を、翌年の 秋までに1500人にまで増やした[54]。 |
| Thule Society |
In 1918 Sebottendorff made
contact with Walter Nauhaus, a member of the Germanenorden who headed a
"Germanic study group" called the Thule Gesellschaft (Thule
Society).[55] The name of Nauhaus's original Thule Society was adopted
as a cover-name for Sebottendorff's Munich lodge of the Germanenorden
Walvater when it was formally dedicated on August 18, 1918, with Pohl's
assistance and approval.[56] Sebottendorff states that the group was
run jointly by himself and Nauhaus. Deriving elements of its ideology and membership from earlier occult groups founded by List (Guido von List Society, established 1908) and Lanz von Liebenfels (the Order of the New Templars, established 1907), the Thule Society was dedicated to the triune god Walvater, identified with Wotan in triple form. For the Society's emblem Sebottendorff selected the oak leaves, dagger and swastika.[53] The name Thule (an island located by Greek geographers at the northernmost extremity of the world) was chosen for its significance in the works of Guido von List. According to Thule Society mythology, Thule was the capital of Hyperborea, a legendary country supposedly in the far North polar regions, originally mentioned by Herodotus from Egyptian sources. In 1679, Olaf Rudbeck equated the Hyperboreans with the survivors of Atlantis, who were first mentioned by Plato, again following Egyptian sources. Friedrich Nietzsche (1844–1900) began his work Der Antichrist (The Antichrist) in 1895 with, "Let us see ourselves for what we are. We are Hyperboreans." From a historian's[whose?] perspective, the importance of the Thule Society lies in its organising the discussion circle that led to the German Workers' Party (Deutsche Arbeiter-Partei, or DAP), founded in January 1919. The Thule Society's Karl Harrer was a co-founder, along with Anton Drexler (the party's first chairman). Later the same year, Adolf Hitler joined the DAP, which was renamed as the NSDAP (or Nazi party) on April 1, 1920. Some conspiracy theorists argue that the NSDAP, when under Hitler's leadership, was a political front for the Thule Society. However, against this theory stands Harrer's and Drexler's resistance to Hitler. After unsuccessful challenges to his growing power, both men resigned from the party, Harrer in 1920 and Drexler in 1923. Speculative authors assert[citation needed]that a number of high Nazi Party officials had been members of the Thule Society (including such prominent figures as Max Amann, Dietrich Eckart, Rudolf Hess, Alfred Rosenberg and Gottfried Feder)[citation needed]. Eckart, the