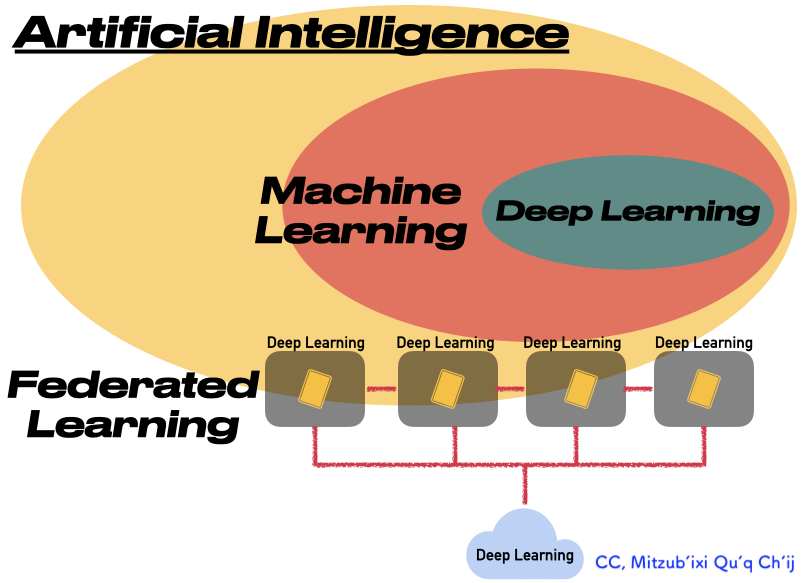
人工知能・機械学習・深層学習・連合=協調学習
Artificial intelligence (AI) , Machine learning, Deep learning, and Federated learning
解説:池田光穂


| Artificial
intelligence (AI) is intelligence demonstrated by machines, as
opposed to the natural intelligence displayed by animals including
humans. AI research has been defined as the field of study of
intelligent agents, which refers to any system that perceives its
environment and takes actions that maximize its chance of achieving its
goals. The term "artificial intelligence" had previously been used to
describe machines that mimic and display "human" cognitive skills that
are associated with the human mind, such as "learning" and
"problem-solving". This definition has since been rejected by major AI
researchers who now describe AI in terms of rationality and acting
rationally, which does not limit how intelligence can be articulated. |
人工知能(AI)とは、人間を含む動物が示す自然知能に対して、機械が
示す知能のことである。AI研究は、知的エージェントの研究分野と定義されており、環境を認識し、目標達成の可能性を最大化する行動をとるあらゆるシステ
ムを指す。人工知能」という言葉は、以前は「学習」や「問題解決」など、人間の心に関連する「人間的」な認知能力を模倣し、表示する機械を指す言葉として
使われていた。その後、この定義は主要なAI研究者によって否定され、現在ではAIを合理性と合理的な行動という観点から説明しており、知能の表現方法を
限定するものではない。 |
| Machine learning (ML) is a field
of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn',
that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set
of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence. Machine
learning algorithms build a model based on sample data, known as
training data, in order to make predictions or decisions without being
explicitly programmed to do so. Machine learning algorithms are used in
a wide variety of applications, such as in medicine, email filtering,
speech recognition, and computer vision, where it is difficult or
unfeasible to develop conventional algorithms to perform the needed
tasks. A subset of machine learning is closely related to computational
statistics, which focuses on making predictions using computers, but
not all machine learning is statistical learning. The study of
mathematical optimization delivers methods, theory and application
domains to the field of machine learning. Data mining is a related
field of study, focusing on exploratory data analysis through
unsupervised learning. Some implementations of machine learning use
data and neural networks in a way that mimics the working of a
biological brain. In its application across business problems, machine
learning is also referred to as predictive analytics. |
機械学習(ML)は、「学習」する手法、つまりデータを活用してあるタ
スクのパフォーマンスを向上させる手法を理解し構築することに専念する研究分野である。機械学習は、人工知能の一部と考えられている。機械学習アルゴリズ
ムは、学習データと呼ばれるサンプルデータに基づいてモデルを構築し、明示的にプログラムされていなくても予測や判断を行えるようにするものである。機械
学習アルゴリズムは、医療、電子メールのフィルタリング、音声認識、コンピュータビジョンなど、必要なタスクを実行するために従来のアルゴリズムを開発す
ることが困難、または実行不可能な幅広いアプリケーションで使用されている。機械学
習の一部は、コンピュータを使って予測を行うことに重点を置いた計算統計学と密接に関係しているが、すべての機械学習が統計学習というわけではない。
数理最適化の研究は、機械学習の分野に手法、理論、応用領域を提供している。また、データマイニングは、教師なし学習による探索的なデータ解析に特化した
研究分野である。機械学習の実装の中には、生物学的な脳の働きを模倣する形でデータとニューラルネットワークを使用するものもある。ビジネス上の問題に適
用される場合、機械学習は予測分析とも呼ばれる。 |
| Deep learning
(also known as deep structured learning) is part of a broader family of
machine learning methods based on artificial neural networks with
representation learning. Learning can be supervised, semi-supervised or
unsupervised. Deep-learning architectures such as deep neural networks,
deep belief networks, deep reinforcement learning, recurrent neural
networks, convolutional neural networks and Transformers have been
applied to fields including computer vision, speech recognition,
