アーリア人
Aryan race, the Aryan
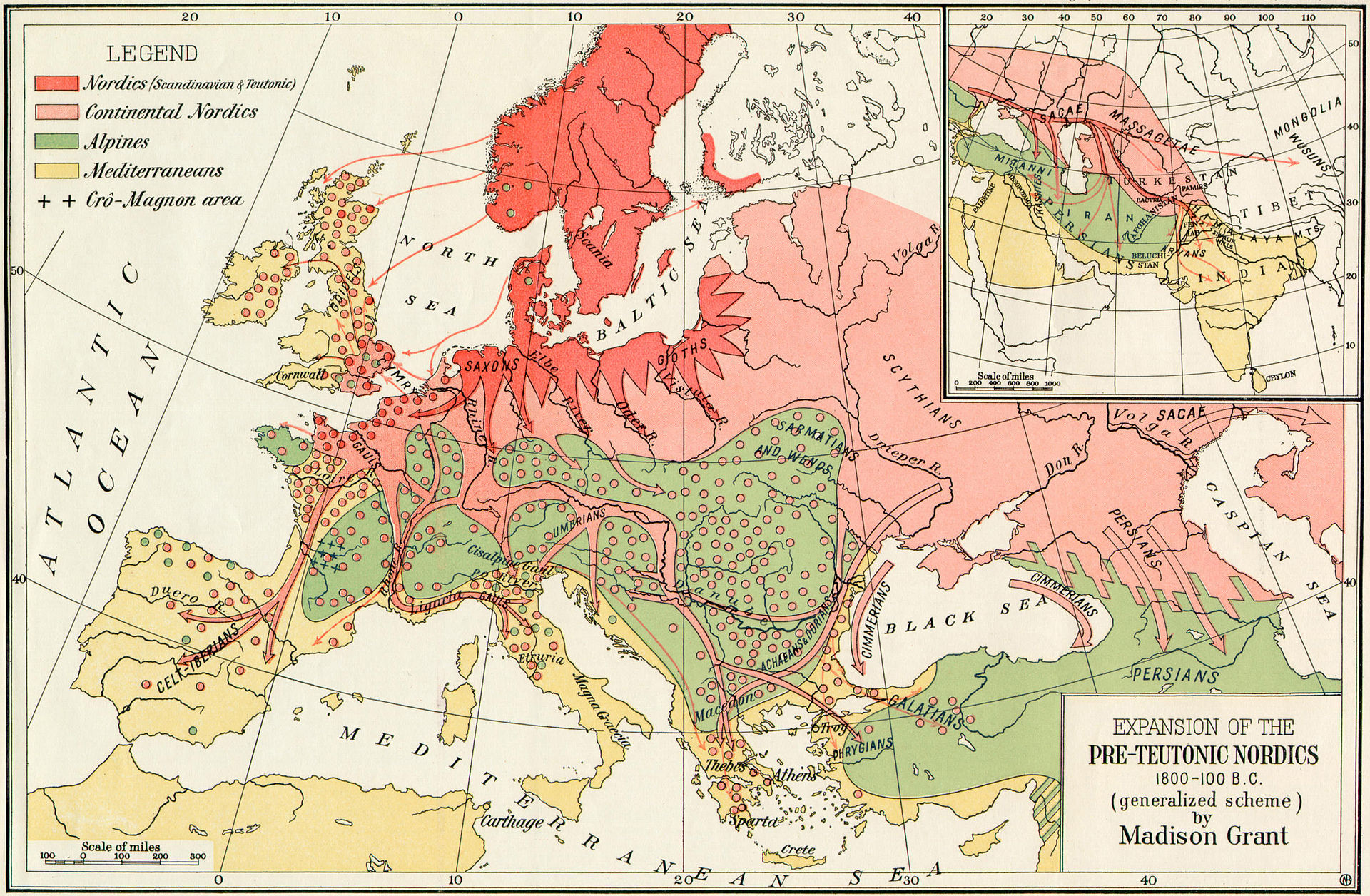
"Expansion of the Pre-Teutonic Nordics" — Map from The Passing of
the Great Race by Madison Grant showing hypothesized migrations of
Nordic peoples.