wealthy publisher of the newspaper Auf gut Deutsch (In Plain German), has been represented[citation needed]as a committed occultist and the most significant Thule influence on Hitler. He is believed to have taught Hitler a number of persuasive techniques[citation needed], and so profound was his influence that the second volume of Hitler's book Mein Kampf was dedicated to him. However, although Eckart attended Thule Society meetings, he was not a member and there is nothing to indicate that he trained Hitler in techniques of a mystical nature. Examining the membership lists, Goodrick-Clarke[57] notes that Hess, Rosenberg and Feder were – like Eckart – guests of the Thule Society in 1918 but not actual members. He also describes a Thule Society membership roll including Hans Frank and Heinrich Himmler as "spurious". There is no evidence that Hitler himself had any connection with the Society, even as an associate or visitor. However, a member of the Thule Society, dentist Dr. Friedrich Krohn, did choose[citation needed] the swastika symbol for the Nazi party (although the design was revised at Hitler's insistence)[citation needed]. In 1923, Sebottendorff was expelled from Germany as an undesirable alien; around 1925, the Thule Society disbanded. In 1933, Sebottendorff returned to Germany and published Bevor Hitler kam: Urkundliches aus der Frühzeit der nationalsozialistischen Bewegung von Rudolf von Sebottendorff.[55] The book was banned by the Bavarian Political Police on March 1, 1934; Sebottendorff was arrested by the Gestapo, interned in a concentration camp, then expelled to Turkey yet again, where he committed suicide by drowning in the Bosphorus on May 9, 1945,[citation needed] as the Nazis surrendered to the Allies. |
1918年、セボッテンドルフはゲルマンノーデンのメンバーで、トゥー
レ協会(Thule Gesellschaft)と呼ばれる「ゲルマン研究グループ」を率いるヴァルター・ナウハウスと接触した[55]
ナウハウスのオリジナルのトゥール協会の名前は、ポールの援助と承認を得て、1918年8月18日に正式に設立されたセボッテンドルフのゲルマンノーデン
ヴァルターのロッジの偽装名として採択された[56] セボッテンドルフはこのグループは彼とノウハウによって共同運営されていたことを明言している。 リスト(ギド・フォン・リスト協会、1908年設立)とランツ・フォン・リーベンフェルス(新テンプル騎士団、1907年設立)が設立した以前のオカルト 集団から思想と会員の要素を受け継ぎ、トゥーレ協会は三位一体神ヴァルヴァターに捧げられ、三重形態のウォータンと同一視された。セボッテンドルフは協会 の紋章に樫の葉、短剣、鉤十字を選んだ[53]。トゥーレ(ギリシャの地理学者によって世界の最北端に位置する島)という名前は、ギド・フォン・リストの 作品における重要性から選ばれたものだった。トゥーレ協会の神話によれば、トゥーレはハイパーボレアという伝説の国の首都であり、もともとはヘロドトスが エジプトの資料から言及した北極圏の果てにあるとされる。1679年、オラフ・ルドベックはハイパーボレア人をプラトンが最初に言及したアトランティスの 生き残りと同一視し、やはりエジプトの資料に従った。フリードリヒ・ニーチェ(1844-1900)は1895年に出版した『反キリスト』(Der Antichrist)の冒頭で、「われわれは自分自身をありのままに見よう。われわれはハイパーボリアンである" 歴史家の[誰の]視点から見ると、トゥーレ協会の重要性は、1919年1月に設立されたドイツ労働者党(Deutsche Arbeiter-Partei、DAP)につながる議論サークルを組織したことにある。トゥール協会のカール・ハラーは、アントン・ドレクスラー(党の 初代議長)と共に共同設立者であった。