Breast enhancement,
breast enlargement or contouring
Cleavage enhancement, an increase in the definition of breast cleavage
Contrast enhancement, enhancement of the contrast of structures or
fluids within the body in medical imaging after administration of a
contrast medium.
Genetic enhancement, the use of genetic engineering to modify a
person's nonpathological human traits
Human enhancement, augmentation of the human body to increase capability
Male enhancement, a euphemism for penis enlargement |
バストアップ、乳房拡大、輪郭形成
乳房の谷間を強調すること。
造影増強(Contrast Enhancement):造影剤投与後の医用画像において、体内の構造物または体液のコントラストを増強すること。
遺伝子強化(Genetic Enhancement):人の非病的形質を修正するための遺伝子工学の使用。
人間強化(human enhancement):能力を高めるために人体を増強すること。
男性強化、陰茎増大の婉曲表現
|
Human enhancement is the
natural, artificial, or technological alteration of the human body in
order to enhance physical or mental capabilities.[1]
|
人間強化とは、身体的または精神的能力を高めるために、人体を自然的、
人工的、または技術的に変化させることである[1]。
|
Technologies
Existing technologies
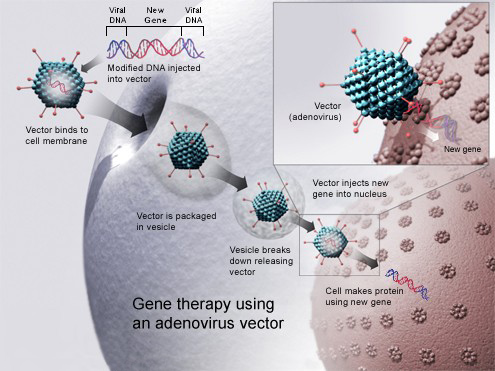
Gene therapy using adenovirus vector
Gene therapy using an adenovirus vector
Three forms of human enhancement currently exist: reproductive,
physical, and mental. Reproductive enhancements include embryo
selection by preimplantation genetic diagnosis, cytoplasmictransfer,
and in vitro-generated gametes. Physical enhancements include cosmetics
(plastic surgery and orthodontics), Drug-induced (doping and
performance-enhancing drugs), functional (prosthetics and powered
exoskeletons), Medical (implants (e.g. pacemaker) and organ
replacements (e.g. bionic lenses)), and strength training (weights
(e.g. barbells) and dietary supplement)). Examples of mental
enhancements are nootropics, neurostimulation, and supplements that
improve mental functions.[2][3] Computers, mobile phones, and
Internet[4] can also be used to enhance cognitive efficiency. Notable
efforts in human augmentation are driven by the interconnected Internet
of Things (IoT) devices,[5] including wearable electronics (e.g.,
augmented reality glasses, smart watches, smart textile), personal
drones, on-body and in-body nanonetworks.[6]
Emerging technologies
Many different forms of human enhancing technologies are either on the
way or are currently being tested and trialed. A few of these emerging
technologies include: human genetic engineering (gene therapy),
neurotechnology (neural implants and brain–computer interfaces),
cyberware, strategies for engineered negligible senescence,
nanomedicine, and 3D bioprinting. Variants of human genetic engineering
with so far limited usage include the artificial creation of
human-animal hybrids (where each cell has partly human and partly
animal genetic contents) and human-animal chimeras (where some cells
are human and some cells are animal in origin).[7]
Speculative technologies
Some other human enhancement technologies are still speculative, such
as: mind uploading, exocortex, and endogenous artificial nutrition.
Mind uploading is the hypothetical process of
"transferring"/"uploading" or copying a conscious mind from a brain to
a non-biological substrate by scanning and mapping a biological brain
in detail and copying its state into a computer system or another
computational device. The exocortex can be defined as a theoretical
artificial external information processing system that would augment a
brain's biological high-level cognitive processes. Endogenous
artificial nutrition can be similar to having a radioisotope generator
that resynthesizes glucose (similarly to photosynthesis), amino acids
and vitamins from their degradation products, theoretically availing
for weeks without food if necessary.