アーリア人
Aryan race, the Aryan

"Expansion of the Pre-Teutonic Nordics" — Map from The Passing of
the Great Race by Madison Grant showing hypothesized migrations of
Nordic peoples.
★アーリア人またはアーヤ(/ˈɛəriən/;インド・イラン語 *arya)は、もともと古代にインド・イラン人が民族文化の自 称として用いた用語で、「非アーリア」(*an-arya)と呼ばれる近隣の部外者に対比して使用されていた。 古代インドでは、ヴェーダ時代のインド・アーリア人の話者が、インド・アーリア文化が生まれたĀryāvarta(「アーリア人の住処」)と 呼ばれる地域を指して、ā́ryaという用語をエンドネーム(自称)として使用していた。 アベスタ聖典では、古代イランの人々も同様に、民族としての自分たちを示すためにエアヤという言葉を使い、彼らの神話上の故郷であるエアヤンバウムヴァエ オー(「アーリア人の広がり」または「アーリア人の伸びしろ」)に言及した。また語幹はイラン(*Aryānām)やアラニア(*Aryāna-)といっ た地名の語源を形成する、と言われる。850年代にフランスの作家アルチュール・ ド・ゴビノーによって 「アーリア人」という言葉が人種カテゴリーとして採用され、後のヒュー ストン・スチュワート・チェンバレンの著作を通じて、ナチスの人種思想に影響を与え た。ナチス支配下(1933-1945)では、ユダヤ人を除くドイツのほとんどの住人にこの言葉が当てはまる。 1935年にニュルンベルク法律が制定されてからドイツ人や血縁関係(アーリアン)者で帝国市民となるためにはアーリアン証明が第一要件であった。ス ウェーデン人やイギリス人、フランス人やチェコ人、ポーランド人やイタリア人」は血縁者、つまり「アーリア人」であるとされた。非アーリア人」に分類され た者、特にユダヤ人は、ホロコーストとして知られる組織的大量殺戮に遭う前に差別さ れた(ロマニ族の大量殺戮についてはポラジュモスを参 照のこと)。アーリア人至上主義思想の名の下に行われた残虐行為により、学者たちは一般的に「アーリア人」という言葉を避けるようになり、ほとんどの場合 「インド・イラン人」に置き換えられているが、南アジアの支部は今でも「インド・アーリア人」と呼ばれる。
| Aryan or Arya
(/ˈɛəriən/;[1] Indo-Iranian *arya) is a term originally used as an
ethnocultural self-designation by Indo-Iranians in ancient times, in
contrast to the nearby outsiders known as 'non-Aryan' (*an-arya).[2][3]
In Ancient India, the term ā́rya was used by the Indo-Aryan speakers of
the Vedic period as an endonym (self-designation) and in reference to a
region known as Āryāvarta ('abode of the Aryas'), where the Indo-Aryan
culture emerged.[4] In the Avesta scriptures, ancient Iranian peoples
similarly used the term airya to designate themselves as an ethnic
group, and in reference to their mythical homeland, Airyanǝm Vaēǰō
('expanse of the Aryas' or 'stretch of the Aryas').[5][6] The stem also
forms the etymological source of place names such as Iran (*Aryānām)
and Alania (*Aryāna-).[7] |
アーリア人またはアーヤ(/ˈɛəriən/;[1]
インド・イラン語 *arya)は、もともと古代にインド・イラン人が民族文化の自
称として用いた用語で、「非アーリア」(*an-arya)と呼ばれる近隣の部外者に対比して使用されていた。
[2][3]古代インドでは、ヴェーダ時代のインド・アーリア人の話者が、インド・アーリア文化が生まれたĀryāvarta(「アーリア人の住処」)と
呼ばれる地域を指して、ā́ryaという用語をエンドネーム(自称)として使用していた。 [4]
アベスタ聖典では、古代イランの人々も同様に、民族としての自分たちを示すためにエアヤという言葉を使い、彼らの神話上の故郷であるエアヤンバウムヴァエ
オー(「アーリア人の広がり」または「アーリア人の伸びしろ」)に言及した。 5][6]
また語幹はイラン(*Aryānām)やアラニア(*Aryāna-)といった地名の語源を形成する[7 |
| In the 1850s the term 'Aryan'
was adopted as a racial category by French writer Arthur de Gobineau,
who, through the later works of Houston Stewart Chamberlain, influenced
the Nazi racial ideology.[12] Under Nazi rule (1933–1945), the term
applied to most inhabitants of Germany excluding Jews.[13][14] Aryan
certificate was a primary requirement to become a Reich citizen for
those who were of German or related blood (Aryan) and wanted to become
Reich citizens after the Nuremberg Laws were passed in 1935. A "Swede
or an Englishman, a Frenchman or Czech, a Pole or Italian" was
considered to be related, that is, "Aryan". Those classified as