同年末、アドルフ・ヒトラーがDAPに参加し、1920年4月1日にNSDAP(ナチス党)と改称された。陰謀論者 の中には、ヒトラー率いるNSDAPはトゥーレ協会の政治的フロントであったと主張する者もいる。しかし、ハラーとドレクスラーのヒトラーに対する抵抗 は、この説に反していた。ハーラーは1920年に、ドレクスラーは1923年に、それぞれ党を辞めた。 推測によると、ナチス党の高官の多くがトゥーレ協会のメンバーであった(マックス・アーマン、ディートリッヒ・エカート、ルドルフ・ヘス、アルフレッド・ ローゼンベルク、ゴットフリート・フェダーなどの著名人が含まれる)[citation needed]と主張されている。エカルトは『アウフ・グート・ドイツ』(In Plain German)という新聞を発行する富豪であり、熱心なオカルト主義者として、ヒトラーに最も大きな影響を与えたとされている[citation needed]。ヒトラーに数々の説得術を教えたとされ[citation needed]、その影響力は大きく、ヒトラーの著書『我が闘争』の第2巻は彼に捧げられている。しかし、エッカートはトゥール協会の会合には出席してい たが、会員ではなかったし、ヒトラーに神秘的な性質の技術を教えたことを示すものは何もない。グドリック=クラーク[57]は、会員名簿を調べて、ヘス、 ローゼンベルク、フェダーは、エッカートのように、1918年にトゥーレ協会のゲストではあったが、実際の会員ではなかったと指摘している。また、ハン ス・フランクとハインリッヒ・ヒムラーを含むトゥーレ協会の会員名簿を「偽者」であると述べている。ヒトラー自身が協会と何らかの関係を持ったという証拠 は、たとえ準会員や訪問者であったとしてもない。しかし、トゥーレ協会のメンバーである歯科医のフリードリヒ・クローン博士は、ナチス党のシンボルである 鉤十字を選んだ(ただし、デザインはヒトラーの主張で修正された)[citation needed]。 1923年、セボッテンドルフは好ましくない外国人としてドイツから追放され、1925年頃にはトゥーレ協会も解散した。1933年、セボッテンダーフは ドイツに戻り、『ヒトラーが来る前に:ルドルフ・フォン・セボッテンダーフの民族主義運動の歴史』を出版した[55]。この本は1934年3月1日にバイ エルン政治警察によって発禁処分を受け、ゲシュタポに逮捕されて強制収容所に収容され、再びトルコに追放されて、ナチスが連合国に降伏すると1945年5 月9日にボスポラス海で溺死している[citation needed]。 |
| Edda Society |
Rudolf John Gorsleben was
associated with the Thule Society during the Bavarian Soviet Republic
of 1919 and, along with Dietrich Eckart, he was taken prisoner by the
Communists, narrowly escaping execution. He threw himself into the
ferment of Bavaria's völkisch politics and formed a close working
relationship with the local Germanenorden before devoting himself to
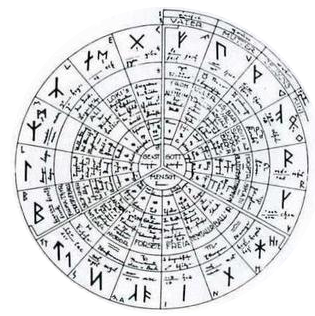
literary pursuits.[58] On 29 November 1925, Gorsleben founded the Edda Society (Edda-Gesellschaft), a mystic study group, at Dinkelsbühl in Franconia. He himself was Chancellor of the Society and published its periodical Deutsche Freiheit (German Freedom), later renamed Arische Freiheit (Aryan Freedom). Assisted by learned contributors to his study-group, Gorsleben developed an original and eclectic mystery religion founded in part upon the Armanism of List, whom he quoted with approval.[59] Grand Master of the Society was Werner von Bülow (1870–1947). The treasurer was Friedrich Schaefer from Mühlhausen, whose wife, Käthe, kept open house for another occult-völkisch circle (the 'Free Sons of the North and Baltic Seas') that gathered around Karl Maria Wiligut in the early 1930s.[60] Mathilde von Kemnitz, a prolific völkisch writer who married General Erich Ludendorff in 1926, was an active member of the Edda Society.[Note 8] When Rudolf John Gorsleben died from heart disease in August 1930, the Edda Society was taken over by Bülow who had designed a 'world-rune-clock' that illustrated the correspondences between the runes, the gods and the zodiac, as well as colours and numbers. Bülow also took over the running of Gorsleben's periodical and changed its name from Arische Freiheit to Hag All All Hag, and then Hagal. |