Nick Bostrom listed some additional capabilities that are expected to
be physically possible in theory, given a sufficient technological
level, such as:[8]
Reversal of aging
Cures for all diseases
Arbitrary sensory inputs (e.g. generating subjective experience of
taste without eating anything)
Precise control of personality, mood, motivation, well-being
|
テクノロジー
既存技術

アデノウイルスベクターを用いた遺伝子治療
アデノウイルスベクターを用いた遺伝子治療
現在、生殖、身体、精神の3種類のヒト強化が存在する。生殖機能強化には、着床前遺伝子診断による胚選択、細胞質移植、体外発生配偶子などがある。身体的
強化には、美容(整形手術や歯科矯正)、薬物誘発(ドーピングやパフォーマンス向上薬)、機能的(人工装具や動力外骨格)、医療(インプラント(ペース
メーカーなど)や臓器置換(バイオニックレンズなど))、筋力トレーニング(ウェイト(バーベルなど)や栄養補助食品)などがある。)
精神強化の例としては、向精神薬、神経刺激、精神機能を向上させるサプリメントなどがある[2][3]。コンピュータ、携帯電話、インターネット[4]
も、認知効率を高めるために使用することができる。人間拡張における注目すべき取り組みは、ウェアラブル・エレクトロニクス(拡張現実メガネ、スマート・
ウォッチ、スマート・テキスタイルなど)、パーソナル・ドローン、オンボディ及びインボディ・ナノネットワーク[6]を含む、相互接続されたモノのイン
ターネット(IoT)デバイス[5]によって推進されている。
新たな技術
人間を向上させるさまざまな技術が、現在開発中であるか、あるいは試験中である。遺伝子工学(遺伝子治療)、ニューロテクノロジー(神経インプラントやブ
レイン・コンピューター・インターフェイス)、サイバーウェア、人工的に老化を無視する戦略、ナノ医療、3Dバイオプリンティングなどである。ヒト遺伝子
工学のバリエーションとして、ヒトと動物のハイブリッド(各細胞の遺伝子の一部がヒトで、一部が動物である)や、ヒトと動物のキメラ(一部の細胞がヒト
で、一部の細胞が動物由来である)の人工的な作製があるが、今のところ利用は限定的である[7]。
投機的技術
マインド・アップロード、エキソコルテックス、内因性人工栄養などである。マインド・アップロードとは、生物学的な脳を詳細にスキャンしてマッピングし、
その状態をコンピュータ・システムや他の計算デバイスにコピーすることで、意識あるマインドを脳から非生物学的な基質に「転送」/「アップロード」または
コピーする仮想的なプロセスである。外皮は、脳の生物学的な高次認知プロセスを補強する理論的な人工外部情報処理システムとして定義できる。内因性人工栄
養は、グルコース(光合成に似ている)、アミノ酸、ビタミンを分解産物から再合成する放射性同位体発生装置を持つことに似ている。
ニック・ボストロムは、十分な技術水準があれば、理論的には物理的に可能であると予想される、以下のような追加能力を挙げている[8]。
老化の逆転
あらゆる病気の治療
恣意的な感覚入力(例えば、何も食べずに味覚の主観的な経験を生み出す)
人格、気分、意欲、幸福感の正確な制御
|
Nootropics
Main article: Nootropic
There are many substances that are purported to have promise in
augmenting human cognition by various means. These substances are
called nootropics and can potentially benefit individuals with
cognitive decline and many different disorders, but may also be capable
of yielding results in cognitively healthy persons. Generally speaking,
nootropics are said to be effective for enhancing focus, learning,
memory function, mood, and in some cases, physical brain development.