'non-Aryans,' especially Jews,[15] were discriminated against before
suffering the systematic mass killing known as the Holocaust[13] (see
Porajmos for the genocide of the Romani people). The atrocities
committed in the name of Aryanist supremacist ideologies have led
academics to generally avoid the term 'Aryan', which has been replaced
in most cases by 'Indo-Iranian', although the South Asian branch is
still known as 'Indo-Aryan'.[16] |
1850年代にフランスの作家アルチュール・ド・ゴビノーによって
「アーリア人」という言葉が人種カテゴリーとして採用され、後のヒュー
ストン・スチュワート・チェンバレンの著作を通じて、ナチスの人種思想に影響を与え
た[12] ナチス支配下(1933-1945)では、ユダヤ人を除くドイツのほとんどの住人にこの言葉が当てはまる[13][14]
1935年にニュルンベルク法律が制定されてからドイツ人や血縁関係(アーリアン)者で帝国市民となるためにはアーリアン証明が第一要件であった。ス
ウェーデン人やイギリス人、フランス人やチェコ人、ポーランド人やイタリア人」は血縁者、つまり「アーリア人」であるとされた。非アーリア人」に分類され
た者、特にユダヤ人[15]は、ホロコースト[13]として知られる組織的大量殺戮に遭う前に差別された(ロマニ族の大量殺戮についてはポラジュモスを参
照のこと)。アーリア人至上主義思想の名の下に行われた残虐行為により、学者たちは一般的に「アーリア人」という言葉を避けるようになり、ほとんどの場合
「インド・イラン人」に置き換えられているが、南アジアの支部は今でも「インド・アーリア人」と呼ばれる[16]。 |
| Origin Drawing on racially-oriented interpretations of the Vedic Aryas as "fair-skinned foreign invaders" coming from the North, the term Aryan came to be adopted in the West as a racial category connected to a supremacist ideology known as Aryanism, which conceived the Aryan race as the 'superior race' responsible for most of the achievements of ancient civilizations.[9] Max Müller, who had himself inaugurated the racial interpretations of the Rigveda,[98] denounced in 1888 those who spoke of an "Aryan race, Aryan blood, Aryan eyes and hair" as a nonsense comparable to a linguist speaking of "a dolichocephalic dictionary or a brachycephalic grammar".[99] But for an increasing number of Western writers, especially among anthropologists and non-specialists influenced by Darwinist theories, the Aryans came to be seen as a "physical-genetic species" contrasting with the other human races rather than an ethnolinguistic category.[100][101] During the late 19th–early 20th century, a fusion of Aryanism with Nordicism promoted by writers such as Arthur de Gobineau, Theodor Poesche, Houston Chamberlain, Paul Broca, Karl Penka and Hans Günther led to the portrayal of the Proto-Indo-Europeans as blond and tall, with blue eyes and dolichocephalic skulls.[102][103] Modern scholars reject those views and remind that the idea of a Vedic opposition between ārya and dāsa underlying a racial division remains problematic, since "most of the [Vedic] passages may not refer to dark or light skinned people, but dark and light worlds."[104] |
起源 アーリア人という言葉は、ヴェーダのアーリア人を北方から来た「色白の外国人侵略者」とする人種的解釈に基づいて、アーリア人を古代文明の成果の大部分を もたらした「優れた人種」と見なすアーリア主義と呼ばれる至上主義思想と結びついた人種カテゴリーとして西洋で採用されるようになった[9]。 リグヴェーダの人種的解釈を始めたマックス・ミュラー[98]は、1888年に「アーリア人種、アーリア人の血、アーリア人の目と髪」を語る人々を、言語 学者が「ドリコム辞書やブラキ頭文法」を語るのと同様のナンセンスであると非難している[99]。 しかし、西洋の作家、特にダーウィニズム理論の影響を受けた人類学者や非専門家の間では、アーリア人は民族的言語的カテゴリーというよりも、他の人類と対 比される「身体的・遺伝的種」として見られるようになった[99][99]。 100][101] 19世紀後半から20世紀初頭にかけて、アルチュール・ド・ゴビノー、テオドール・ポエッシュ、ヒューストン・チェンバレン、ポール・ブロカ、カール・ペ ンカ、ハンス・ギュンターなどの作家が推進した北欧主義との融合により、原インド・ヨーロッパ人は金髪で長身、青い目と多頭性の頭蓋骨を持つと描写される に至った[102][103]。 [102][103] 現代の学者はこれらの見解を否定し、「(ヴェーダの)聖句のほとんどは肌の黒い人や明るい人に言及しているのではなく、暗い世界や明るい世界に言及してい るかもしれない」ため、人種的区分の根底にあるナーリヤとダーサの間のヴェーダの対立という考えには問題が残っていると想起している[104]. |