ルドルフ・ヨン・ゴルスレーベンは、1919年のバイエルン・ソビエト
共和国時代にトゥーレ協会と関わり、ディートリッヒ・エッカートとともに共産主義者の捕虜となったが、辛うじて処刑を免れることができた。バイエルンの
ヴォルキッシュ政治に身を投じ、地元のゲルマンノルデンと密接な協力関係を築いた後、文学活動に専念した[58]。 1925年11月29日、ゴルスレーベンはフランケンのディンケルスビュールで神秘学研究グループであるエッダ協会(Edda- Gesellschaft)を設立した。ゴルスレーベン自身が会長となり、定期刊行物『Deutsche Freiheit(ドイツの自由)』(後に『Arische Freiheit(アーリア人の自由)』と改題)を発行した。ゴルスレーベンは、彼の研究グループへの学識ある寄稿者の助けを借りて、彼が承認して引用し たリストのアルマニズムを部分的に基礎とした、独創的で折衷的な神秘宗教を発展させた[59]。 協会のグランドマスターはヴェルナー・フォン・ビューロー(1870-1947)であった。会計はミュールハウゼンのフリードリヒ・シェーファーで、彼の 妻ケーテは、1930年代初頭にカール・マリア・ウィリグートを中心に集まった別のオカルト・ヴェルキッシュ・サークル(「北海とバルト海の自由息子た ち」)のために家を開けていた[60]。多作のヴェルキッシュ作家で1926年にエーリヒ・ルーデンドルフ将軍に結婚したマチルデ・フォン・ケンニツはエ ドダ協会のアクティブメンバーである[注 8]。 1930年8月にルドルフ・ジョン・ゴルスレーベンが心臓病で亡くなると、エッダ協会は、ルーン文字と神々と星座の対応関係や色や数を図解した「世界ルー ン時計」をデザインしたビューローに引き継がれることになる。ビューローはまた、ゴルスレーベンの定期刊行物の運営を引き継ぎ、その名前を「アリシェ・フ ライハイト」から「ハグ・オール・ハグ」、そして「ハガル」に変えた。 |
| Research on Ariosophy |
After the war, Lanz von
Liebenfels was first brought to a wider (and scholarly) attention with
Wilfried Daim's book Der Mann, der Hitler die Ideen gab (The Man Who
Gave Hitler His Ideas) (1957). Although the book was not always taken
seriously within academia, for some time Lanz was seen as one of the
most important influences on Hitler. Since the 1990s, however,
historians have cast doubt on Lanz' significance. The historian
Brigitte Hamann, who has written Hitler's Vienna: A Dictator's
Apprenticeship, is of the view that Lanz partly influenced Hitler's
diction, but had only marginal influences on Adolf Hitler's religious
views. |
戦後、ランツ・フォン・リーベンフェルスが広く(学問的に)注目される
ようになったのは、ヴィルフリート・ダイム著『ヒトラーに思想を与えた男』(1957年)である。この本は学界では必ずしも真剣に受け止められてはいな
かったが、しばらくの間、ランツはヒトラーに最も重要な影響を与えた一人と見なされていた。しかし、1990年代以降、歴史家たちはランツの存在意義に疑
問を投げかけている。歴史家のブリジット・ハマン(Brigitte Hamann)は、『ヒトラーのウィーン(Hitler's
Vienna)』を書いている。A Dictator's Apprenticeship
"を書いた歴史家ブリジット・ハマンは、ランツはヒトラーの言葉遣いに一部影響を与えたが、ヒトラーの宗教観にはわずかしか影響を与えなかったという見方
をしている。 |
| The occult roots of Nazism |
Some of Lanz's proposals for
racial purification anticipate the Nazis. The sterilisation of those
deemed to be genetically "unfit" was in fact implemented under the Nazi
eugenics policies, but its basis lay in the theories of scientific
racial hygienists. The Nazi eugenics programme has no proven connection
with Lanz's mystical rationale. Eugenic ideas were widespread in his
lifetime, whereas he himself was banned from publishing in the Third