natural language processing, machine translation, bioinformatics, drug
design, medical image analysis, climate science, material inspection
and board game programs, where they have produced results comparable to
and in some cases surpassing human expert performance. Artificial
neural networks (ANNs) were inspired by information processing and
distributed communication nodes in biological systems. ANNs have
various differences from biological brains. Specifically, artificial
neural networks tend to be static and symbolic, while the biological
brain of most living organisms is dynamic (plastic) and analogue. The
adjective "deep" in deep learning refers to the use of multiple layers
in the network. Early work showed that a linear perceptron cannot be a
universal classifier, but that a network with a nonpolynomial
activation function with one hidden layer of unbounded width can. Deep
learning is a modern variation which is concerned with an unbounded
number of layers of bounded size, which permits practical application
and optimized implementation, while retaining theoretical universality
under mild conditions. In deep learning the layers are also permitted
to be heterogeneous and to deviate widely from biologically informed
connectionist models, for the sake of efficiency, trainability and
understandability, hence the "structured" part. |
ディープラーニング(深層構造学習とも呼ばれる)は、表現学習を用いた
人工ニューラルネットワークに基づく、より幅広い機械学習手法のファミリーの一部である。学習は、教師あり、半教師あり、教師なしができる。ディープ
ニューラルネットワーク、ディープビリーフネットワーク、ディープ強化学習、リカレントニューラルネットワーク、畳み込みニューラルネットワーク、トラン
スフォーマーなどの深層学習アーキテクチャは、コンピュータービジョン、音声認識、自然言語処理、機械翻訳、バイオインフォマティクス、ドラッグデザイ
ン、医療画像解析、気候科学、材料検査、ボードゲームプログラムなどの分野に応用され、人間の専門家の性能と同等であったり時にはそれを超える結果を出し
ている。人工ニューラルネットワーク(ANN)は、生体システムにおける情報処理や分散通信のノードにヒントを得て開発された。ANNは、生物の脳とは様
々な違いがある。具体的には、ほとんどの生物の生物脳が動的(可塑的)かつアナログであるのに対し、人工ニューラルネットワークは静的かつ記号的である傾
向がある。深層学習の「深い」という形容詞は、ネットワークに複数の層を使用することを意味する。初期の研究では、線形パーセプトロンは万能分類器になり
得ないが、非多項式活性化関数を持ち、幅が無限の隠れ層を1層持つネットワークは万能分類器になり得ることが示された。深層学習はその現代的なバリエー
ションで、境界のある大きさの境界のない層の数に関係し、実用的な応用と最適化された実装を可能にし、かつ穏やかな条件下で理論的な普遍性を保持するもの
である。深層学習では、効率性、訓練性、理解しやすさのために、層は異種であってもよく、生物学的情報に基づくコネクショニストモデルから大きく逸脱して
もよいことになっており、それゆえ「構造化」された部分がある。 |
| Federated learning (also known as collaborative learning) is a machine learning technique that trains an algorithm across multiple decentralized edge devices or servers holding local data samples, without exchanging them. This approach stands in contrast to traditional centralized machine learning techniques where all the local datasets are uploaded to one server, as well as to more classical decentralized approaches which often assume that local data samples are identically distributed./ Federated learning enables multiple actors to build a common, robust machine learning model without sharing data, thus allowing to address critical issues such as data privacy, data security, data access rights and access to heterogeneous data. Its applications are spread over a number of industries including defense, telecommunications, IoT, and pharmaceutics."-Federated learning. | Federated
Learning(連合=協調学習とも呼ばれる)は、ローカルなデータサンプルを保持する複数の分散型エッジデバイスまたはサーバー間で、データサンプル
を交換することなくアルゴリズムを学習する機械学習技術である。このアプローチは、すべてのローカルデータセットが1つのサーバーにアップロードされる従
来の集中型機械学習技術や、ローカルデータサンプルが同一に分散していることを前提としたより古典的な分散型アプローチとは対照的である
/Federated
Learningにより、複数の関係者がデータを共有せずに共通の堅牢な機械学習モデルを構築できるため、データプライバシー、データセキュリティ、デー
タアクセス権、異種データへのアクセスといった重要な問題に対処することが可能になる。その応用は、防衛、通信、IoT、薬剤など多くの産業に広がってい
る。 |
リンク
文献
その他の情報
++
Copyleft, CC,
Mitzub'ixi Quq Chi'j, 1997-2099
++
Copyleft,
CC, Mitzub'ixi Quq Chi'j, 1996-2099