| Theories of racial supremacy Arthur de Gobineau, the author of the influential Essay on the Inequality of the Human Races (1853), viewed the white or Aryan race as the only civilized one, and conceived cultural decline and miscegenation as intimately intertwined. According to him, northern Europeans had migrated across the world and founded the major civilizations, before being diluted through racial mixing with indigenous populations described as racially inferior, leading to the progressive decay of the ancient Aryan civilizations.[105] In 1878, German American anthropologist Theodor Poesche published a survey of historical references attempting to demonstrate that the Aryans were light-skinned blue-eyed blonds.[102] The use of Arier to mean 'non-Jewish' seems to have first occurred in 1887, when a Viennese physical fitness society decided to allow as members only "Germans of Aryan descent" (Deutsche arischer Abkunft).[84] In The Foundations of the Nineteenth Century (1899), described as "one of the most important proto-Nazi texts", British-German writer Houston Chamberlain theorized an existential struggle to death between a superior German-Aryan race and a destructive Jewish-Semitic race.[106] The best-seller The Passing of the Great Race, published by American writer Madison Grant in 1916, warns of a danger of miscegenation with the immigrant "inferior races" – including speakers of Indo-European languages such as Slavs, Italians and Yiddish-speaking Jews – allegedly faced by the "racially superior" Germanic Aryans, that is Americans of English, German and Scandinavian descent.[12] Led by Guido von List (1848–1919) and Jörg Lanz von Liebenfels (1874–1954), Ariosophists founded an ideological system combining Völkisch nationalism with esoterism. Prophesying a coming era of German (Aryan) world rule, they argued that a conspiracy against Germans – said to have been instigated by the non-Aryan races, the Jews, or the early Church – had "sought to ruin this ideal Germanic world by emancipating the non-German inferiors in the name of a spurious egalitarianism."[107] |
人種至上主義の理論 アルチュール・ド・ゴビノーは、『人種間の不平等に関する論 考』 (1853年)を著し、白人またはアーリア人を唯一の文明人と見なし、文化の衰退と異種族混血を密接に関連させる考えをもっていた。彼によれば、北ヨー ロッパ人は世界中に移住して主要な文明を築いたが、その後、人種的に劣るとされる先住民との人種的混合によって希釈され、古代アーリア文明の衰退を進行さ せるに至った。 1878年、ドイツ系アメリカ人の人類学者テオドール・ポエッシュは、アーリア人が明るい肌の青い目のブロンドであったことを証明しようとする歴史的文献 の調査を発表した[102]。 非ユダヤ人」を意味するアリエの使用は、1887年にウィーンの体力学会が「アーリア系のドイツ人」(Deutsche arischer Abkunft)だけを会員として認めることになった時に始まったようである[84]。 84] 「最も重要なナチス原典の一つ」とされる『19世紀の基礎』(1899年)では、イギリス系ドイツ人の作家ヒューストン・チェンバレンが、優れたドイツ系 アーリア人と破壊的なユダヤ系ユダヤ人の間の死闘の存在を理論化している[106]。 [1916年にアメリカの作家マディソン・グラントによって出版されたベストセラー『偉大なる人種の通過』は、「人種的に優れた」ゲルマン系アーリア人、 すなわちイギリス、ドイツ、スカンジナビア系のアメリカ人が直面するとされる、スラブ人、イタリア人、イディッシュ語を話すユダヤ人といったインドヨー ロッパ言語を話す移民「劣等人種」との混血の危険性を警告している[12]。 グイド・フォン・リスト(1848-1919)とイェルク・ランツ・フォン・リーベンフェルス(1874-1954)に導かれたアリオス主義者は、ヴェル キッシュ民族主義と秘教を組み合わせた思想体系を設立した。ドイツ人(アーリア人)の世界支配の時代の到来を予言し、彼らはドイツ人に対する陰謀-非アー リア人、ユダヤ人、または初期の教会によって扇動されたと言われている-が「偽りの平等主義の名の下に非ドイツ人の劣等者を解放することによってこの理想 のゲルマン世界を台無しにしようとした」[107]と主張している。 |