Reich and his writings were suppressed. Following Goodrick-Clarke's caution in assessing the relation between the two,[68] Adolf Hitler cannot be considered a pupil of Lanz von Liebenfels, as Lanz himself had claimed.[69] However, it has been suggested with some evidential basis that the young Hitler did read and collect Lanz's Ostara magazine while living in Vienna: In view of the similarity of their ideas relating to the glorification and preservation of the endangered Aryan race, the suppression and ultimate extermination of the non-Aryans, and the establishment of a fabulous Aryan-German millennial empire, the link between the two men looks highly probable.[70] Nevertheless: "It also remains a fact that Hitler never mentioned the name of Lanz in any recorded conversation, speech, or document. If Hitler had been importantly influenced by [Lanz], he cannot be said to have ever acknowledged this debt".[71] |
ランツの人種浄化の提案の中には、ナチスを先取りするものもある。遺伝
的に「不適合」とみなされた人々の不妊手術は、実際、ナチスの優生学政策の下で実施されたが、その基礎は科学的な人種衛生学者の理論にあったのである。ナ
チスの優生学計画は、ランツの神秘的な根拠との関連は証明されていない。優生思想はランツ存命中には広く浸透していたが、彼自身は第三帝国での出版を禁じ
られ、著作も弾圧された。 グドリック=クラークの両者の関係を評価する際の注意に従って、アドルフ・ヒトラーは、ランツ自身が主張していたように、ランツ・フォン・リーベンフェル スの弟子とは考えられない[68]。 しかし、若いヒトラーがウィーンに住んでいた時にランツの『オスタラ』誌を読み、収集していたことは一定の証拠に基づいて提案されている[69]。 絶滅の危機に瀕したアーリア人種の美化と保存、非アーリア人種の弾圧と究極の絶滅、そしてアーリア人とドイツ人の素晴らしい千年帝国の建設に関する彼らの 考えの類似性から見て、二人の間のつながりは非常にありそうだ」[70]。 とはいえ 「また、ヒトラーが記録された会話、演説、文書の中でランツの名を口にしたことがないことも事実である。もしヒトラーが(ランツから)重要な影響を受けて いたとしても、その恩義を認めたとは言えない」[71]。 |
| https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ariosophy |
https://www.deepl.com/ja/translator |
◎Goodrick-Clarke, Nicholas, The occult roots of Nazism : secret Aryan cults and their influence on Nazi ideology. Tauris Parke Paperbacks, 2004.
ナチズムは、世紀末にドイツとオーストリアで隆盛を 誇った強力なオカルト・千年王国主義の宗派から影響を受けるとともに、微妙な距離をとる(ヒムラーの熱狂的信奉からシューペアの冷淡な無視まで)。彼らの 思想とシンボルは、初期のナチ党に属する民族主義・人種主義グループに伝わり、その幻想は第三帝国において恐ろしい結末を迎えることになった。しかし、 グッドリック=クラークがいうように「アウシュビッツ、ソビボル、トレブリンカは、ナチスの黙示録を示す地獄のような博物館」だったのか?——私(池田) は、もっと別タイプの原理が働いていたと思う。すなわち合理的計算に基づいていると同時に「狂った目的論化した」反ユダヤ主義という黙示録である。この奇 妙で魅力的な物語は、私たちが無視することのできない教訓を含んでいるのは確かだが……
| Part 1.:The background |
第1部:その背景 |
| 1. the Pan-German vision, |
1.汎ドイツのビジョン |
| 2. the modern German occult revival 1880-1910 |
2.近代ドイツのオカルト復興 1880-1910 |
| Part 2.: the ariosophists of Vienna |
第2部:ウィーンのアリオソフィストたち |
| 3. Guido von List, |
3. グイド・フォン・リスト |
| 4. Wotanism and Germanic theosophy |
4. ヴォータニズムとゲルマン神智学 |
| 5. the armanenschaft, |
5.アルマネンシャフト |
| 6. the secret heritage, |
6.秘密の遺産 |
| 7. the German millennium, | 7.ドイツ・ミレニアム |
| 8.Jorg Lanz von Liebenfels and theozoology, |
8.ヨルグ・ランツ・フォン・リーベンフェルスと神獣学 |