Some examples of these include Citicoline,[9] Huperzine A,
Phosphatidylserine,[10] Bacopa monnieri,[11] Acetyl-L-carnitine,[12]
Uridine monophosphate, L-theanine,[13][14][15] Rhodiola rosea, and
Pycnogenol which are all forms of dietary supplement. There are also
nootropic drugs such as the common racetams, e.g. piracetam (Nootropil)
and omberacetam (Noopept)[16][17][18] along with the neuroprotective
Semax, and N-Acetyl Semax.[19] There are also nootropics related to
naturally occurring substances but that are either modified in a lab or
are analogs such as Vinpocetine and Sulbutiamine. Some authors have
explored nootropics as relationship enhancements to help couples
maintain bonds over time.[20]
|
向精神薬
主な記事 向精神薬
様々な手段で人間の認知力を増強することが期待できるとされる物質が数多く存在する。これらの物質は向精神薬と呼ばれ、認知機能の低下や様々な障害を持つ
人々に恩恵をもたらす可能性があるが、認知機能が健康な人にも結果をもたらす可能性がある。一般的に言えば、向精神薬は集中力、学習、記憶機能、気分、場
合によっては身体的な脳の発達を高めるのに効果的と言われている。これらの例としては、シチコリン、[9]ヒュペルジンA、ホスファチジルセリン、
[10]バコパ・モニエリ、[11]アセチル-L-カルニチン、[12]ウリジン一リン酸、L-テアニン、[13][14][15]ロディオラ・ロゼア、
ピクノジェノールなどがあり、これらはすべて栄養補助食品の一種である。また、神経保護作用のあるセマックスやN-アセチルセマックス[19]に加えて、
ピラセタム(ヌートロピル)やオムベラセタム(ヌーペプト)などの一般的なラセタム類[16][17][18]といった向知性薬もある。一部の著者は、
カップルが長期にわたって絆を維持するための関係強化として、向精神薬を研究している[20]。
|
Ethics
Much debate surrounds the topic of human enhancement and the means used
to achieve one's enhancement goals.[21] Ethical attitudes toward human
enhancement can depend on many factors such as religious affiliation,
age, gender, ethnicity, culture of origin, and nationality.[22]
In some circles the expression "human enhancement" is roughly
synonymous with human genetic engineering,[23][24] but most often it is
referred to the general application of the convergence of
nanotechnology, biotechnology, information technology and cognitive
science (NBIC) to improve human performance.[25]
Since the 1990s, several academics (such as some of the fellows of the
Institute for Ethics and Emerging Technologies[26]) have risen to
become advocates of the case for human enhancement while other
academics (such as the members of President Bush's Council on
Bioethics[27]) have become outspoken critics.[28]
Advocacy of the case for human enhancement is increasingly becoming
synonymous with "transhumanism", a controversial ideology and movement
which has emerged to support the recognition and protection of the
right of citizens to either maintain or modify their own minds and
bodies; so as to guarantee them the freedom of choice and informed
consent of using human enhancement technologies on themselves and their
children.[29] Their common understanding of the world can be seen from
a physicist perspective rather than a biological perspective.[30] Based
on the idea of technological singularity, human enhancement is merging
with technological innovation that will advance post-humanism.[30]
Neuromarketing consultant Zack Lynch argues that neurotechnologies will
have a more immediate effect on society than gene therapy and will face
less resistance as a pathway of radical human enhancement. He also
argues that the concept of "enablement" needs to be added to the debate
over "therapy" versus "enhancement".[31]
The prospect of human enhancement has sparked public
controversy.[32][33][34] The main ethical question in the debate about