| North European hypothesis In the meantime, the idea that Indo-European languages originated from South Asia gradually lost support among academics. After the end of the 1860s, alternative models of Indo-European migrations began to emerge, some of them locating their ancestral homeland in Northern Europe.[102][108] Karl Penka, credited as "a transitional figure between Aryanism and Nordicism",[109] argued in 1883 that the Aryans originated in southern Scandinavia.[102] In the early 20th century, German scholar Gustaf Kossinna, attempting to equal a prehistoric material culture with the reconstructed Proto-Indo-European language, contended on archaeological grounds that the 'Indo-Germanic' (Indogermanische) migrations originated from a homeland located in northern Europe.[12] Until the end of World War II, scholarship was broadly divided between Kossinna's followers and those, initially led by Otto Schrader, who supported a steppe homeland in Eurasia, now the most widespread hypothesis among scholars.[99] |
北欧仮説 一方、インド・ヨーロッパ語族の起源を南アジアとする考え方は、学者の間で次第に支持されなくなった。1860年代末以降、インド・ヨーロッパ人の移動に 関する代替モデルが現れ始め、その中には祖先を北ヨーロッパに置くものもあった[102][108]。 アーリア主義と北欧主義の間の過渡的人物」とされるカール・ペンカは1883年にアーリア人が南スカンジナビアに起源を持つと主張した[109]。 20世紀初頭、ドイツの学者であるグスタフ・コシンナは、先史時代の物質文化と復元されたインド・ヨーロッパ語族の言語を等しくしようとし、考古学的根拠 に基づいて「インド・ゲルマン」(インドゲルマン)の移住は北ヨーロッパに位置する故郷から始まったと主張した[102]。 [第二次世界大戦の終わりまでは、コシナの信奉者と、オットー・シュレーダーを筆頭に、現在最も広く研究者の間で支持されているユーラシア大陸のステップ 民族の仮説を支持する研究者に大きく分かれた[99]。 |
| British Raj In India, the British colonial government had followed de Gobineau's arguments along another line, and had fostered the idea of a superior "Aryan race" that co-opted the Indian caste system in favor of imperial interests.[110][111] In its fully developed form, the British-mediated interpretation foresaw a segregation of Aryan and non-Aryan along the lines of caste, with the upper castes being "Aryan" and the lower ones being "non-Aryan". The European developments not only allowed the British to identify themselves as high-caste, but also allowed the Brahmins to view themselves as on-par with the British. Further, it provoked the reinterpretation of Indian history in racialist and, in opposition, Indian Nationalist terms.[110][111] |
イギリスのラージ インドでは、イギリスの植民地政府はド・ゴビノーの議論を別の路線で踏襲し、帝国の利益を優先してインドのカースト制度を共用して優れた「アーリア人種」 の考えを育てた[110][111]。 完全に発展した形では、イギリスの媒介による解釈はカーストの線に沿ってアーリアン人と非アーリアン人を隔離し、上位カーストを「アーリア人」、下位を 「非アーリアン」と見なすことが予見された。ヨーロッパの発展は、イギリス人が自分たちをハイカーストと認識することを可能にしただけでなく、バラモンが 自分たちをイギリス人と同列にみなすことを可能にした。さらに、インドの歴史を人種主義的に、またそれに対抗してインド・ナショナリズムに再解釈すること を誘発した[110][111]。 |