| 9. the order of the new templars |
9.新テンプル騎士団 |
| Part 3. : ariosophy in Germany |
第3部:ドイツにおける哲学 |
| 10. the Germanenorden, |
10.ドイツ北方人種 |
| 11. Rudolf von Sebottendorff and the Thule society, |
11. ルドルフ・フォン・セボッテンドルフとトゥーレ協会 |
| 12. the holy Runes and the Edda society, |
12.聖なるルーン文字とエッダ協会。 |
| 13. Herbert Reichstein and ariosophy, |
13. ハーバート・ライヒシュタインと宇宙哲学 |
| 14. Karl Maria Wiligut - the private magus of Heinrich Himmler, |
14. カール・マリア・ヴィリグート-ハインリッヒ・ヒムラーの私的魔術師。 |
| 15. ariosophy and Adolf Hitler. |
15.アリオゾフィーとアドルフ・ヒトラー。 |
| Appendices: |
付録 |
| genealogy of Lanz von Liebenfels |
ランツ・フォン・リーベンフェルツの系譜 |
| genealogy of the Sebottendorff family |
セボッテンダーフ家の系譜 |
| the history of ariosophy, |
アリオゾフィーの歴史。 |
| new templar verse |
新テンプル騎士団の詩 |
| the modern mythology of Nazi occultism. |
ナチスのオカルティズムの現代神話。 |
◎カール・マリア・ヴィリグート(Karl Maria Wiligut, 1866-1946)
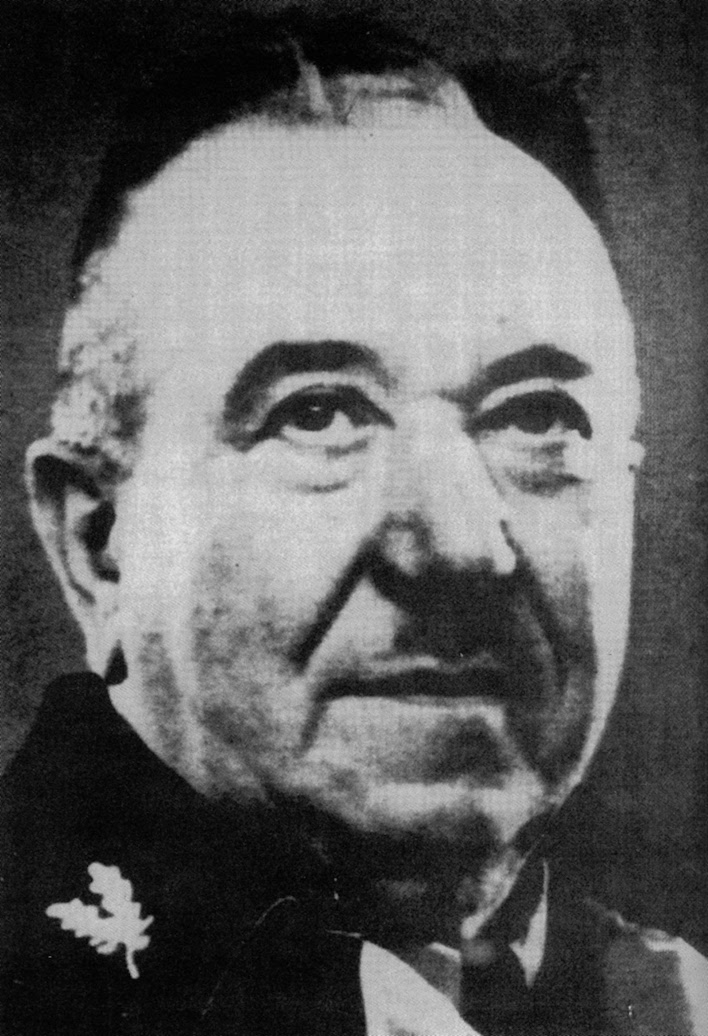 カー
ル・マリア・ヴィリグート(Karl Maria Wiligut、1866年12月10日 ‐
1946年1月3日)は、ナチス・ドイツの親衛隊員。独特な神秘主義とオカルトを信仰し、親衛隊全国指導者ハインリヒ・ヒムラーから絶大な信任を得て、彼
および親衛隊の宗教思想に大きな影響を与えたとされる。「ヒムラーのラスプーチン」の異名をとる。オーストリア・ハンガリー帝国の首都ウィーンに生まれ
る。ローマ・カトリック教会の洗礼を受けた[1]
。17歳の時にオーストリア軍に徴兵された。歩兵部隊に配属され、1888年に中尉に昇進した。1889年に準フリーメイソン団体
「Schlaraffia-Loge」に参加。1903年には「Lobesam」のペンネームで最初の自著「Seyfrieds
Runen」を出版した。1906年に結婚して三人の子供(男女の双子と娘)を授かったが、このうち男児は早世している。1908年には「Neun
Gebote
Gots」を出版。ここで初めて自分が「イルミン教(英語版)」(イルミネンシャフト)なる古代宗教の継承者であることを主張しだした。第一次世界大戦中
には南部や東部戦線に従軍。1917年8月1日には大佐に昇進。まもなく前線勤務を離れてレンベルク近くの療養収容所の司令官となった。第一次世界大戦敗
戦後の1919年1月1日に軍を退職した。40年にも及ぶ軍隊生活であった。その後はザルツブルク近くのモルツクに移り、ここでオカルト研究に没頭した。
また新聞「Der Eiserne
Besen」を発行した。「暗黒の力の陰謀」が世界中にあると確信して、反ユダヤ主義・反フリーメーソン・反カトリック教会の思想をばらまくようになった
[2]。妻は彼の奇妙な思想にはついていけず、精神病院への入院を勧めた。1924年11月29日に警察に逮捕されたのを機に、ヴィリグートは実際に数年
間精神病院で過ごすこととなった。ヴィリグートの医療記録には、妻に「殺す」と言って脅迫することを含む家庭内暴力の傾向、変人行動、オカルトへの興味な
どが特筆されている。病院から統合失調症と誇大妄想を診断された。ザルツブルクの法廷からも責任能力なしと断定され、1927年から1932年までザルツ
ブルクの精神病院で過ごした。妻とは離婚し、家族とも縁を切ってドイツのミュンヘンへと移住していった。ヒトラー政権成立後の1933年9月に親衛隊全国
指導者ハインリヒ・ヒムラーと知り合い、彼に気にいられて北方人種文化政治協会(Nordische
Gesellschaft)のメンバーに招かれた。さらに親衛隊にも入隊。この際になぜか「カール・マリア・ヴァイストール(Karl Maria
Weisthor)」という偽名で入隊している。親衛隊人種及び移住本部(RuSHA)の先史学部長に任じられた。1934年4月には親衛隊大佐の階級が
与えられた。1934年10月にRuSHA
VIII部(公文書保存部)の部長となった。11月には親衛隊上級大佐(SS-Oberführer)に昇進。1935年春にベルリンへ移動し、カール・
ヴォルフが長官をつとめる親衛隊全国指導者個人幕僚部(Persönlicher Stab Reichsführer
SS)に配属されてヒムラーの個人スタッフの一人となった。1936年9月に親衛隊少将に昇進。1934
年には「世界の中心」という寓話のある古城ヴェヴェルスブルク城(Wewelsburg)を親衛隊で購入して立て直すようヒムラーに薦めた。以降親衛隊は
この城でヴィリグートのイルミン教の宗教観念に基づく怪しげな魔術の儀式を執り行うようになった。親衛隊員の結婚式もこの城で頻繁に行われるようになり、
ヴィリグートは司祭のような役割を果たしていた。1937年1月4日にはヴィリグートの上司のカール・ヴォルフの長男もここで洗礼を受けている。
一方グイド・フォン・リストの起こした民族主義的なゲルマン異教思想「ヴォータニズム(Wotanismus)」とは、似た思想でありながら敵視してい