human enhancement involves which legal restrictions, if any, should
exist.[35]
Dale Carrico wrote that "human enhancement" is a loaded term which has
eugenic overtones because it may imply the improvement of human
hereditary traits to attain a universally accepted norm of biological
fitness (at the possible expense of human biodiversity and
neurodiversity), and therefore can evoke negative reactions far beyond
the specific meaning of the term.[36] Michael Selgelid terms this as a
phase of "neugenics" suggesting that gene enhancements occurring now
have already revived the idea of eugenics in our society. Practices of
prenatal diagnosis, selective abortion and in-vitro fertilization aims
to improve human life allowing for parents to decide via genetic
information if they want to continue or terminate the pregnancy.[37]
A criticism of human enhancement is that it will create unfair physical
or mental advantages, or unequal access to such enhancements, can and
will further the gulf between the "haves" and
"have-nots".[38][39][40][41]
Futurist Ray Kurzweil has shown some concern that, within the century,
humans may be required to merge with this technology in order to
compete in the marketplace.[30] Enhanced individuals have a better
chance of being chosen for better opportunities in careers,
entertainment and resources.[42] For example, life extending
technologies can increase the average individual life span, affecting
the distribution of pension throughout the society. Increasing lifespan
will affect human population, further dividing limited resources such
as food, energy, monetary resources and habitat.[42] Other critics of
human enhancement fear that such capabilities would change, for the
worse, the dynamic relations within a family. Given the choices of
superior qualities, parents make their child as opposed to merely
birthing it, and the newborn becomes a product of their will rather
than a gift of nature to be loved unconditionally.[43]
Effects on identity
Human enhancement technologies can impact human identity by affecting
one's self-conception.[44] The argument does not necessarily come from
the idea of improving the individual but rather changing who they are
and becoming someone new. Altering an individual identity affects their
personal story, development and mental capabilities. The basis of this
argument comes from two main points : the charge of inauthenticity and
the charge of violating an individual's core characteristics.[44] Gene
therapy has the ability to alter one’s mental capacity, and through
this argument, has the ability to affect their narrative identity.[44]
An individual's core characteristics may include internal psychological
style, personality, general intelligence, necessity to sleep, normal
aging, gender and being Homo sapiens. Technologies threaten to alter
the self fundamentally to the point where the result is, essentially, a
different person entirely.[44] For example, extreme changes in
personality may affect the individual's relationships because others
can no longer relate to the new person.[41]
The capability approach focuses on a normative framework that can be
applied to how human enhancement technologies affects human
capabilities.[45] The ethics of this does not necessarily focus on the