| Nazism and white supremacy An intertitle from the silent film blockbuster The Birth of a Nation (1915). "Aryan birthright" is here "white birthright", the "defense" of which unites "whites" in the Northern and Southern U.S. against "coloreds". In another film of the same year, The Aryan, William S. Hart's "Aryan" identity is defined in distinction from other peoples. Through the works of Houston Stewart Chamberlain, Gobineau's ideas influenced the Nazi racial ideology, which saw the "Aryan race" as innately superior to other putative racial groups.[12] The Nazi official Alfred Rosenberg argued for a new "religion of the blood" based on the supposed innate promptings of the Nordic soul to defend its "noble" character against racial and cultural degeneration. Rosenberg believed the Nordic race to be descended from Proto-Aryans, a hypothetical prehistoric people who dwelt on the North German Plain and who had ultimately originated from the lost continent of Atlantis.[note 1] Under Rosenberg, the theories of Arthur de Gobineau, Georges Vacher de Lapouge, Blavatsky, Houston Stewart Chamberlain, Madison Grant, and those of Hitler,[112] all culminated in Nazi Germany's race policies and the "Aryanization" decrees of the 1920s, 1930s, and early 1940s. In its "appalling medical model", the annihilation of the "racially inferior" Untermenschen was sanctified as the excision of a diseased organ in an otherwise healthy body,[113] which led to the Holocaust. According to Nazi racial theorists, the term "Aryans" (Arier) described the Germanic peoples,[114] and they considered the purest Aryans to be those that belonged to a "Nordic race" physical ideal, which they referred to as the "master race".[note 2] However, a satisfactory definition of "Aryan" remained problematic during Nazi Germany.[116] Although the physical ideal of Nazi racial theorists was typically the tall, blond haired and light-eyed Nordic individual, such theorists accepted the fact that a considerable variety of hair and eye colour existed within the racial categories they recognised. For example, Adolf Hitler and many Nazi officials had dark hair and were still considered members of the Aryan race under Nazi racial doctrine, because the determination of an individual's racial type depended on a preponderance of many characteristics in an individual rather than on just one defining feature.[117] In September 1935, the Nazis passed the Nuremberg Laws. All Aryan Reich citizens were required to prove their Aryan ancestry; one way was to obtain an Ahnenpass ("ancestor pass") by providing proof through baptismal certificates that all four grandparents were of Aryan descent.[118] In December of the same year, the Nazis founded Lebensborn ("Fount of Life") to counteract the falling Aryan birth rates in Germany, and to promote Nazi eugenics.[119] Many American white supremacist neo-Nazi groups and prison gangs refer to themselves as 'Aryans', including the Aryan Brotherhood, the Aryan Nations, the Aryan Republican Army, the White Aryan Resistance, or the Aryan Circle.[120][121] Modern nationalist political groups and neo-Pagan movements in Russia claim a direct linkage between themselves as Slavs and the ancient 'Aryans',[12] and in some Indian nationalist circles, the term 'Aryan' can also be used in reference to an alleged Aryan 'race'.[21] |