た。ヴィリグートはヒムラーに求めてヴォータニズムの信者たちを次々とナチス強制収容所へ送らせている。またヴォータニズムが提唱する「アルマネン・ルー
ン(Armanen runes)」に対抗して「ヴィリグート・ルーン(Wiligut
runes)」を創出した。ヴィリグートのヴォータニズム敵視の理由については下記のイルミン教の項目を参照のこと。アーネンエルベの初代長官ヘルマン・ヴィルト(Herman Wirth)は、ヴィリグートにいい印象を持っていなかっ
カー
ル・マリア・ヴィリグート(Karl Maria Wiligut、1866年12月10日 ‐
1946年1月3日)は、ナチス・ドイツの親衛隊員。独特な神秘主義とオカルトを信仰し、親衛隊全国指導者ハインリヒ・ヒムラーから絶大な信任を得て、彼
および親衛隊の宗教思想に大きな影響を与えたとされる。「ヒムラーのラスプーチン」の異名をとる。オーストリア・ハンガリー帝国の首都ウィーンに生まれ
る。ローマ・カトリック教会の洗礼を受けた[1]
。17歳の時にオーストリア軍に徴兵された。歩兵部隊に配属され、1888年に中尉に昇進した。1889年に準フリーメイソン団体
「Schlaraffia-Loge」に参加。1903年には「Lobesam」のペンネームで最初の自著「Seyfrieds
Runen」を出版した。1906年に結婚して三人の子供(男女の双子と娘)を授かったが、このうち男児は早世している。1908年には「Neun
Gebote
Gots」を出版。ここで初めて自分が「イルミン教(英語版)」(イルミネンシャフト)なる古代宗教の継承者であることを主張しだした。第一次世界大戦中
には南部や東部戦線に従軍。1917年8月1日には大佐に昇進。まもなく前線勤務を離れてレンベルク近くの療養収容所の司令官となった。第一次世界大戦敗
戦後の1919年1月1日に軍を退職した。40年にも及ぶ軍隊生活であった。その後はザルツブルク近くのモルツクに移り、ここでオカルト研究に没頭した。
また新聞「Der Eiserne
Besen」を発行した。「暗黒の力の陰謀」が世界中にあると確信して、反ユダヤ主義・反フリーメーソン・反カトリック教会の思想をばらまくようになった
[2]。妻は彼の奇妙な思想にはついていけず、精神病院への入院を勧めた。1924年11月29日に警察に逮捕されたのを機に、ヴィリグートは実際に数年
間精神病院で過ごすこととなった。ヴィリグートの医療記録には、妻に「殺す」と言って脅迫することを含む家庭内暴力の傾向、変人行動、オカルトへの興味な
どが特筆されている。病院から統合失調症と誇大妄想を診断された。ザルツブルクの法廷からも責任能力なしと断定され、1927年から1932年までザルツ
ブルクの精神病院で過ごした。妻とは離婚し、家族とも縁を切ってドイツのミュンヘンへと移住していった。ヒトラー政権成立後の1933年9月に親衛隊全国
指導者ハインリヒ・ヒムラーと知り合い、彼に気にいられて北方人種文化政治協会(Nordische
Gesellschaft)のメンバーに招かれた。さらに親衛隊にも入隊。この際になぜか「カール・マリア・ヴァイストール(Karl Maria
Weisthor)」という偽名で入隊している。親衛隊人種及び移住本部(RuSHA)の先史学部長に任じられた。1934年4月には親衛隊大佐の階級が
与えられた。1934年10月にRuSHA
VIII部(公文書保存部)の部長となった。11月には親衛隊上級大佐(SS-Oberführer)に昇進。1935年春にベルリンへ移動し、カール・
ヴォルフが長官をつとめる親衛隊全国指導者個人幕僚部(Persönlicher Stab Reichsführer
SS)に配属されてヒムラーの個人スタッフの一人となった。1936年9月に親衛隊少将に昇進。1934
年には「世界の中心」という寓話のある古城ヴェヴェルスブルク城(Wewelsburg)を親衛隊で購入して立て直すようヒムラーに薦めた。以降親衛隊は
この城でヴィリグートのイルミン教の宗教観念に基づく怪しげな魔術の儀式を執り行うようになった。親衛隊員の結婚式もこの城で頻繁に行われるようになり、
ヴィリグートは司祭のような役割を果たしていた。1937年1月4日にはヴィリグートの上司のカール・ヴォルフの長男もここで洗礼を受けている。
一方グイド・フォン・リストの起こした民族主義的なゲルマン異教思想「ヴォータニズム(Wotanismus)」とは、似た思想でありながら敵視してい
た。ヴィリグートはヒムラーに求めてヴォータニズムの信者たちを次々とナチス強制収容所へ送らせている。またヴォータニズムが提唱する「アルマネン・ルー
ン(Armanen runes)」に対抗して「ヴィリグート・ルーン(Wiligut
runes)」を創出した。ヴィリグートのヴォータニズム敵視の理由については下記のイルミン教の項目を参照のこと。アーネンエルベの初代長官ヘルマン・ヴィルト(Herman Wirth)は、ヴィリグートにいい印象を持っていなかっ た。
彼のことを「もうろくしたアルコール中毒者」「グイド・フォン・リストの泥棒」と酷評して敵対した。しかしヒムラーのヴィリグートへの信任は厚く、
1937年にヒムラーはヴィルトを長官の地位から降ろした。しかし、オーストリア併合後の1938年10月、オーストリアでのヴィリグートの経歴、すなわ
ち精神病院入院の過去がカール・ヴォルフ(Karl Friedrich Otto Wolff, 1900-1984)に漏れ、彼はただちにヒムラーにこれを報告した。しかもちょうどこの頃、ヴィリグートはヒムラーの側近の女性に「親衛隊全国指導者は私の子供が欲しいそうだ。
つまり私と貴女の子供だ。貴女は大変に名誉あるご指名を受けたのだ」などと言って関係を迫っていた。彼女からの抗議を受けたヒムラーは怒り、これにより
ヴィリグートは完全に彼の信任を失った。1939年8月28日にヴィリグートは高齢や病を理由に親衛隊から除隊させられた。彼と完全に手を切りたがってい
たヒムラーは、髑髏リングや長剣、短剣などの親衛隊員の装飾品の返却を求めたが、ヴィリグートは「最後の連帯の証しだ」として拒否し、自分の物にしてし