make up of the individual but rather what it allows individuals to do
in today's society. This approach was first termed by Amartya Sen,
where he mainly focused on the objectives of the approach rather than
the aim for those objectives which entail resources, technological
processes, and economic arrangement.[45] The central human capabilities
include life, bodily health, bodily integrity, sense, emotions,
practical reason, affiliation, other species, play, and control over
one's environment. This normative framework recognizes that human
capabilities are always changing and technology has already played a
part in this.[45]
|
倫理
ヒトの強化や、強化の目標を達成するために使用される手段について、多くの議論が巻き起こっている。
一部の世界では、「人間強化」という表現は、人間の遺伝子工学とほぼ同義であるが[23][24]、多くの場合、人間のパフォーマンスを向上させるための
ナノテクノロジー、バイオテクノロジー、情報技術、認知科学(NBIC)の融合の一般的な応用を指している[25]。
1990年代以降、何人かの学者(Institute for Ethics and Emerging
Technologies[26]のフェローの一部など)が人間強化のケースの擁護者となる一方で、他の学者(ブッシュ大統領の生命倫理評議会[27]の
メンバーなど)は率直な批判者となった[28]。
このイデオロギーは、市民が自分自身の心と体を維持したり改造したりする権利の承認と保護を支持し、自分自身や自分の子どもに人間強化技術を使用する選択
の自由とインフォームド・コンセントを保証するために出現した論争を呼ぶイデオロギーであり運動である。
[技術的特異点(シンギュラリティ)の考え方に基づき、人間強化はポスト・ヒューマニズムを推進する技術革新と融合している[30]。
ニューロマーケティングのコンサルタントであるザック・リンチは、ニューロテクノロジーは遺伝子治療よりも社会に即効性があり、根本的な人間強化の経路と
して抵抗が少ないと主張する。彼はまた、「治療」対「強化」をめぐる議論に「有効化」の概念を加える必要があるとも主張している[31]。
ヒトの強化に関する議論における主な倫理的問題は、法的規制が存在するとすればどのような規制が存在すべきかということである[35]。
デール・カリコは、「ヒトの強化」とは、(ヒトの生物多様性や神経多様性を犠牲にして)普遍的に受け入れられている生物学的適合性の規範を達成するために
ヒトの遺伝形質を改善することを意味する可能性があるため、優生学的な含みを持つ、負荷のかかる用語であり、したがって、この用語の特定の意味をはるかに
超えて否定的な反応を呼び起こす可能性があると書いている[36]。
マイケル・セルゲリドは、現在起こっている遺伝子の強化が、すでに私たちの社会で優生学の考えを復活させていることを示唆する「新生児学」の段階としてこ
れを呼んでいる。出生前診断、選択的中絶、体外受精の実践は、両親が遺伝子情報を通じて妊娠を継続するか終了するかを決定できるようにすることで、人間の
生命を向上させることを目的としている[37]。
人間強化に対する批判は、肉体的または精神的に不公平な利点を生み出す、あるいはそのような強化への不平等なアクセスが可能であり、「持てる者」と「持た
ざる者」の間の溝をさらに深めることになるというものである[38][39][40][41]。
未来学者のレイ・カーツワイルは、今世紀中に、市場で競争するために人間はこのテクノロジーと融合することが求められるようになるかもしれないという懸念
を示している[30]
。寿命が延びることは人間の人口に影響を与え、食料、エネルギー、金銭的資源、生息地などの限られた資源をさらに分割することになる[42]。人間強化の
他の批判者は、そのような能力が家族内の力動的関係を悪い方向に変えてしまうことを恐れている。優れた資質を選択できるようになると、親は単に子供を産む
のとは対照的に子供を作るようになり、新生児は無条件に愛されるべき自然の贈り物ではなく、親の意志の産物となる[43]。
アイデンティティへの影響
人間強化技術は、自己概念に影響を与えることによって人間のアイデンティティに影響を与える可能性がある[44]。個人のアイデンティティを変更すること
は、個人の物語、成長、精神的能力に影響を与える。この主張の根拠は主に2つの点から来る:不真面目さの告発と個人の中核的特性の侵害の告発である
[44]。遺伝子治療には人の精神的能力を変える能力があり、この主張を通じて、その人の物語上のアイデンティティに影響を与える能力がある[44]。個
人の中核的特性には、内面的な心理的スタイル、性格、一般的な知能、睡眠の必要性、正常な老化、性別、ホモ・サピエンスであることなどが含まれる。例え
ば、人格の極端な変化は、他者がもはや新しい自分に関わることができないため、個人の人間関係に影響を与える可能性がある。
ケーパビリティ・アプローチは、人間強化技術が人間の能力にどのような影響を与えるかに適用できる規範的枠組みに焦点を当てている。このアプローチはアマ
ルティア・センによって最初に提唱されたものであり、彼は資源、技術的プロセス、経済的配置を伴う目的よりも、むしろアプローチの目的に主眼を置いている
[45]。この規範的枠組みは、人間の能力は常に変化しており、テクノロジーはすでにその一翼を担っていることを認識している[45]。
|
Anti-aging movement
Assisted reproductive technologies
Biohappiness
Body modification
Cloning
Directed evolution (transhumanism)
Evidence-based learning
Gene therapy
Genetic engineering
Grinder (biohacking)
Human-animal hybrid
Life extension
Moral enhancement
Posthuman
Posthumanization
Technological singularity
Transhumanism
Outline of transhumanism § Human enhancement technologies
|
アンチエイジング運動
生殖補助医療技術
バイオハピネス
身体改造
クローン技術
指示進化(トランスヒューマニズム)
エビデンスに基づく学習
遺伝子治療
遺伝子工学
グラインダー(バイオハッキング)
人間と動物のハイブリッド
生命延長
モラル強化
ポストヒューマン
ポスト・ヒューマニゼーション
技術的特異点
トランスヒューマニズム
トランスヒューマニズムの概要 § 人間強化技術
|


 ★
★

 ☆
☆