ナチズムと白人至上主義 無声映画超大作『国家の誕生』(1915年)の挿入歌。"Aryan birthright" はここでは "white birthright" であり、その「防衛」がアメリカ北部と南部の「白人」を「有色人種」に対して団結させるのである。同年の別の作品『アーリア人』では、ウィリアム・S・ ハートの「アーリア人」としてのアイデンティティは、他の民族との区別のもとに定義されている。 ヒューストン・スチュワート・チェンバレンの 作品を通じて、ゴビノーの思想はナチスの人種思想に影響を与え、「アーリア人」を他の人種とされる集団よりも 生来的に優れていると考えた[12] ナチの幹部アルフレッド・ローゼンベルクは、人種や文化の退化からその「気高い」性質を守るために北欧人の魂の生来の衝動を仮定した新しい「血液の宗教」 を主張している。ローゼンベルクは、北欧の民族は、北ドイツ平原に住んでいた仮説上の先史時代の人々である原アーリア人の子孫であり、最終的には失われた 大陸であるアトランティスに起源があると信じていた。 [ローゼンベルクの下で、アルチュール・ド・ゴビノー、ジョルジュ・ヴァシェール・ド・ラプージュ、ブラヴァツキー、ヒューストン・スチュワート・チェン バレン、マディソン・グラント、そしてヒトラーの理論が、1920年代、1930年代、1940年代初頭のナチスドイツの人種政策と「アーリア化」令に集 約されることになった[112]。その「ぞっとするような医学的モデル」において、「人種的に劣った」Untermenschenの消滅は、そうでなけれ ば健康な身体における病気の器官の切除として神聖化され、ホロコーストにつながった[113]。 ナチスの人種理論家によれば、「アーリア人」(Arier)という用語はゲルマン民族を表し[114]、彼らは「北欧人種」の身体的理想に属するものを最 も純粋なアーリア人と考え、それを「主人類」と呼んだ[注 2] しかし、「アーリア人」の満足できる定義は、ナチスドイツにおいて問題を残したままであった。 [116] ナチスの人種論者の身体的理想は、典型的には背が高く、金髪で明るい目の北欧人であったが、そうした論者は、彼らが認識する人種的カテゴリーの中にかなり の多様な髪と目の色が存在するという事実を受け入れていた。例えば、アドルフ・ヒトラーや多くのナチスの高官は黒髪であったが、ナチスの人種的教義の下で はアーリア人種の一員とみなされていた。1935年9月にナチスはニュルンベルク法を可決した。同年12月、ナチスはドイツにおけるアーリア人の出生率の 低下に対抗し、ナチスの優生学を促進するためにレーベンスボルン(「生命の泉」)を設立した[119]。 アメリカの白人至上主義のネオナチグループや刑務所ギャングの多くは、アーリア人同胞団、アーリア・ネーションズ、アーリア共和国軍、ホワイト・アーリ ア・レジスタンス、アーリアン・サークルなど、自らを「アーリア人」と称している[120][121]。 [120][121]ロシアの現代ナショナリスト政治団体やネオ・ペイガン運動は、スラブ人としての自分たちと古代の「アーリア人」との直接的なつながり を主張しており[12]、またインドの一部のナショナリスト界では、「アーリア人」という言葉はアーリア人とされる「民族」に言及して使われることがある [21]。 |
| "Aryan invasion theory" Translating the sacred Indian texts of the Rig Veda in the 1840s, German linguist Friedrich Max Muller found what he believed was evidence of an ancient invasion of India by Hindu Brahmins, a group which he called "the Arya." In his later works, Muller was careful to note that he thought that Aryan was a linguistic rather than a racial category. Nevertheless, scholars used Muller's invasion theory to propose their own visions of racial conquest through South Asia and the Indian Ocean. In 1885, the New Zealand polymath Edward Tregear argued that an "Aryan tidal-wave" had washed over India and continued to push south, through the islands of the East Indian archipelago, reaching the distant shores of New Zealand. Scholars such as John Batchelor, Armand de Quatrefages, and Daniel Brinton extended this invasion theory to the Philippines, Hawaii, and Japan, identifying indigenous peoples who they believed were the descendants of early Aryan conquerors.[122] With the discovery of the Indus Valley civilisation, mid-20th century archeologist Mortimer Wheeler argued that the large urban civilisation had been destroyed by the Aryans.