まった。この後勃発した第二次世界大戦中にはアウフキルヒェン(Aufkirchen)、1940年からゴスラー(Goslar)、
1943年からヴェルター湖(Wörthersee)で暮らした。戦後はヴァルター湖近くの聖ヨハンの難民キャンプで生活したが、脳出血に苦しんだ。この
後ザルツブルクへ戻る許可を得た。しかしすぐにヘッセン州のアロルゼンへと移住した。1946年1月3日にここで死去している。彼の墓石には「私たちの人
生は無駄なおしゃべりのように過ぎ去る(UNSER LEBEN GEHT DAHIN WIE EIN
GESCHWÄTZ)」と刻まれている。【イルミン教】ヴィリグートは自分が霊的な力を持っていて、自分の先祖の記憶にアクセスできると主張していたが、
その記憶によるとイルミン教こそがドイツ民族の本来の民族宗教であるという。そしてその神は「Krist」であり、後にキリスト教がそれを盗用して
「Christ(キリスト)」を作り出したのだという。さらにドイツ民族の歴史は紀元前22万8000年にさかのぼるという。この時代太陽は3つあり、地
球には巨人と小人、その他神話の生物が暮らしていたという。そして紀元前1万2500年前まではドイツ民族はKristのイルミン教の宗教を奉じていたと
いう。しかしその後ヴォタニズムの分離主義者たちが現れて優勢になり、紀元前1200年にゴスターでヴォタニズムによってイルミン教の信仰が破壊されてし
まったのだという。イルミン教はエクステルンシュタイネ(Externsteine)に新たな神殿を建てたが、紀元前460年にヴォタニズムがここも盗ん
でいったという。ヴィリグートの祖先はアース神族とヴァン神族が結合した氷の王(Ueiskunings)であり、ドイツ帝国の中心としてビリニュスの町
を作ったのだという。ここにはイルミン教の信仰が常に残っていたという。[3]このイルミン教はヴィリグートの被害妄想にも使われた。彼と彼の家族は現在
も続くイルミン教迫害の犠牲者であるのだという。イルミン教迫害は現在ローマ・カトリック教会、ユダヤ人、フリーメイソンによって行われているという。第
一次世界大戦の敗戦やハプスブルク家の没落もすべてはこれらの者たちの陰謀であったという。【写真】ハインリヒ・ヒムラー(左)とカール・ヴォルフ(右)、1933年12月12日:Bundesarchiv, Bild 183-H0226-501-003 / CC-BY-SA 3.0
た。
彼のことを「もうろくしたアルコール中毒者」「グイド・フォン・リストの泥棒」と酷評して敵対した。しかしヒムラーのヴィリグートへの信任は厚く、
1937年にヒムラーはヴィルトを長官の地位から降ろした。しかし、オーストリア併合後の1938年10月、オーストリアでのヴィリグートの経歴、すなわ
ち精神病院入院の過去がカール・ヴォルフ(Karl Friedrich Otto Wolff, 1900-1984)に漏れ、彼はただちにヒムラーにこれを報告した。しかもちょうどこの頃、ヴィリグートはヒムラーの側近の女性に「親衛隊全国指導者は私の子供が欲しいそうだ。
つまり私と貴女の子供だ。貴女は大変に名誉あるご指名を受けたのだ」などと言って関係を迫っていた。彼女からの抗議を受けたヒムラーは怒り、これにより
ヴィリグートは完全に彼の信任を失った。1939年8月28日にヴィリグートは高齢や病を理由に親衛隊から除隊させられた。彼と完全に手を切りたがってい
たヒムラーは、髑髏リングや長剣、短剣などの親衛隊員の装飾品の返却を求めたが、ヴィリグートは「最後の連帯の証しだ」として拒否し、自分の物にしてし
まった。この後勃発した第二次世界大戦中にはアウフキルヒェン(Aufkirchen)、1940年からゴスラー(Goslar)、
1943年からヴェルター湖(Wörthersee)で暮らした。戦後はヴァルター湖近くの聖ヨハンの難民キャンプで生活したが、脳出血に苦しんだ。この
後ザルツブルクへ戻る許可を得た。しかしすぐにヘッセン州のアロルゼンへと移住した。1946年1月3日にここで死去している。彼の墓石には「私たちの人
生は無駄なおしゃべりのように過ぎ去る(UNSER LEBEN GEHT DAHIN WIE EIN
GESCHWÄTZ)」と刻まれている。【イルミン教】ヴィリグートは自分が霊的な力を持っていて、自分の先祖の記憶にアクセスできると主張していたが、
その記憶によるとイルミン教こそがドイツ民族の本来の民族宗教であるという。そしてその神は「Krist」であり、後にキリスト教がそれを盗用して
「Christ(キリスト)」を作り出したのだという。さらにドイツ民族の歴史は紀元前22万8000年にさかのぼるという。この時代太陽は3つあり、地
球には巨人と小人、その他神話の生物が暮らしていたという。そして紀元前1万2500年前まではドイツ民族はKristのイルミン教の宗教を奉じていたと
いう。しかしその後ヴォタニズムの分離主義者たちが現れて優勢になり、紀元前1200年にゴスターでヴォタニズムによってイルミン教の信仰が破壊されてし
まったのだという。イルミン教はエクステルンシュタイネ(Externsteine)に新たな神殿を建てたが、紀元前460年にヴォタニズムがここも盗ん
でいったという。ヴィリグートの祖先はアース神族とヴァン神族が結合した氷の王(Ueiskunings)であり、ドイツ帝国の中心としてビリニュスの町
を作ったのだという。ここにはイルミン教の信仰が常に残っていたという。[3]このイルミン教はヴィリグートの被害妄想にも使われた。彼と彼の家族は現在
も続くイルミン教迫害の犠牲者であるのだという。イルミン教迫害は現在ローマ・カトリック教会、ユダヤ人、フリーメイソンによって行われているという。第
一次世界大戦の敗戦やハプスブルク家の没落もすべてはこれらの者たちの陰謀であったという。【写真】ハインリヒ・ヒムラー(左)とカール・ヴォルフ(右)、1933年12月12日:Bundesarchiv, Bild 183-H0226-501-003 / CC-BY-SA 3.0
+++
Links
リンク
文献
その他の情報