[123] This position was later discredited, with climate aridification becoming the likely cause of the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilisation.[124] The term "invasion", while it was once commonly used in regard to Indo-Aryan migration, is now usually used only by opponents of the Indo-Aryan migration theory.[125] The term "invasion" does not any longer reflect the scholarly understanding of the Indo-Aryan migrations,[125] and is now generally regarded as polemical, distracting and unscholarly. In recent decades, the idea of an Aryan migration into India has been disputed mainly by Indian scholars, who claim various alternate Indigenous Aryans scenarios contrary to established Kurgan model. However, these alternate scenarios are rooted in traditional and religious views on Indian history and identity and are universally rejected in mainstream scholarship.[126][note 3] According to Michael Witzel, the "indigenous Aryans" position is not scholarship in the usual sense, but an "apologetic, ultimately religious undertaking".[129] A number of other alternative theories have been proposed including Anatolian hypothesis, Armenian hypothesis, the Paleolithic Continuity Theory but these are not widely accepted and have received little or no interest in mainstream scholarship.[130][131] |
"アーリア人侵略説" 1840年代にインドの聖典リグ・ヴェーダを翻訳したドイツの言語学者フリードリヒ・マックス・ミュラーは、ヒンドゥー教のバラモンが古代からインドに侵 入した証拠と思われるものを発見し、その集団を "アーリア人 "と名付けました。ミュラーは後の著作で、アーリア人は人種ではなく言語的なカテゴリーだと考えていることを注意深く述べている。しかし、学者たちはミュ ラーの侵略理論を利用して、南アジアとインド洋を通じた人種的征服のビジョンを提案した。1885年、ニュージーランドの学者エドワード・トレギアは、 「アーリア人の潮流」がインドに押し寄せ、東インド群島の島々を経て、遠くニュージーランドの海岸まで南下し続けたと主張した。ジョン・バチェラー、アル マン・ド・カトルファージュ、ダニエル・ブリントンなどの学者はこの侵略説をフィリピン、ハワイ、日本にまで広げ、彼らが初期のアーリア人征服者の子孫で あると信じる先住民を特定した[122]。 20世紀半ばにインダス渓谷文明が発見されると、考古学者のモーティマー・ウィラーはこの巨大都市文明の破壊をアーリア人が行ったと主張した[123]。 [123] この立場は後に信用されなくなり、気候の乾燥化がインダスバレー文明の崩壊の原因として考えられるようになった[124]。 侵略」という用語は、かつてインド・アーリア人の移動に関してよく使われていたが、現在は通常インド・アーリア人移動説の反対者によってのみ使われてい る。「侵略」という用語はもはやインド・アーリア人の移動に対する学術的理解を反映しておらず[125]、現在一般に極論であるとされるとともに気を散ら す、非学問的であるともみなされている。 ここ数十年、インドへのアーリア人の移住という考えは、主にインドの学者によって論争されており、彼らは確立されたクルガンモデルに反する様々な別の先住 民アーリア人のシナリオを主張している。しかし、これらの代替シナリオはインドの歴史とアイデンティティに関する伝統的・宗教的見解に根ざしており、主流 の学問では普遍的に否定されている[126][注釈 3]。マイケル・ウィッツェルによれば、「先住民アーリア人」の立場は通常の意味での学問ではなく、「弁明的、究極的には宗教的事業」であるとのことであ る[129]。 [129] アナトリア仮説、アルメニア仮説、旧石器時代連続説など、他にも多くの代替理論が提案されているが、これらは広く受け入れられておらず、主流の学問分野で はほとんど、あるいは全く関心を持たれていない[130][131]。 |
| https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aryan. |
|
| ドイツ血液証明書 |
ドイツ血液証明(ド
イツけつえきしょうめいしょ、 ドイツ語: Deutschblütigkeitserklärung)[1]
は、ナチスの指導者アドルフ・ヒトラーがミシュリンゲ(ユダヤ人の血を一部引く者)に対して、ドイツ人の血液を持っていることを宣言する文書[2] 。
この慣習は1935年のニュルンベルク法以降しばらくして始まり、ドイツの人種法のほとんどを免れることができる証明書であった[2]。 |
| ミシュリング(Jüdischer Mischling) |
ミシュリング(ド イツ語: [ˈmɪʃ; 複数形:
Mischlinge)は、1935年のニュルンベルク人種法に基づき、アーリア人とユダヤ人などの非アーリア人の両方の祖先を示すためにナチスドイツで
使われた卑語的な法律用語である[1][2]。 [1] ドイツ語では、この言葉は雑種、雑種、混血という一般的な意味を持つ[a]
ナチの公式用語での使用以外では、Mischlingskinder(「混合児」)という言葉は後に第二次世界大戦後に非白人兵士とドイツ人母の間に生ま
れた戦争孤児を指すのに使用された[2][b]。 |
Links
リンク
文献
その他の情報